Kresoxim-methyl
Synonym(s):Kresoxim-methyl;Methyl (E)-α-(methoxyimino)-2-(2-methylphenoxymethyl)phenylacetate
- CAS NO.:143390-89-0
- Empirical Formula: C18H19NO4
- Molecular Weight: 313.35
- MDL number: MFCD00871777
- EINECS: 604-351-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-11-10 14:44:25
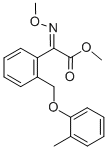
What is Kresoxim-methyl?
Description
Kresoxim-methyl is a strobilurin fungicide. It inhibits conidial germination of V. inaequalis isolates from apple orchards (EC50s = 0.00033-0.0078 mg/L). Kresoxim-methyl also inhibits mycelial growth (EC50 = 0.240 mg/L) and is fungicidal against Saprolegnia (MIC = 1 mg/L). It increases intracellular calcium levels and disrupts the mitochondrial membrane potential in mouse cortical cultures in a concentration-dependent manner. Kresoxim-methyl is toxic to goldfish (C. auratus; LC50 = 0.807 mg/L).
The Uses of Kresoxim-methyl
Kresoxim-methyl is used for the control of several diseases (scab, mildews, blast, sheath blight and others) on a range of crops including apples, pears, vines, sugar beet and cereals.
The Uses of Kresoxim-methyl
An agricultural fungicide.
The Uses of Kresoxim-methyl
Agricultural fungicide.
What are the applications of Application
Kresoxim-methyl is a reagent also known as benzeneacetic acid methyl ester
Definition
ChEBI: A carboxylic ester that is the methyl ester of (2E)-(methoxyimino){2-[(2-methylphenoxy)methyl]phenyl}acetic acid. A fungicide for the control of scab on apples and pears and other fungal diseases on a wide range of crops.
Hazard
Moderately toxic by skin contact. Low tox-icity by ingestion and inhalation.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by skin contact. Low toxicity by ingestion and inhalation. Questionable carcinogen with experimental data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of NOx.
Metabolic pathway
By hepatocyte suspensions prepared from goats, pigs, hens, and rats that have been cryopreserved and thawed, BAS 490 F is metabolized via the same pathways as observed using fresh rat hepatocytes. The rate of hydrolysis of 14C-BAS 490 F leading to a carboxylic acid derivative seems to be constant between the cryopreserved and fresh hepatocytes except for goats. The oxidation reaction at the methyl group of the phenoxy ring, leading to the hydroxymethyl analog of the carboxylic acid of BAS 490 F, significantly decreases after cryopreservation, whereas the formation of (E)-2-methoxyimino-2[2-(4- hydroxy-2-methylphenyloxymethyl)phenyl] acetic acid by hydroxylation at the 4-position of the phenoxy ring remains at a constant rate. In pig hepatocytes, the two hydroxylated metabolites of the phenoxy ring, carboxy BAS 409 F and (E)-2-methoxyimino-2-o- hydroxymethylphenyl acetic acid, are formed to a lesser extent after cryopreservation.
Metabolism
Kresoxim-methyl is rapidly metabolized in mammalian systems to the virtually inactive carboxylic acid, accounting for its low toxicity and high level of selectivity. Atharvest residues in cereals and top fruit are <0.05 mg/kg and <1 mg/kg in grapes and vegetables. The soil DT50 = <3 days, and the Koc is 219 to 372. For the main metabolite, the Koc is 17 to 24. Hydrolytic stability tests indicate a DT50 of 34 days at pH 7 but only 7 h at pH 9.
Degradation
Kresoxim-methyl is a stable crystalline solid with limited water solubility.
It is stable in the pH range 3-8 but it is hydrolysed to the carboxylic acid
(2, see Scheme 1) in base. DT50 values (25 °C) at pH 5,7 and 9 were 875,34
and 0.29 days, respectively. The product (2) was stable under these
conditions.
Kresoxim-methyl undergoes rapid photodegradation in water when
irradiated with UV light. Its DT50 was 3 days and several products were
formed, one of which was the Z-isomer. Details of the other products are
not available. Under conditions of simulated sunlight the compound was
degraded with a DT50 of 37 days in pure water and 19 days in natural
pond water.
Toxicity evaluation
Kresoxim-methyl has an acute oral LD50 > 5,000 and an acute dermal LD50 > 2,000 mg/kg in rats. The NOEL for rats is 800 ppm, and the ADI = 0.4 mg/kg bw (body weight). Kresoxim-methyl is not a skin or eye irritant, is nonmutagenic and nonteratogenic. It shows toxicity to aquatic organisms (fish 96-h LC50 = 0.681 to 1 mg/L) but does not cause permanent damage. Other nontarget organisms show the following levels of sensitivity: bird: 14-day LD50 = 2,150 mg/kg; bee: 48- h LD50 ≥ 20 μg/bee; worm: LC50 ≥ 937 mg/kg; Daphnia: 48-h EC50 = 0.186 mg/L; and algae 0- to 2-h EC50 = 63 μg/L.
Properties of Kresoxim-methyl
| Melting point: | 98-100°C |
| Boiling point: | 429.4±47.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.28 |
| vapor pressure | 2.3 x 10-6 P a (20 °C) |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform: Slightly Soluble,Methanol: Slightly Soluble |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 2 mg l-1(20 °C) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless to light yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 1.28 (20℃) |
| BRN | 8330581 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 143390-89-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Kresoxim-methyl (143390-89-0) |
Safety information for Kresoxim-methyl
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H351:Carcinogenicity H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Kresoxim-methyl
| InChIKey | ZOTBXTZVPHCKPN-HTXNQAPBSA-N |
Kresoxim-methyl manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Kresoxim-methyl 98% (HPLC) CAS 143390-89-0View Details
Kresoxim-methyl 98% (HPLC) CAS 143390-89-0View Details
143390-89-0 -
 Kresoxim-methyl 95%) CAS 143390-89-0View Details
Kresoxim-methyl 95%) CAS 143390-89-0View Details
143390-89-0 -
 Kresoxim-methyl CAS 143390-89-0View Details
Kresoxim-methyl CAS 143390-89-0View Details
143390-89-0 -
 Kresoxim-methyl CAS 143390-89-0View Details
Kresoxim-methyl CAS 143390-89-0View Details
143390-89-0 -
 Kresoxim Methyl 44.3% SCView Details
Kresoxim Methyl 44.3% SCView Details
143390-89-0 -
 Kresoxim Methyl 44.3% SC FungicideView Details
Kresoxim Methyl 44.3% SC FungicideView Details
143390-89-0 -
 Liquid Dragan Kresoxim Methyl Systemic FungicideView Details
Liquid Dragan Kresoxim Methyl Systemic FungicideView Details
143390-89-0 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0
