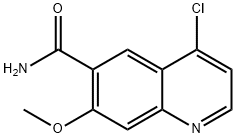
Lenvatinib
- CAS NO.:417716-92-8
- Empirical Formula: C21H19ClN4O4
- Molecular Weight: 426.85
- MDL number: MFCD16038644
- EINECS: 1592732-453-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-15 15:57:13
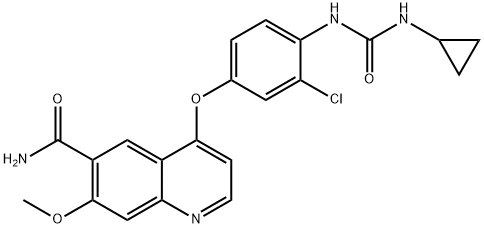
What is Lenvatinib?
Absorption
Time to peak plasma concentration occurred from 1 to 4 hours post-dose. Administration with food did not affect the extent of absorption, but decreased the rate of absorption and delayed the median Tmax from 2 hours to 4 hours.
Toxicity
The most common adverse events that occurred in lenvatinib recipients were hypertension (67.8 vs. 9.2 % in the placebo group), diarrhea (59.4 vs. 8.4 %), fatigue or asthenia (59.0 vs. 27.5 %), decreased appetite (50.2 vs. 11.5 %), decreased bodyweight (46.4 vs. 9.2 %), nausea (41.0 vs. 13.7 %), stomatitis (35.6 vs. 3.8 %), palmar-plantar erythrodysethesia syndrome (31.8 vs. 8.0 %) and proteinuria (31.0 vs. 1.5 %). Adverse events that occurred in clinical trials and for which there is a warning/precaution in US manufacturer’s pre- scribing information were hypertension, cardiac dysfunction (decreased left or right ventricular function, cardiac failure or pulmonary edema), arterial thromboembolic events, hepatotoxicity, proteinuria, renal failure and impairment, gastrointestinal perforation and fistula formation, QT interval prolongation, hypocalcaemia, reversible posterior leucoencephalopathy syndrome, haemorrhagic events, and impairment of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) suppression. Based on the mechanism of action of lenvatinib and results from animal reproduction studies, which showed embryotoxicity, foetotoxicity and teratogenicity at lenvatinib doses below the recommended dose in humans, females of reproductive potential should be advised to use effective contraception during treatment and for at least 2 weeks following completion of therapy.
Description
Lenvatinib is an inhibitor of the receptor tyrosine kinases VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR2) and VEGFR3 (IC50s = 4 and 5.2 nM, respectively). It also inhibits the related kinases VEGFR1, FGFR1, PDGFRα, PDGFRβ and Kit (IC50s = 22, 46, 51, 39, and 100 nM, respectively). Lenvatinib (30 mg/kg, twice per day) reduces tumor growth in an H146 small cell lung cancer mouse xenograft model and induces tumor regression when administered at a dose of 100 mg/kg twice per day. Formulations containing lenvatinib have been used in the treatment of differentiated thyroid cancer, renal cell carcinoma, and hepatocellular carcinoma.
Characteristics
Class: receptor protein-tyrosine kinase
Treatment: DTC, RCC, HCC
Elimination half-life = 28 h
Protein binding = 98–99%
The Uses of Lenvatinib
E7080 (Lenvatinib) is a multi-target inhibitor of VEGFR2 and VEGFR3 with IC50 of 4 nM and 5.2 nM, respectively.
The Uses of Lenvatinib
Lenvatinib is an orally active inhibitor of multiple receptor tyrosine kinases including VEGF, FGF and SCF receptors.
Background
Lenvatinib is a receptor tyrosine kinase (RTK) inhibitor that inhibits the kinase activities of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptors VEGFR1 (FLT1), VEGFR2 (KDR), and VEGFR3 (FLT4). Lenvatinib also inhibits other RTKs that have been implicated in pathogenic angiogenesis, tumor growth, and cancer progression in addition to their normal cellular functions, including fibroblast growth factor (FGF) receptors FGFR1, 2, 3, and 4; the platelet derived growth factor receptor alpha (PDGFRα), KIT, and RET. These receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) located in the cell membrane play a central role in the activation of signal transduction pathways involved in the normal regulation of cellular processes, such as cell proliferation, migration, apoptosis and differentiation, and in pathogenic angiogenesis, lymphogenesis, tumour growth and cancer progression. In particular, VEGF has been identified as a crucial regulator of both physiologic and pathologic angiogenesis and increased expression of VEGF is associated with a poor prognosis in many types of cancers.
Lenvatinib is indicated for the treatment of patients with locally recurrent or metastatic, progressive, radioactive iodine (RAI)-refractory differentiated thyroid cancer. Most patients with thyroid cancer have a very good prognosis with treatment (98% 5 year survival rate) involving surgery and hormone therapy. However, for patients with RAI-refractory thyroid cancer, treatment options are limited and the prognosis is poor, leading to a push for the development of more targeted therapies such as lenvatinib.
Indications
Lenvatinib is indicated for the treatment of the following cancerous conditions:
Differentiated Thyroid Cancer (DTC)
Renal Cell Carcinoma (RCC)
Hepatocellular Carcinoma (HCC)
Endometrial Carcinoma
What are the applications of Application
Lenvatinib is an orally active inhibitor of multiple receptor tyrosine kinases including VEGF, FGF and SCF receptors
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of quinolines that is the carboxamide of 4-{3-chloro-4-[(cyclopropylcarbamoyl)amino]phenoxy}-7-methoxyquinoline-6-carboxylic acid. A multi-kinase inhibitor and orphan drug used (as its mesylate salt) for the treatment of various types of thyroid cancer that do not respond to radioiodine.
