Calcium fluoride
Synonym(s):Calcium fluoride;Fluorite;Fluorspar
- CAS NO.:7789-75-5
- Empirical Formula: CaF2
- Molecular Weight: 78.07
- MDL number: MFCD00010907
- EINECS: 232-188-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:51
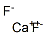
What is Calcium fluoride?
Description
Calcium fluoride (CaF2) is the primary source of fluorine worldwide. It occurs as the mineral fluorite or fluorspar. Unlike the other calcium halides, it is practically insoluble in water. Its industrial uses range from fluxes in the metallurgy industries (primarily steel) to window materials in ultraviolet and infrared devices.
Description
Calcium fluoride is colorless crystalline orwhite, powdery substance. Molecular weight=78.08;Specific gravity (H2O:1)=3.18 at 20℃; Boilingpoint=2495℃; Freezing/Melting point=1423℃. HazardIdentification (based on NFPA-704 M Rating System):Health 2, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0. Practically insolublein water.
Chemical properties
Calcium fluoride, CaF2, also known as fluorite and feldspar, is a colorless solid composed of cubic crystals. It has a low water solubility, but is readily soluble in ammonium salt solutions. Calcium fluoride is used in the synthesis of hydrofluoric acid and in etching glass.
Calcium Fluoride is not hygroscopic and is relatively inert. It has a sufficiently high resistance to thermal and mechanical shock, and it is easily fabricated into a variety of detector geometries.
Calcium Fluoride has a very low vapor pressure, allowing it to be used in a wide variety of vacuum applications. It is insoluble in water and most organic solvents, permitting radioactive samples in solution to be placed in direct contact with the crystal.
Calcium Fluoride is a transparent material used for detecting γ-rays up to several hundred keV and for detecting charged particles. Because of its low atomic number, the material’s photofraction is relatively small which limits its use in γ-ray spectrometry at higher energies. However, the low atomic number makes Calcium Fluoride an ideal material for the detection of β-particles because of the small amount of backscattering.
Physical properties
White cubic crystal or powder; refractive index 1.434; density 3.18 g/cm3; hardness 4 Mohs; melts at 1,418°C; vaporizes at 2,533°C; insoluble in water (16 mg/L at 20°C); Ksp 3.9x10-11; slightly soluble in dilute mineral acid; soluble in concentrated acids (with reaction).
The Uses of Calcium fluoride
Fluorspar is the main primary source of fluorine and its Compounds. In ferrous metallurgy it is used as a flux to increase the fluidity of the slag. The steel industry is the largest consumer; the chemical industry, second and glass and ceramics, third. Synthetic fluorspar is used in the optical industry (transmits u.v. rays), and pure calcium fluoride is used as catalyst in dehydration and dehydrogenations. Used to fluoridate drinking water.
The Uses of Calcium fluoride
Naturally occurring CaF2 is the principal source of
hydrogenfluoride, a commodity chemicalusedto produce
a wide range of materials. Fluoride is liberated from the
mineral by the action of concentrated sulfuric acid:
CaF2 (solid)+H2SO4 (liq)→CaSO4 (solid)+2HF (gas)
CaF2 is used as an optical component because of its
chemical stability under adverse conditions.Calcium fluoride is commonly used as a window
material for both infrared and ultraviolet wavelengths,
since it is transparent in these regions (about 0.15 to
9 mm) and exhibits an extremely low-refractive index.
Calcium Fluoride is a water insoluble calcium source
for use in oxygen-sensitive applications, such as metal
production. In extremely low concentrations (ppm),
fluoride compounds are used in health applications.
Fluoride compounds also have significant uses in
synthetic organic chemistry. They are also commonly
used to alloy metal and for optical deposition.
It is also used as a flux for melting and liquid processing
of iron, steel and their composites. Its action is based
on its similar melting point to iron, on its ability to
dissolve oxides and on its ability to wet oxides and
metals.
The Uses of Calcium fluoride
Calcium fluoride is the commercially important source for fluoride compounds as well as hydrogen fluoride. It is transparent from ultraviolet to infrared region. It is used in spectroscopy, thermal imaging systems and excimer lasers; it is also used in the manufacturing of optical components including windows, prisms and lenses. In addition, it is also used in aluminum-metallurgy, brake lining manufacturing industries, and in tooth enamel.
Definition
A pure naturally occurring form of calcium fluoride.
Definition
A mineral form of calcium fluoride (CaF2), used in making some cements and types of glass.
Production Methods
The commercial product is obtained from naturally occurring mineral fluorspar, which is purified and powdered. Also, it may be precipitated by mixing a solution of sodium fluoride with a soluble calcium salt:
Ca(NO3)2 + 2NaF → CaF2 + NaNO3
Alternatively, it may be obtained by treating calcium carbonate with hydrofluoric acid:CaCO3 + 2HF → CaF2 + CO2 + H2O.
