Methyl salicylate
Synonym(s):2-Hydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester;Methyl 2-hydroxybenzoate;Methylis salicylas;Oil of wintergreen;Wintergreen oil
- CAS NO.:119-36-8
- Empirical Formula: C8H8O3
- Molecular Weight: 152.15
- MDL number: MFCD00002214
- EINECS: 204-317-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 21:30:31
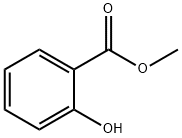
What is Methyl salicylate?
Absorption
Approximately 12-20% of topically applied methyl salicylate may be systemically absorbed through intact skin within 10 hours of application, and absorption varies with different conditions such as surface area and pH. Dermal bioavailability is in the range of 11.8 – 30.7%. For the assessment of potential oral exposure to salicylates, bioavailability is assumed to be 100% .
Toxicity
Oral LD50 values (mg/kg) for mouse, rat and rabbit are 1110, 887 and 1300, respectively. Oral LD50 values for child and adult human (mg/kg) are 228 and 506, respectively. Although systemic toxicity from topical administration is rare, methyl salicylate can be absorbed in intract skin to cause stimulation of the central nervous system respiratory center, disturbance of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, and disturbance of intracellular respiration. Severe toxicity can result in acute lung injury, lethargy, coma, seizures, cerebral edema, and death. In case of salicylate poisoning, the treatment consists of general supportive care, gastrointestinal decontamination with activated charcoal in cases of salicylate ingestion, and monitoring of serum salicylate concentrations. Bicarbonate infusions or hemodialysis can be used to achieve enhanced salicylate elimination .
Description
Methyl salicylate (wintergreen oil) is an organic ester that is naturally produced by the holly plant. It has the odour and taste of wintergreen oil. It is used as a fragrance and in topical ointments.Methyl salicylate is hydrolysed to produce salicylic acid which has similar chemicals to aspirin and is used to relieve inflammation in headaches and muscle pain. Concentrated methyl salicylate is toxic, especially to children.
Description
Methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil) is an organic ester that is naturally produced by many species of plants. Some of the plants which produce it are called wintergreens, hence the common name. This compound is used as a fragrance. It is also found in liniments (rubbing ointments).
Chemical properties
Methyl Salicylate is the main component of wintergreen oil and occurs in small quantities in other essential oils and fruits. It is a colorless liquid with a sweet, phenolic odor.
Chemical properties
Methyl salicylate has a characteristic wintergreen-like odor. May be prepared by extraction from natural sources; or by esterification of salicylic acid with methanol.
Chemical properties
Wintergreen is an evergreen shrub with slender, creeping stems, assurgent, flowering branches with toothed leaves clustered at the top, white, bell-shaped flowers blossoming July to August, followed by red berries (checkerberries). The plant grows extensively in the woods of Canada and the United States (Pennsylvania). The leaves are harvested between June and September. Wintergreen has an aromatic odor and flavor similar to methyl salicylate.
Occurrence
Numerous plants produce methyl salicylate in very small amounts. Some plants, such as the following, produce more:
Some species of the genus Gaultheria in the family Ericaceae, including Gaultheria procumbens, the wintergreen or eastern teaberry;
Some species of the genus Betula in the family Betulaceae, particularly those in the subgenus Betulenta such as B. lenta, the black birch;
All species of the genus Spiraea in the family Rosaceae, also called the meadowsweets.
This compound is produced most likely as an anti-herbivore defense. If the plant is infected with herbivorous insects, the release of methyl salicylate may function as an aid in the recruitment of beneficial insects to kill the herbivorous insects.Aside from its toxicity, methyl salicylate may also be used by plants as a pheromone to warn other plants of pathogens such as tobacco mosaic virus.
The Uses of Methyl salicylate
Methyl salicylate is an organic ester that is commonly produced naturally by wintergreens. Methyl salicylate is utilize as a anti-herbivore defense system in various plants that produces it. Methyl sa licylate is also used in high concentrations as a rubefacient to treat joint, muscular pain and acute pain. Methyl slicylate is also used as a flavoring agent and often used to provide fragrance to pr oducts.
The Uses of Methyl salicylate
Potent inhibitor of ornithine decarboxylase
The Uses of Methyl salicylate
Methyl salicylate occurs in the leaves ofGaultheria procumbens L. and in the barkof Betulaceae. It is produced by esterificationof salicylic acid with methanol. It is used inperfumery and as a flavoring agent.
