Doxorubicin hydrochloride
Synonym(s):DOX;Doxorubicin hydrochloride;Adriamycin;Adriamycin, HCl, 14-Hydroxydaunomycin, HCl;Hydroxydaunorubicin hydrochloride
- CAS NO.:25316-40-9
- Empirical Formula: C27H29NO11.ClH
- Molecular Weight: 579.98
- MDL number: MFCD00077757
- EINECS: 246-818-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-25 18:47:31
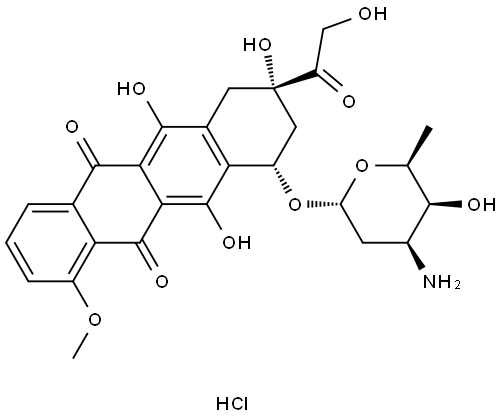
What is Doxorubicin hydrochloride?
Chemical properties
Doxorubicin is an orange to red cake-like or needle-like crystalline solid. It is a cytotoxic anthracycline antibiotic isolated from cultures of Streptomyces peucetius var. caesius. Doxorubicin hydrochloride is an orange-red, crystalline, hygroscopic powder that is soluble in water and slightly soluble in methanol.
Originator
Adriblastina,Farmitalia,Italy,1971
The Uses of Doxorubicin hydrochloride
Doxorubicin hydrochloride (adriamycin hydrochloride) is an antitumour agent that has been formulated as a salt to achieve higher water solubility. While the salt shares the same pharmacological properties as doxorubicin free base, its greater water solubility may offer advantages in some in vitro applications. Physicochemical properties and chromatographic behaviour will depend on whether the pH is buffered. In non-pH controlled systems the free base and salt may behave differently.
The Uses of Doxorubicin hydrochloride
Strong fluorescent dye intercalating into DNA. Antitumour antibiotic. Effect of adriamycin on heart mitochondrial DNA. Inhibitor of reverse transcriptase and RNA polymerase; immunosuppressive agent.
The Uses of Doxorubicin hydrochloride
Doxorubicin is an anthracycline antitumor antibiotic that inhibits DNA topoisomerase II by inducing double-stranded DNA breaks. By intercalating within DNA, doxorubicin inhibits nucleic acid synthesis and induces apoptosis by inducing the accumulation of the p53 tumor suppressor protein.[Cayman Chemical]
What are the applications of Application
Doxorubicin hydrochloride is an anthracycline antitumor antibiotic topoisomerase II inhibitor, DNA intercalator and powerful cytotoxic agent.
Definition
ChEBI: Doxorubicin hydrochloride is an anthracycline.
Manufacturing Process
Two 300 ml Erlenmeyer flasks, each containing 60 ml of the following culture
medium for the vegetative phase, were prepared: peptone 0.6%; dry yeast
0.3%; hydrated calcium carbonate 0.2%; magnesium sulfate 0.01%; the pH
after sterilization was 7.2. Sterilization has been effected by heating in
autoclave to 120°C for 20 minutes. Each flask was inoculated with a quantity
of mycelium of the mutant F.I.106 (the new strain thus obtained has been
given the code F.I.106 of the Farmitalia microbiological collection and has
been called Streptomycespeucetius var. caesius) corresponding to 1/9 of a
suspension in sterile water of the mycelium of a 10 day old culture grown in a
big test tube on the following medium: saccharose 2%; dry yeast 0.1%;
bipotassium phosphate 0.2%; sodium nitrate 0.2%; magnesium sulfate 0.2%;
agar 2%; tap water up to 100%. The flasks were then incubated at 28°C for
48 hours on a rotary shaker with a stroke of 30 mm at 220 rpm.,
2 ml of a vegetative medium thus grown were used to inoculate 300 ml
Erlenmeyer flasks with 60 ml of the following medium for the productive
phase: glucose 6%; dry yeast 2.5%; sodium chloride 0.2%; bipotassium
phosphate 0.1%; calcium carbonate 0.2%; magnesium sulfate 0.01%; ferrous
sulfate 0.001%; zinc sulfate 0.001%; copper sulfate 0.001%; tap water to
100%. The glucose was previously sterilized separately at 110°C for 20
minutes. The resulting pH was 7. This was sterilized at 120°C for 20 minutes
and incubated at 28°C under the same conditions by stirring, as for the
vegetative media.