General Description
Odorless gray powder or granules. Sinks in water.
Reactivity Profile
Calcium fluoride has weak oxidizing or reducing powers. Redox reactions can however still occur. The majority of compounds in this class are slightly soluble or insoluble in water. If soluble in water, then the solutions are usually neither strongly acidic nor strongly basic. These compounds are not water-reactive.
Hazard
An irritant.
Health Hazard
Little acute toxicity
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Industrial uses
Also called fluorite, fluorspar is a crystalline or massive granular mineral of the composition CaF2, used as a flux in the making of steel, for making hydrofluoric acid, in opalescent glass, in ceramic enamels, for snaking artificial cryolite, as a binder for vitreous abrasive wheels,and in the production of white cement. It is a better flux for steel than limestone, making a fluid slag, and freeing the iron of sulfur and phosphorus.
Acid spar is a grade used in making hydrofluoric acid. It is also used for making refrigerants, plastics, and chemicals, and for aluminum reduction. Optical fluorspar is the highest grade but is not common. Fluoride crystals for optical lenses are grown artificially from acid-grade fluorspar. Pure calcium fluoride, Ca2F6, is a colorless crystalline powder used for etching glass, in enamels, and for reducing friction in machine bearings. It is also used for ceramic parts resistant to hydrofluoric acid and most other acids. Calcium fluorite has silicon in the molecule and is a crystalline powder used for enamels. The clear rhombic fluoride crystals used for transforming electric energy into light are lead fluoride, PbF2.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Mildly toxic by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. Other experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. See also FLUORIDES and CALCIUM COMPOUNDS. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of F-.
Potential Exposure
Calcium fluoride is used for production of hydrofluoric acid; as a flux in steel manufacture; in smelting; electric arc welding, making glass and ceramics; and to fluoridate drinking water.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for atleast 15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids.Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemicalcontacts the skin, remove contaminated clothing and washimmediately with soap and water. Seek medical attentionimmediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, removefrom exposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing hasstopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemicalhas been swallowed, get medical attention. A doctoror authorized paramedic may consider administeringaluminum hydroxide gel, if conscious.
Storage
Color Code—Green: General storage may be used.Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilatedarea away from acids and chemically active metals (such aspotassium, sodium, magnesium, and zinc) because corrosivehydrogen fluoride will be produced.
Shipping
Calcium fluoride is not specifically covered by DOT in its Performance-Oriented Packaging Standards.
Incompatibilities
Dust may form explosive mixture with air. Reacts with water, moist air, and steam, releasing flammable hydrogen gas; and may self-ignite in air. A strong reducing agent; incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Incompatible with metal halogenates, silver fluoride, and tetrahydrofuran
Properties of Calcium fluoride
| Melting point: | 1402 °C |
| Boiling point: | 2500 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 3.18 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | 1.434 |
| Flash point: | 2500°C |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Slightly soluble in acid; insoluble in acetone. |
| form | rod |
| color | white |
| Specific Gravity | 3.18 |
| Water Solubility | 0.015 g. per 100g H20 at room temperature.(INSOLUBLE) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,1667 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 8.28 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2.5 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 250 mg/m3; TWA 2.5 mg/m3 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.5(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. Calcium fluoride is inert to organic chemicals and many acids, including HF. It will slowly dissolve in nitric acid. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7789-75-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Calcium fluoride(7789-75-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Calcium difluoride (7789-75-5) |
Safety information for Calcium fluoride
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H303:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Calcium fluoride
| InChIKey | WUKWITHWXAAZEY-UHFFFAOYSA-L |
Calcium fluoride manufacturer
NRS Chemicals LLP
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Calcium fluoride 98%View Details
Calcium fluoride 98%View Details -
 Calcium fluoride CAS 7789-75-5View Details
Calcium fluoride CAS 7789-75-5View Details
7789-75-5 -
 Calcium fluoride CAS 7789-75-5View Details
Calcium fluoride CAS 7789-75-5View Details
7789-75-5 -
 Calcium fluoride crystal optic disc, 13mm x 1mm, Polished both sides CASView Details
Calcium fluoride crystal optic disc, 13mm x 1mm, Polished both sides CASView Details -
 Calcium fluoride crystal optic disc, 38mm x 6mm, Polished both sides CASView Details
Calcium fluoride crystal optic disc, 38mm x 6mm, Polished both sides CASView Details -
 Calcium fluoride crystal optic disc, 22mm x 4mm, Polished both sides CASView Details
Calcium fluoride crystal optic disc, 22mm x 4mm, Polished both sides CASView Details -
 Calcium fluoride Crystal Optic Disk, Polished on both sides CASView Details
Calcium fluoride Crystal Optic Disk, Polished on both sides CASView Details -
 calcium fluoride CASView Details
calcium fluoride CASView Details