The Uses of Methyl salicylate
In high concentrations as a rubefacient in deep heating liniments (such as Bengay) to treat joint and muscular pain. Randomised double blind trial reviews report evidence of its effectiveness that is weak, but stronger for acute pain than chronic pain, and that effectiveness may be due entirely to counter-irritation. However, in the body it metabolizes into salicylates, including salicylic acid, a known NSAID.
In low concentrations as a flavoring agent (no more than 0.04%; it is toxic).
providing fragrance to various products and as an odor-masking agent for some organophosphate pesticides. If used excessively, it can cause stomach and kidney problems.
Attracting male orchid bees, who apparently gather the chemical to synthesize pheromones; it is commonly used as bait to attract and collect these bees for study.
Clear plant or animal tissue samples of color, and as such is useful for microscopy and immunohistochemistry when excess pigments obscure structures or block light in the tissue being examined. This clearing generally only takes a few minutes, but the tissue must first be dehydrated in alcohol.
A mint flavoring in some kinds of chewing gum and candy, as an alternative to the more common peppermint and spearmint oils. It can also be found as a flavoring of root beer. It is also a potentially entertaining source of tri boluminescence ; when mixed with sugar and dried, it gains the tendency to build up electrical charge when crushed or rubbed. This effect can be observed by crushing wintergreen Life Savers candy in a dark room.
The Uses of Methyl salicylate
Methyl salicylate is used in high concentrations as a rubefacient in deep heating liniments (such as Bengay) to treat joint and muscular pain. Randomised double blind trial reviews report evidence of its effectiveness that is weak, but stronger for acute pain than chronic pain, and that effectiveness may be due entirely to counter-irritation. However, in the body it metabolizes into salicylates, including salicylic acid, a known NSAID.
It is used in low concentrations as a flavoring agent (no more than 0.04 %; it is toxic). It is also used to provide fragrance to various products and as an odor-masking agent for some organophosphate pesticides . If used excessively, it can cause stomach and kidney problems.
Methyl salicylate is among the compounds that attract male orchid bees, who apparently gather the chemical to synthesize pheromones; it is commonly used as bait to attract and collect these bees for study.
Background
Methyl salicylate (oil of wintergreen or wintergreen oil) is an organic ester naturally produced by many species of plants, particularly wintergreens. The compound was first extracted and isolated from plant species Gaultheria procumbens in 1843. It can be manufactured synthetically and it used as a fragrance, in foods, beverages, and liniments. It forms a colorless to yellow or reddish liquid and exhibits a characteristic odor and taste of wintergreen. For acute joint and muscular pain, methyl salicylate is used as a rubefacient and analgesic in deep heating liniments. It is used as a flavoring agent in chewing gums and mints in small concentrations and added as antiseptic in mouthwash solutions.
Indications
Ointments or liniments containing methyl salicylate are applied topically as counter irritant for relief of acute pain associated with lumbago,sciatica and rheumatic conditions. Local analgesics for human and veterinary medicine.
What are the applications of Application
Methyl Salicylate is an anticoagulant that interrupts the vitamin K1-epoxide cycle
Definition
ChEBI: A benzoate ester that is the methyl ester of salicylic acid.
Production Methods
Methyl acetate, a novel acyl acceptor for biodiesel production has been developed, and a comparative study on Novozym 435-catalyzed transesterification of soybean oil for biodiesel production with different acyl acceptors has been studied (Noureddini et al., 2005).

Figure 1 shows the effect of the molar ratio of methanol to sunflower oil on the methyl ester yield for catalytic (3% CaO) transesterification in supercritical methanol at 523 K.
Preparation
Methyl salicylate can be produced by esterifying salicylic acid with methanol. Commercial methyl salicylate is now synthesized, but in the past, it was commonly distilled from the twigs of Betula lenta (sweet birch) and Gaultheria procumbens (eastern teaberry or winter green).
Chemical properties
Methyl salicylate is a yellowish or reddish oily liquid with the odor and taste of gaultheria (wintergreen). Its melting point is-8.6°C and its boiling point is between 220°–224°C. Methyl salicylate is soluble in water at 1 g in about 1500 ml, and is soluble in chloroform and ether O'Neil et al. Plastic containers, such as those made of polystyrene, are unsuitable for liniments or ointments containing methyl salicylate. Methyl salicylate should be stored in an air tight container and protected from light.
