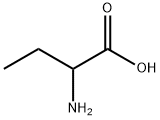
L-Glutamic acid
Synonym(s):L-Glutamic acid;Glu;Heavy carbon and nitrogen isotopes in L -glutamic acid;L-α-Aminoglutaric acid, Glu, L-alpha-Aminoglutaric acid;(S)-2-Aminopentanedioic acid
- CAS NO.:56-86-0
- Empirical Formula: C5H9NO4
- Molecular Weight: 147.13
- MDL number: MFCD00002634
- EINECS: 200-293-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:46
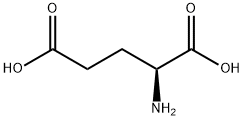
What is L-Glutamic acid?
Absorption
Absorbed from the lumen of the small intestine into the enterocytes.Absorption is efficient and occurs by an active transport mechanism.
Toxicity
Glutamate causes neuronal damage and eventual cell death, particularly when NMDA receptors are activated, High dosages of glutamic acid may include symptoms such as headaches and neurological problems.
Description
L-Glutamic acid, or L-2-aminopentanedioic acid, is a naturally
occurring amino acid of plant and animal proteins. It has a very
faint odor reminiscent of yeast or freshly baked bread. It has a
mild, somewhat sweet, meat-like taste.
The average glutamic acid content of food proteins is 20 percent.
Expressed as glutamic acid per 100 g of the edible portions,
medium fat beef contains about 2.65 g of glutamic acid; whole
liquid cow milk, 0.82 g; lean pork, 2.16 g; haddock, 2.32 g; peas,
5.58 g; soybeans, 7.01 g; commeal, 1.62 g; and whole grain wheat
flour, 4.16 g. In addition, free glutamic acid is present in many
vegetables, fish, and meats in small amounts (0. 005 to 0.23 g per
100 g) and as high as 2 g per 100 g in some varieties of cheese.
Recent estimates of free amino acids in the milk of various species
indicated that the free glutamic acid in human milk is about 0.22
g per 100 mL.
Glutamic acid and its salts are prepared commercially by hydrolysis
of gluten (wheat, corn, soybean, sugarbeet protein); by fermentation
from glucose-containing raw materials; the racemic acid
may be resolved into the d- and ι-isomer by fractional crystallization;
from 2 -cyclopentenylamine; by microbial conversion of aketoglutaric
acid; or by an alternative method, using Bacillus
megatherium-cereus; from fumaric acid using B. pumilus; from
starch.
Glutamic acid and the hydrochloride as well as the mono-sodium,
-potassium, and -ammonium salts of L-glutamic acid share similar
physical properties: they are nearly odorless, white, free-flowing
crystalline powders, and except for glutamic acid and glutamic
acid hydrochloride, are freely soluble in water. Glutamic acid is
slightly soluble and glutamic acid hydrochloride moderately soluble
in water. The pH of a saturated solution is about 3.2.
Chemical properties
White cryst. powder
Chemical properties
L-Glutamic acid has a very faint odor reminiscent of yeast or freshly baked bread and a mild, somewhat sweet, meat- like taste This is a naturally occurring amino acid of plant and animal proteins The average glutamic acid content of food proteins is 20%, expressed as glutamic acid per 100 g of the edible portions For a detailed description, see Burdock (1997).
Occurrence
Reported as occurring in many vegetable proteins, in beef fbrin, in the chrysalis of silkworm, in the hydro- lysate of crystalline insulin Also present in other important peptides, such as glutathione, tyrocidin, folic acid, β-lactoglobulin, secretin and bacitracin, and in growth hormone
The Uses of L-Glutamic acid
Glutamic acid is an amino acid used to form proteins. In the body, it turns into glutamate.
This is a chemical that helps nerve cells in the brain send and receive information from other cells. It may be involved in learning and memory. It may help people with hypochlorhydria (low stomach acid) or achlorhydria (no stomach acid).
The Uses of L-Glutamic acid
A non-essential amino acid. Its salt form (glutamate) is an important neurotransmitter that plays a key role in long-term potentiation and is important for learning and memory. It is also a key molecu le in cellular metabolism.
The Uses of L-Glutamic acid
Amino acid/exptl antieplileptic
Indications
Considered to be nature's "Brain food" by improving mental capacities; helps speed the healing of ulcers; gives a "lift" from fatigue; helps control alcoholism, schizophrenia and the craving for sugar.
Background
A peptide that is a homopolymer of glutamic acid.
Definition
ChEBI: An optically active form of glutamic acid having L-configuration.