The maximum concentration of the antibiotic was reached on the 6th day of
fermentation. The quantity of adriamycin produced at this time corresponds to
a concentration of 15 μg/ml.
brand name
Adriamycin (Pharmacia & Upjohn); Doxil (ALZA); Rubex (Bristol-Myers Squibb).
Therapeutic Function
Cancer chemotherapy
Biological Functions
The C13 substituent of doxorubicin is hydroxymethyl, which retards the action of cytosolic aldoketoreductase and slows the conversion to the equally active, but chronically cardiotoxic, doxorubicinol.
General Description
Adriamycin hydrochloride appears as orange-red thin needles. Aqueous solutions yellow-orange at acid pHs, orange-red at neutral pHs, and violet blue over pH 9. Doxorubicin is available as both the conventional dosageform and a liposomal preparation, both of which are administeredby infusion. Doxorubicin HCl powder is available in10-, 20-, 50-, and 150-mg vials and is widely used in treatingvarious cancers, including leukemias, soft and bone tissuesarcomas, Wilms tumor, neuroblastoma, small cell lungcancer, and ovarian and testicular cancer.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Amines, like Doxorubicin hydrochloride, are weak chemical bases. They neutralize acids to form salts plus water. These acid-base reactions are exothermic. Amines may be incompatible with isocyanates, halogenated organics, peroxides, phenols (acidic), epoxides, anhydrides, and acid halides. Flammable gaseous hydrogen is generated by amines in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Fire Hazard
Doxorubicin hydrochloride is probably combustible.
Biological Activity
Antitumor antibiotic agent that inhibits DNA topoisomerase II. DNA intercalator that inhibits nucleic acid synthesis and induces apoptosis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Naturally fluorescent anthracycline antibiotic, anticancer drug. Doxorubicin is a substrate of MRP1 which was first cloned from a DOX-resistant lung cancer cell line. Fluorescent property has been exploited for the measurement of drug efflux pump activities as well as resolving the important question of intracellular localization of various multidrug resistance proteins and the role of subcellular organelles (Golgi and lysosome) in the sequestration of drugs and its implication in drug resistant phenotypes.
Mechanism of action
Liposomes are taken up selectively into tumor cells, presumably because of their persistence in the bloodstream and enhanced permeability of tumor vascular membranes. In liposomal form, the drug is protected against enzymes that generate cardiotoxic free radicals, although this form of the drug can still induce potentially fatal congestive heart failure. Clinical experience with the liposomal formulation is limited, and few studies comparing the long-term toxicity with that of conventional doxorubicin therapy have been conducted. Therefore, all precautions outlined for the use of doxorubin also are employed when the liposomal formulation is used.
Clinical Use
Doxorubicin is utilized either alone or in combination therapy to treat a wide range of neoplastic disorders, including hematologic cancers and solid tumors in breast, ovary, stomach, bladder, and thyroid gland. A liposomal formulation of doxorubicin is used in the treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi's sarcoma and organoplatinum-resistant ovarian cancer.
Potential Exposure
An antibiotic product from streptomyces, used as anticancer drug
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Doxorubicin is perhaps the most widely used antineoplastic agent at present in small animal medicine. It may be useful in the treatment of a variety of lymphomas, carcinomas, leukemias, and sarcomas in both the dog and cat, either alone or in combination protocols. Refer to the Dosage references or the Protocols found in the appendix for more information.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Antipsychotics: avoid with clozapine, increased risk
of agranulocytosis.
Ciclosporin: increased risk of neurotoxicity
Cytotoxics: possible increased risk of cardiotoxicity
with trastuzumab - avoid for 28 weeks after
stopping trastuzumab.
Avoid with live vaccines.