Composition
The leaves of wintergreen are reported to contain arbutin, caffeic acid, ericolin, ferulic acid, gaultherase, gaultheric acid, gaultherin, gentisinc acid, methyl salicylate (5445 to 7920 ppm) o-pyrocatachuic acid, p-coumaric acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, primverose, protocatachuic acid, syringic acid, tannic acid, tannin, tricontane and vallininc acid.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 40 ppb
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 10 ppm: sweet, salicylate and root beer with aromatic and balsamic nuances
Synthesis Reference(s)
Canadian Journal of Chemistry, 61, p. 688, 1983 DOI: 10.1139/v83-127
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 40, p. 3649, 1975 DOI: 10.1021/jo00913a007
Tetrahedron Letters, 37, p. 153, 1996 DOI: 10.1016/0040-4039(95)02120-5
General Description
Colorless yellowish or reddish liquid with odor of wintergreen.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Methyl Salicylate is an ester. Esters react with acids to liberate heat along with alcohols and acids. Strong oxidizing acids may cause a vigorous reaction that is sufficiently exothermic to ignite the reaction products. Heat is also generated by the interaction of esters with caustic solutions. Flammable hydrogen is generated by mixing esters with alkali metals and hydrides. Birch-Me is incompatible with oxidizers. Birch-Me is also incompatible with strong bases. Birch-Me may react with iron salts.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion; use in foods restrictedby FDA, lethal dose 30 cc in adults, 10 cc in chil-dren.
Health Hazard
Methyl salicylate is a highly toxic compound.The toxic symptoms in humans include nausea, vomiting, gastritis, diarrhea, respiratorystimulation, labored breathing, pulmonaryedema, convulsions, and coma. Ingestion of15 to 25 mL of this compound may befatal to humans. Application of the liquidon the skin and eyes produced severe irrita tion in rabbits. Oral, subcutaneous, or der mal administration of methyl salicylate intest animals produced specific developmen tal abnormalities affecting the eyes, ears, andcentral nervous system
Toxicity of this compound is relativelymore severe in humans than in many com mon laboratory animals. The oral LD50 values in test animals were within the range800–1300 mg/kg.
Fire Hazard
Methyl salicylate is combustible.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Contact allergens
This anti-inflammatory agent is found in a wide number of ointments and can induce allergic contact dermatitis.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Methyl salicylate plays an important role in fruit ripening. It is known to attract natural enemies of herbivores. MeSA inhibits the activity of aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid synthase (ACC synthase) and aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid oxidase (ACC oxidase) in plums and tomatoes, it can inhibit fungal infections and reduce chilling injury symptoms in fruits like pomegranates. This oil of wintergreen is of great interest in the tobacco industry as a flavorant. It has counter irritant and anti-inflammatory effects.
Pharmacokinetics
Methyl salicylate relieve musculoskeletal pain in the muscles, joints, and tendons by causing irritation and reddening of the skin due to dilated capillaries and increased blood flow. It is pharmacologically similar to aspirin and other NSAIDs but as a topical agent it primarily acts as a rubefacient and skin irritant. Counter-irritation is believed to cause a soothing sensation of warmth.
Safety Profile
Human poison by ingestion. Moderately toxic to humans by an unspecified route. Moderately toxic experimentally by intraperitoneal, intravenous, and subcutaneous routes. An experimental teratogen. Human systemic effects by ingestion: flaccid paralysis without anesthesia, general anesthesia, dyspnea, nausea, vomiting, and respiratory stimulation. Experimental reproductive effects. A severe skin and eye irritant. Ingestion of relatively small amounts has caused severe poisoning and death. Combustible liquid when exposed to heat or flame; can react with oxibzing materials. To fight fire, use CO2, dry chemical. When heated to decomposition it emits acrid smoke and irritating fumes.
Safety
In pure form, methyl salicylate is toxic, especially when taken internally. A single teaspoon (5ml) of methyl salicylate contains 7g of salicylate, which is equivalent to more than twenty- three 300 mg aspirin tablets. The lowest published lethal dose is 101 mg / kg body weight in adult humans , (or 7.07 grams for a 70 - kg adult). It has proven fatal to small children in doses as small as 4 ml.[6] A seventeen-year- old cross - country runner at Notre Dame Academy on Staten Island, died in April 2007, after her body absorbed methyl salicylate through excessive use of topical muscle-pain relief products.
