Lithium hydroxide
- CAS NO.:1310-65-2
- Empirical Formula: LiOH
- Molecular Weight: 23.95
- MDL number: MFCD00011095
- EINECS: 215-183-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
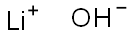
What is Lithium hydroxide?
Chemical properties
lithium hydroxide (LiOH) is a white solid made industrially as the monohydrate (LiOH.H2O) by reacting lime with a lithium ore or with a salt made from the ore. Lithium hydroxide has a closer resemblance to the group 2 hydroxides than to the group 1 hydroxides.
Physical properties
White tetragonal crystals; refractive index 1.464; density 1.46 g/cm3; melts at 450°C; decomposes at 924°C; dissolves in water (12.8g/100g at 20°C and 17.5 g/100g at 100°C); slightly soluble in alcohol. The monohydrate is white monoclinic crystalline solid; refractive index 1.460; density 1.51 g/cm3; soluble in water, more soluble than the anhydrous salt (22.3g and 26.8g/100g at 10 and 100°C, respectively); slightly soluble in alcohol; insoluble in ether.
The Uses of Lithium hydroxide
Lithium hydroxide is used in storage batteries and soaps and as CO2 absorber in spacecrafts.
The Uses of Lithium hydroxide
The compound is soluble in water. The compound is used in the formulation of lithium soaps used in multipurpose greases; also in the manufacture of various lithium salts; and as an additive to the electrolyte of alkaline storage batteries. LiOH also is an efficient, light-weight absorbent for carbon dioxide.
The Uses of Lithium hydroxide
Lithium hydroxide is used as a heat transfer medium, as a storage-battery electrolyte and also used for the production of lithium greases. It is also used in ceramics, in some portland cement formulations, in the absoption of carbondioxide from sealed enviornments such as submarines, spacecrafts and breathing apparatus. It is used in esterification reactions, as stabilizer in photographic developments and as a coolant in pressurized water reactors for corrosion control.
Background
Used for tryptophan determinations in proteins & foods.
What are the applications of Application
Lithium hydroxide is a widely employed hydroxide salt
Definition
A white crystallinesolid, LiOH, soluble in water,slightly soluble in ethanol and insolublein ether. It is known as the monohydrate(monoclinic; r.d. 1.51) and inthe anhydrous form (tetragonal, r.d.1.46; m.p. 450°C; decomposes at924°C). The compound is made by reacting lime with lithium salts orlithium ores. Lithium hydroxide isbasic but has a closer resemblance togroup 2 hydroxides than to the othergroup 1 hydroxides (an example ofthe first member of a periodic grouphaving atypical properties).
General Description
A clear to water-white liquid which may have a pungent odor. Contact may cause severe irritation to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. Lithium hydroxide may be toxic by ingestion, inhalation and skin absorption. Lithium hydroxide is used to make other chemicals.
Air & Water Reactions
Dilution with water may generate enough heat to cause steaming or spattering.
Reactivity Profile
LITHIUM HYDROXIDE SOLUTION neutralizes acids exothermically to form salts plus water. Reacts with certain metals (such as aluminum and zinc) to form oxides or hydroxides of the metal and generate gaseous hydrogen. May initiate polymerization reactions in polymerizable organic compounds, especially epoxides. May generate flammable and/or toxic gases with ammonium salts, nitrides, halogenated organics, various metals, peroxides, and hydroperoxides. May serve as a catalyst. Reacts when heated above about 84°C with aqueous solutions of reducing sugars other than sucrose, to evolve toxic levels of carbon monoxide [Bretherick, 5th Ed., 1995].
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and subcutaneous routes. Mtldly toxic by inhalation. A corrosive. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Li.
Metabolism
Not Available
Purification Methods
It crystallises from hot water (3mL/g) as the monohydrate. It is dehydrated at 150o in a stream of CO2-free air. It sublimes at 220o with partial decomposition [Cohen Inorg Synth V 3 1957, Bravo Inorg Synth VII 1 1963].
Properties of Lithium hydroxide
| Melting point: | 470 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 925°C |
| Density | 1.43 |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | water: soluble71g/L at 20°C |
| form | Solid |
| appearance | White solid |
| pka | 14[at 20 ℃] |
| Specific Gravity | 2.54 |
| color | White to light yellow |
| PH | 12 (50g/l, H2O, 50℃) |
| Odor | odorless |
| Water Solubility | 113 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive & Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,5534 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with moisture. strong acids, carbon dioxide. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1310-65-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Lithium hydroxide(1310-65-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lithium hydroxide (1310-65-2) |
Safety information for Lithium hydroxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Lithium hydroxide
| InChIKey | WMFOQBRAJBCJND-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Lithium hydroxide manufacturer
New Products
Ethyl 3,3- diethoxypropionate 7-Bromo-2-chloroquinoxaline N-Benzyl-3-hydroxypiperidine 2-(4-bromophenyl)-2-methylpropanoic acid Benzylacetoacetate Radiator Flux Zinc Chloride Solution (All Grades) Phenylazomalononitrile 2-Fluoro-6-iodobenzoic acid 3-(4-bromo-3-methyl-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1H-benzo[d]imidazol-1-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 2,3-Difluoro-6-methoxybenzyl Chloride 2-(6-(benzyloxy)-3,4-dihydronaphthalen-2-yl)-4,4,5,5-tetramethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborolane Ethyl2-oxo-2,3,9,10-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3',4':4,5]pyrrolo[1,2,3-de]quinoxaline-8(7H)-carboxylate Acetyl-meldrum's acid 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 3-Iodophenylacetic acid N Ethylmethylamine Ethyl Methanesulfonate N N' DimethylEthylenediamine Lead II BromideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
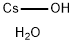
You may like
-
 1310-65-2 Lithium hydroxide 98%View Details
1310-65-2 Lithium hydroxide 98%View Details
1310-65-2 -
 Lithium hydroxide, anhydrous CAS 1310-65-2View Details
Lithium hydroxide, anhydrous CAS 1310-65-2View Details
1310-65-2 -
 Lithium hydroxide, anhydrous CAS 1310-65-2View Details
Lithium hydroxide, anhydrous CAS 1310-65-2View Details
1310-65-2 -
 Lithium hydroxide, anhydrous CAS 1310-65-2View Details
Lithium hydroxide, anhydrous CAS 1310-65-2View Details
1310-65-2 -
 Lithium Hydroxide Anhydrous extrapure CAS 1310-65-2View Details
Lithium Hydroxide Anhydrous extrapure CAS 1310-65-2View Details
1310-65-2 -
 Lithium Hydroxide CASView Details
Lithium Hydroxide CASView Details -
 Lithium Hydroxide Anhydrous CAS 1310-65-2View Details
Lithium Hydroxide Anhydrous CAS 1310-65-2View Details
1310-65-2 -
 Lithium hydroxide 98%+ CAS 1310-65-2View Details
Lithium hydroxide 98%+ CAS 1310-65-2View Details
1310-65-2