Preparation
By hydrolysis of gluten (wheat, corn or other vegetable sources); by fermentation from glucose-containing raw materials; the racemic acid may be resolved into the d- and l-isomer by fractional crystallization; from 2-cyclopentenylamine; by microbial conversion of α-ketoglutaric acid; or by an alternative method, using Bacillus megatherium-cereus; from fumaric acid, using B pumilus; from starch.
Biotechnological Production
For industrial production of L-glutamic acid, molasses (sucrose), starch hydrolysates (glucose) and ammonium sulfate are generally used as carbon and nitrogen sources, respectively. Key factors in controlling the fermentation are the presence of biotin in optimal concentration – to optimize cell growth and the excretion of Lglutamate – and sufficient supply of oxygen to reduce the accumulation of byproducts, such as lactic and succinic acid. In biotin-rich fermentation media the addition of penicillin or cephalosporin C favors the overproduction of L-glutamic acid due to effects on the cell membrane. The supplementation of fatty acids also results in an increased permeability of the cells thus enhancing glutamate excretion.
A strain of Microbacterium ammoniaphilum cultured under biotin-deficient conditions produced 58 % of L-glutamic acid formed from glucose via phosphoenolpyruvate, citrate, and of a-ketoglutarate and the other 42 % via the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) or the glyoxylate cycle.
Biological Activity
The predominant excitatory transmitter in the mammalian central nervous system. Acts at ionotropic and metabotropic glutamate receptors.
Biochem/physiol Actions
L-Glutamic acid along with l-Lysine is used for preparation of bifunctional DTPA-like ligands. L-glutamic acid can stimulate the spontaneous release of [3H] dopamine ( [3H] DA).
Pharmacokinetics
In addition to being one of the building blocks in protein synthesis, it is the most widespread neurotransmitter in brain function, as an excitatory neurotransmitter and as a precursor for the synthesis of GABA in GABAergic neurons.
Safety Profile
Human systemic effects by ingestion and intravenous routes: headache and nausea or vomiting. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NOx.
Metabolism
Hepatic
Storage
Room temperature
Purification Methods
Crystallise L-glutamic acid from H2O acidified to pH 3.2 by adding 4volumes of EtOH, and drying at 110o. Likely impurities are aspartic acid and cysteine. It sublimes at 170-175o/10mm. It melts at 160o with cyclisation to L-pyrrolidone carboxylic acid. [Dunn & Brophy J Biol Chem 99 224 1958, Parikh et al. J Am Chem Soc 80 9571958, Greenstein & Winitz The Chemistry of the Amino Acids J. Wiley, Vol 3 pp 1929-1952 1961, Beilstein 4 III 1530, 4 IV 3028.]
Properties of L-Glutamic acid
| Melting point: | 205 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 267.21°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 32 º (c=10,2N HCl) |
| Density | 1.54 g/cm3 at 20 °C |
| refractive index | 1.4300 (estimate) |
| FEMA | 3285 | L-GLUTAMIC ACID |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 1 M HCl: 100 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 2.13(at 25℃) |
| color | White |
| PH | 3.0-3.5 (8.6g/l, H2O, 25℃) |
| Odor | at 100.00 %. mild yeast baked bread |
| optical activity | [α]20/D +32°, c = 10 in 2 M HCl |
| Water Solubility | 7.5 g/L (20 ºC) |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.1 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.1 |
| Merck | 14,4469 |
| JECFA Number | 1420 |
| BRN | 1723801 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 56-86-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | L-Glutamic acid(56-86-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | L-Glutamic acid (56-86-0) |
Safety information for L-Glutamic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for L-Glutamic acid
| InChIKey | WHUUTDBJXJRKMK-VKHMYHEASA-N |
L-Glutamic acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Hexon Laboratories Private Limited
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 L-Glutamic Acid for tissue culture CAS 56-86-0View Details
L-Glutamic Acid for tissue culture CAS 56-86-0View Details
56-86-0 -
 L-Glutamic Acid (SQ) CAS 56-86-0View Details
L-Glutamic Acid (SQ) CAS 56-86-0View Details
56-86-0 -
 L Glutamic Acid Powder, Packaging Size: 25/50 KgView Details
L Glutamic Acid Powder, Packaging Size: 25/50 KgView Details
56-45-1 -
 Powder L-Glutamic AcidView Details
Powder L-Glutamic AcidView Details
56-86-0 -
 L-Glutamic AcidView Details
L-Glutamic AcidView Details
56-86-0 -
 L Glutamic AcidView Details
L Glutamic AcidView Details
56-86-0 -
 L Glutamic AcidView Details
L Glutamic AcidView Details
56-86-0 -
 L-Glutamic AcidView Details
L-Glutamic AcidView Details
56-86-0