Mechanism of action
Lenvatinib exerts its mechanism of action via inhibition of multiple receptors of tyrosine kinases: VEGFR-1 (FLT1), VEGFR-2( KDR), VEGFR-3 (FLT4), FGFR-1, FGFR-2, FGFR-3, FGFR-4, PDGFRa, RET, and c-KIT. Tumor growth is dependent on the development and proliferation of new blood vessels (neovascularization). Tumor growth and angiogenesis occur when the ligands bind to their respective tyrosine kinase receptors in the cellular membrane, initiating an intracellular signal transduction phosphorylation cascade promoting angiogenesis and cell proliferation. The inhibition of the VEGF receptors prevents tumor angiogenesis, and the inhibition of FGFR, RET, PDGFRα, and KIT prevents the further proliferation of malignant cells. The concurrent inhibition of both receptor pathways results in the inhibition of nuclear signal transduction and concomitant suppression of the activity of factors involved in tumor growth[5]. It inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor receptor family , fibroblast growth factor receptor family (FGFR1–4), platelet-derived growth factor receptor–alpha (PDGFRα), tyrosine-kinase receptor (KIT) and rearranged during transfection receptor (RET).
Pharmacokinetics
Based on x-ray crystallography and kinetic interaction studies, lenvatinib binds to the adenosine 5'-triphosphate binding site of VEGFR2 and to a neighbouring region via a cyclopropane ring and thereby inhibits tyrosine kinase activity and associated signalling pathways.
Side Effects
The most common side effects of LENVIMA (lenvatinib) in people treated for thyroid cancer include tiredness; joint and muscle pain; decreased appetite; weight loss; nausea; mouth sores; headache; vomiting; rash, redness, itching, or peeling of your skin on your hands and feet; stomach (abdomen) pain; and hoarseness.
The most common side effects of LENVIMA when given with everolimus in people treated for kidney cancer include tiredness; joint and muscle pain; decreased appetite; vomiting; nausea; mouth sores; swelling in your arms and legs; cough; stomach (abdomen) pain; trouble breathing; rash; weight loss; and bleeding.
The most common side effects of LENVIMA in people treated for liver cancer include tiredness; decreased appetite; joint and muscle pain; weight loss; stomach (abdomen) pain; rash, redness, itching, or peeling of your skin on your hands and feet; hoarseness; bleeding; change in thyroid hormone levels; nausea.
Metabolism
Lenvatinib is metabolized by CYP3A and aldehyde oxidase.
References
1) Matsui et al. (2008), E7080, a novel inhibitor that targets multiple kinases, has potent antitumor activities against stem cell factor producing human small cell lung cancer H146, based on angiogenesis inhibition; Int. J. Cancer, 122 664
2) Matsui et al. (2008), Multi-kinase inhibitor E7080 suppresses lymph node and lung metastases of human mammary breast tumor MDA-MB-231 via inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-receptor (VEGF-R)2 and VEGF-R3 kinase; Clin. Cancer Res., 14 5459
3) Glen et al. (2011), E7080, a multi-targeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor suppresses tumor cell migration and invasion; BMC Cancer, 11 309
4) Yamamoto et al. (2014), Lenvatinib, an angiogenesis inhibitor targeting VEGFR/FGFR, shows broad antitumor activity in human tumor xenograft models associated with microvessel density and pericyte coverage; Vasc. Cell, 6 18
[5] Capozzi M, et al. Lenvatinib, a molecule with versatile application: from preclinical evidence to future development in anti-cancer treatment. Cancer Management and Research, 2019; 11: 3847–3860.
Properties of Lenvatinib
| Melting point: | >216°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 627.2±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.46 |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 20 mg/ml) |
| form | solid |
| pka | 13.09±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | White |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 3 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 417716-92-8 |
Safety information for Lenvatinib
Computed Descriptors for Lenvatinib
Lenvatinib manufacturer
Shreyaa Medilife Private Limited
Aspen Biopharma Labs Pvt Ltd
New Products
6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole 7-Bromo-1H-indazole 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione N-octanoyl benzotriazole 4-Hydrazinobenzoic acid ELECTROLYTIC IRON POWDER 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) 4-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 4-Bromopyrazole 1-Boc-4-cyanopiperidine 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE (R)-5-(2-aminopropyl)-2-methoxybenzenesulfonamide 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone Cycloleucine 1-Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid 1-Amino-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid 1-(2-Ethoxyethyl)-2-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole hydrochloride TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE 4-bromo-3,5-dimethylbenzenesulfonyl chloride N-(5-Amino-2-methylphenyl)acetamide 4-EthylbenzylamineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 417716-92-8 Lenavatinib Mesylate 98%View Details
417716-92-8 Lenavatinib Mesylate 98%View Details
417716-92-8 -
 417716-92-8 98%View Details
417716-92-8 98%View Details
417716-92-8 -
 Lenvatinib 98%View Details
Lenvatinib 98%View Details
417716-92-8 -
 417716-92-8 98%View Details
417716-92-8 98%View Details
417716-92-8 -
 E7080 >95% CAS 417716-92-8View Details
E7080 >95% CAS 417716-92-8View Details
417716-92-8 -
 52-52-8 Cycloleucine 98+View Details
52-52-8 Cycloleucine 98+View Details
52-52-8 -
 1-Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid 98+View Details
1-Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid 98+View Details
22264-50-2 -
![1841081-72-8 1-(2-Ethoxyethyl)-2-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole hydrochloride 98+](https://img.chemicalbook.in//Content/image/CP5.jpg) 1841081-72-8 1-(2-Ethoxyethyl)-2-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole hydrochloride 98+View Details
1841081-72-8 1-(2-Ethoxyethyl)-2-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole hydrochloride 98+View Details
1841081-72-8