Most instances of human toxicity due to methyl salicylate are a result of over-application of topical analgesics, especially involving children. Some people have intentionally ingested large amounts of oil of wintergreen. Salicylate, the major metabolite of methyl salicylate, may be quantitated in blood, plasma or serum to confirm a diagnosis of poisoning in hospitalized patients or to assist in an autopsy.
Synthesis
By esterification from natural sources; by esterification of salicylic acid with methanol
Carcinogenicity
Available data suggest that methyl salicylate is not carcinogenic.
Metabolism
Minor metabolism may occur in various tissues but hepatic metabolism constitutes the majority of metabolic processes of absorbed methyl salicylate. It is mainly hydrolyzed to salicylic acid via hepatic esterase enzymes. Conjugation with glycine forms salicyluric acid and conjugation with glucuronic forms ester or acyl and ether or phenolic glucuronide, which are the three main metabolites.
Purification Methods
Dilute the ester with Et2O, wash with saturated NaHCO3 (it may effervesce due to the presence of free acid), brine, dry MgSO4, filter, evaporate and distil it. Its solubility is 1g/1.5L of H2O. The benzoyl derivative has m 92o (b 270-280o/120mm), and the 3,5-dinitrobenzoate has m 107.5o, and the 3,5-dinitrocarbamoyl derivative has m 180-181o. [Hallas J Chem Soc 5770 1965, Beilstein 10 IV 143.]
Toxicity evaluation
Oral LD50 values (mg/kg) for mouse, rat and rabbit are 1110, 887 and 1300, respectively. Oral LD50 values for child and adult human (mg/kg) are 228 and 506, respectively. Topical methyl salicylate generally rarely causes systemic toxicity, but it can be absorbed by the skin leading to stimulation of the central nervous system respiratory center, disturbance of lipid and carbohydrate metabolism, and disturbance of intracellular respiration. Severe poisoning can lead to acute lung injury, lethargy, coma, seizures, cerebral edema, and death. In the case of salicylate intoxication, treatment includes general supportive care, purification of the gastrointestinal tract with activated charcoal in the case of ingestion of salicylic acid, and monitoring of serum salicylic acid concentration. Bicarbonate infusion or hemodialysis can be used to enhance the elimination of salicylic acid.
Properties of Methyl salicylate
| Melting point: | -8--7 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 222 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.174 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 5.26 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1 mm Hg ( 54 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2745 | METHYL SALICYLATE |
| Flash point: | 226 °F |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Very slightly soluble in water, miscible with ethanol (96 per cent) and with fatty and essential oils. |
| form | Liquid |
| pka | pKa 9.90 (Uncertain) |
| color | Clear colorless to pale yellow |
| Odor | at 10.00 % in dipropylene glycol. wintergreen mint |
| Water Solubility | 0.07 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| JECFA Number | 899 |
| Merck | 14,6120 |
| BRN | 971516 |
| Dielectric constant | 9.0(20℃) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 119-36-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | 2-Hydroxybenzoic acid methyl ester(119-36-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Methyl salicylate (119-36-8) |
Safety information for Methyl salicylate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Methyl salicylate
| InChIKey | OSWPMRLSEDHDFF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Methyl salicylate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
SAKEM LLP
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 METHYL SALICYLATE 99%View Details
METHYL SALICYLATE 99%View Details -
 Methyl Salicylate (SQ) CAS 119-36-8View Details
Methyl Salicylate (SQ) CAS 119-36-8View Details
119-36-8 -
 Methyl Salicylate CAS 119-36-8View Details
Methyl Salicylate CAS 119-36-8View Details
119-36-8 -
 Methyl Salicylate api, 50Kg drumView Details
Methyl Salicylate api, 50Kg drumView Details
119-36-8 -
 Ethylene Glycol (107-21-1)View Details
Ethylene Glycol (107-21-1)View Details
107-21-1 -
 Methyl SalicylateView Details
Methyl SalicylateView Details
119-36-8 -
 Methyl SalicylateView Details
Methyl SalicylateView Details
119-36-8 -
 Methyl Salicylate, 35kg DrumView Details
Methyl Salicylate, 35kg DrumView Details
119-36-8