Metabolism
This contributes to the longer duration of action compared to analogues that have CH3 at this position (e.g., daunorubicin). Doxorubicin is highly lipophilic and concentrates in the liver, lymph nodes, muscle, bone marrow, fat, and skin. Elimination is triphasic, and the drug has a terminal half-life of 30 to 40 hours. The majority of an administered dose is excreted in the feces.
storage
Room temperature
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides
Waste Disposal
It is inappropriate and possibly dangerous to the environment to dispose of expired or waste pharmaceuticals by flushing them down the toilet or discarding them to the trash. Household quantities of expired or waste pharmaceuticals may be mixed with wet cat litter or coffee grounds, double-bagged in plastic, discard in trash. Larger quantities shall carefully take into consideration applicable DEA, EPA, and FDA regulations. If possible return the pharmaceutical to the manufacturer for proper disposal being careful to properly label and securely package the material. Alternatively, the waste pharmaceutical shall be labeled, securely packaged and transported by a state licensed medical waste contractor to dispose by burial in a licensed hazardous or toxic waste landfill or incinerator.
References
1) Zeman et al. (1998), Characterization of covalent adriamycin-DNA adducts; Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., 95 11561 2) Katoh et al. (1998), Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibits apoptotic death in hematopoietic cells after exposure to chemotherapeutic drugs by inducing MCL1 acting as an antiapoptotic factor; Cancer Res., 58 5565 3) Perez et al. (2011), Anti-MDR-1 siRNA restores chemosensitivity in chemoresistant breast carcinoma and osteosarcoma cell lines; Anticancer Res., 31 2813
Properties of Doxorubicin hydrochloride
| Melting point: | 216 °C (dec.)(lit.) |
| alpha | D20 +248±2° (c = 0.1 in methanol) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO at 100 mg/ml; very poorly soluble in ethanol; soluble in water at 10 mg/ml with slight warming. |
| form | solid |
| pka | pKa 8.25±0.60 (Uncertain);8.43±0.70 (Uncertain);11.9±0.4 (Uncertain);12.95±0.1 (Uncertain);13.8±0.70 (Uncertain) |
| color | orange to dark red |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. |
| λmax | 497nm(H2O)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,3439 |
| BRN | 4229251 |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in distilled water may be stored at -20° for up to 3 months. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 25316-40-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Doxorubicin hydrochloride (25316-40-9) |
Safety information for Doxorubicin hydrochloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H340:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Doxorubicin hydrochloride
| InChIKey | MWWSFMDVAYGXBV-RUELKSSGSA-N |
Doxorubicin hydrochloride manufacturer
Archerchem Healthcare Pvt., Ltd. (part of Archerchem Group)
New Products
1-Boc-4-cyanopiperidine tert-Butyl carbazate 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE TETRABUTYLAMMONIUM CYANIDE TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 3-Pyridineacrylic acid Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% Tadalafil Clopidogrel bisulfate Sitagliptin Phosphate Monohydrate Cabergoline Fexofinadine HCl Etoricoxib 4-Amino Acetophenone 2-Chloro Acetophenone Amlodipine Base 2,3,5-Triiodobenzoic Acid Pyrrolidine Diiodo PentoxideRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Doxorubicin CAS 25316-40-9View Details
Doxorubicin CAS 25316-40-9View Details
25316-40-9 -
 Doxorubicin hydrochloride (suitable for fluorescence) CAS 25316-40-9View Details
Doxorubicin hydrochloride (suitable for fluorescence) CAS 25316-40-9View Details
25316-40-9 -
 Doxorubicin hydrochloride, >95% (HPLC) CAS 25316-40-9View Details
Doxorubicin hydrochloride, >95% (HPLC) CAS 25316-40-9View Details
25316-40-9 -
 Doxorubicin hydrochloride CAS 25316-40-9View Details
Doxorubicin hydrochloride CAS 25316-40-9View Details
25316-40-9 -
 Doxorubicin Hydrochloride CAS 25316-40-9View Details
Doxorubicin Hydrochloride CAS 25316-40-9View Details
25316-40-9 -
 Doxorubicin hydrochloride CAS 25316-40-9View Details
Doxorubicin hydrochloride CAS 25316-40-9View Details
25316-40-9 -
 Doxorubicin hydrochloride CAS 25316-40-9View Details
Doxorubicin hydrochloride CAS 25316-40-9View Details
25316-40-9 -
 Doxorubicin Hydrochloride CAS 25316-40-9View Details
Doxorubicin Hydrochloride CAS 25316-40-9View Details
25316-40-9
