Lead fluoride
- CAS NO.:7783-46-2
- Empirical Formula: F2Pb
- Molecular Weight: 245.2
- MDL number: MFCD00011162
- EINECS: 231-998-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
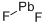
What is Lead fluoride ?
Description
Lead fluoride is a white to colorless, odorlesscrystalline (rhombic, orthorhombic) solid. Molecularweight =245.19; Boiling point=1292℃; Freezing/Meltingpoint = 825℃. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704M Rating System): Health 1, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0.Slightly soluble in water.
Chemical properties
Lead fluoride is a white to colorless, odorless crystalline (rhombic, orthorhombic) solid
The Uses of Lead fluoride
Lead(II) fluoride is used in fuses, glass coatings to reflect infrared rays and phosphors for television screens and in low melting glasses. Further, it serves as a catalyst for the preparation of picoline.
What are the applications of Application
It is used as the transmission window in λ: 250 nm–10 mm and as the prism in the infrared region.
General Description
Odorless white solid. Sinks in water.
Reactivity Profile
Calcium carbide mixed with Lead fluoride , at ordinary temperatures, becomes incandescent [Mellor 5:862-64. 1946-47].
Health Hazard
Not irritating to skin or mucuous membranes; protect against chronic poisoning. Early symptoms of lead intoxication via inhalation or ingestion are most commonly gastrointestinal disorders, colic, constipation, etc.; weakness, which may go on to paralysis chiefly of the extensor muscles of the wrists and less often the ankles, is noticeable in the most serious cases. Ingestion of a large amount causes local irritation of the alimentary tract; pain, leg cramps, muscle weakness, paresthesias, depression, coma, and death may follow in 1 or 2 days. Contact with eyes causes irritation.
Fire Hazard
Non-combustible, substance itself does not burn but may decompose upon heating to produce corrosive and/or toxic fumes. Some are oxidizers and may ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated.
Potential Exposure
Used to make other chemicals, underwater paints; electronic and optical parts (for growing single-crystal, solid-state lasers); in high-temperature dryfilm lubricants; and making special grades of glass.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Note to physician: Administer saline cathartic and anenema. For relief of colic, administer antispasmodic (calcium gluconate, atropine, papaverine). Consider morphinesulfate for severe pain.Whole blood lead levels, circulating plasma/erythrocytelead concentration ratio, urine ALA, and erythrocyte protoporphyrin fluorescent microscopy may all be useful in monitoring or assessing lead exposure. Chelating agents, such as edetate disodium calcium (Ca EDTA) and penicillamine(not penicillin), are generally useful in the therapy of acutelead intoxication.Antidotes and special procedures for lead: Persons with significant lead poisoning are sometimes treated with CaEDTA while hospitalized. This “chelating” drug causes arush of lead from the body organs into the blood and kidneys, and thus has its own hazards, and must be administered only by highly experienced medical personnel undercontrolled conditions and careful observation. Ca EDTA orsimilar drugs should never be used to prevent poisoningwhile exposure continues or without strict exposure control,as severe kidney damage can result.
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area. Lead is regulated by an OSHA Standard1910.1025. All requirements of the standard must befollowed.
Shipping
UN3288 Toxic solids, inorganic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN2291 Lead compounds, soluble n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required
Incompatibilities
Violent reaction with oxidizers, chemically active metals; calcium carbide. May ignite combustibles, such as wood, paper, oil, etc
Properties of Lead fluoride
| Melting point: | 824 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1293 °C |
| Density | 8.445 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| Flash point: | 1290°C |
| form | powder |
| color | White to off-white |
| Specific Gravity | 8.445 |
| Water Solubility | 0.065 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,5408 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 7.48 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.05 mg/m3; TWA 2.5 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 100 mg/m3; IDLH 250 mg/m3; TWA 0.050 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7783-46-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Lead difluoride(7783-46-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lead(II) fluoride (7783-46-2) |
Safety information for Lead fluoride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Lead fluoride
Lead fluoride manufacturer
New Products
1-Amino-1-cyclohexanecarboxylic acid 3-(2,4-Dimethoxybenzyl)dihydropyrimidine-2,4(1H,3H)-dione 6-Bromo-3-iodo-1-methyl-1H-indazole S-Methylisothiosemicarbazide hydroiodide ELECTROLYTIC IRON POWDER 1-Aminocyclobutanecarboxylic acid 1-(2-Ethoxyethyl)-2-(piperidin-4-yl)-1H-benzo[d]imidazole hydrochloride tert-butyl 4-(1H-benzo[d]iMidazol-2-yl)piperidine-1-carboxylate Decanonitrile N,N'-diallyl-1,3-diaminopropanedihydrochloride 4-(4-Nitrophenyl)piperidine N-(3-Nitrophenyl)cyclopropanecarboxamide (2-amino-2-phenylethyl)(methyl)amine methyl 6-chloro-2-(chloromethyl)nicotinate 2-methoxy-4-methyl-5-nitro pyridine 2-iodo-5-bromo pyridine 2-amino-4-methyl-5-nitro pyridine 4-cyano benzaldehyde 2-hydroxy-5-bromo pyridine 5-Fluoro-2-Oxindole 3,5-Dichloro-2,6-Dimethyl-1h-Pyridin-4-One (S)-1-(tert-butoxycarbonyl)-4-oxopyrrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (9H-fluoren-9-yl)methyl carbonochloridate 2-methyl-5-nitroanilineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Lead(II) fluoride CAS 7783-46-2View Details
Lead(II) fluoride CAS 7783-46-2View Details
7783-46-2 -
 Lead(II) fluoride CAS 7783-46-2View Details
Lead(II) fluoride CAS 7783-46-2View Details
7783-46-2 -
 Lead fluoride, 98% CAS 7783-46-2View Details
Lead fluoride, 98% CAS 7783-46-2View Details
7783-46-2 -
 Lead(II) fluoride CAS 7783-46-2View Details
Lead(II) fluoride CAS 7783-46-2View Details
7783-46-2 -
 Lead(II) fluoride CAS 7783-46-2View Details
Lead(II) fluoride CAS 7783-46-2View Details
7783-46-2 -
 3,4 Difluoro benzaldehydeView Details
3,4 Difluoro benzaldehydeView Details
34036-07-2 -
 Methyl 3 cyclohexene 1 carboxylateView Details
Methyl 3 cyclohexene 1 carboxylateView Details
6493-77-2 -
 2 Hydroxy 4 methoxy benzoic acidView Details
2 Hydroxy 4 methoxy benzoic acidView Details
2237-36-7