Pirimiphos-methyl
- CAS NO.:29232-93-7
- Empirical Formula: C11H20N3O3PS
- Molecular Weight: 305.33
- MDL number: MFCD00055366
- EINECS: 249-528-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
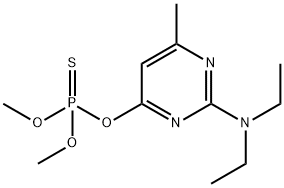
What is Pirimiphos-methyl ?
Chemical properties
Light yellow, straw colored, or amber oily liquid. Odorless when pure.
The Uses of Pirimiphos-methyl
Pirimiphos-methyl is a phosphorothioate used as an insecticide. Pirimiphos-methyl is commonly used for mosquito control as well as control of greenhouse crop pests and stored-product insects.
The Uses of Pirimiphos-methyl
Pirimiphos-methyl is used to control a wide range of insect and mite pests in stored products and a wide range of insects and mites on agricultural crops, particularly sucking pests under glass.
Definition
ChEBI: An organic thiophosphate that is O,O-dimethyl O-pyrimidin-4-yl phosphorothioate substituted by a methyl group at position 6 and a diethylamino group at position 2.
General Description
Yellow liquid. Corrosive to tin and mild steel. Used as an insecticide.
Air & Water Reactions
Hydrolyzed by strong acid or base.
Reactivity Profile
Organophosphates are susceptible to formation of highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas in the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides. Partial oxidation by oxidizing agents may result in the release of toxic phosphorus oxides.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Agricultural Uses
Insecticide, Acaricide: Pirimiphos-methyl is a post-harvest insecticide used to control a variety of insects in stored grain products and seed such as corn, rice, wheat and sorghum. It is also incorporated into cattle ear tags, and used for the fogging treatment of iris bulbs and pre-harvest clean up of fruits and vegetables.
Trade name
ACTELLIC®; ACTELLIFOG®; BLEX®; ENT 27699Gc®; DOMINATOR® EAR TAG; DOUBLE BARREL® EAR TAG; PLANT PROTECTION PP511®; PP511®; SILOSAN®; SYBOL®; TOMAHAWK®[C]
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by ingestion. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx, POx, and SOx.
Potential Exposure
Pirimiphos-methyl is a post -harves organophosphate insecticide/acaricide used to control a variety of insects in stored grain products and seed such as corn, rice, wheat and sorghum. It is also incorporated into cattle ear tags, and used for the fogging treatment of iris bulbs and preharvest cleanup of fruits and vegetables.
Carcinogenicity
When rats were given diets with 0, 10, 50, or 300 ppm pirimiphos methyl (equivalent to 0, 0.4, 2.1, or 12.6 mg/kg/day) for 2 years, 4 of the 42 high-dose male rats had pancreatic islet cell adenomas and 1 had a carcinoma compared to none in control male rats . In a carcinogenicity study, mice were given diets with 0, 50, 200, or 400/300 ppm pirimiphos methyl (equivalent to 0, 8.3, 33, or 52 mg/kg/day (males); 0, 9.7, 39, or 61 mg/kg/day (females)) for 78 weeks . The initial 400 ppm dose resulted in excessive toxicity and moribundity and was reduced to 300 ppm after 8 days. There was no evidence of carcinogenicity. In another mouse carcinogenicity study, pirimiphos methyl was administered in the diet at levels of 0, 5, 250, or 500 ppm (equivalent to 0, 0.5, 25.9, or 45.0 mg/kg/ day (males) and 0, 0.6, 27.6, or 50.6 mg/kg/day (females), respectively) for 80 weeks. The test diet for the highest dose groups initially contained 300 ppm of the test compound (the duration of treatment was not specified). The dose was then increased weekly by 50 ppm to 500 ppm. No evidence of carcinogenicity was observed.
Metabolic pathway
The metabolism of pirimiphos-methyl is similar in soils, plants and animals and can be represented by initial hydrolysis to yield 2-diethylamino- 6-methyl-p yrimidin-4-0l which may be either conjugated or successively N-de-ethylated. In plants, pirimiphos-methyl itself is N-de-ethylated. It is probable that the oxon form of the compound is formed in many systems but it is more labile than the parent compound and is often not detected. 0-Dealkylation, as with most organophosphates, is most probably a major detoxification route in mammals but the evidence for it in the case of pirimiphos-methyl is poor.
Shipping
UN2783 Organophosphorus pesticides, solid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials. UN3018 Organophosphorus pesticides, liquid, toxic, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Degradation
Pirimiphos-methyl is hydrolysed under both acidic and basic conditions and is most stable at pH 7 (PM). The main product of hydrolysis was the pyrimidinol (2). There is no information, however, on the degradation products formed under either acidic or basic conditions. The DT50 of degradation was in the range of 3-4 days in sterile deionised water in the dark. Photolysis was rapid but the products of photolytic breakdown were not described (PSD, 1997).
Incompatibilities
May react violently with antimony(V) pentafluoride. Incompatible with strong acids and alkalies, lead diacetate, magnesium, silver nitrate. In the presence of strong reducing agents such as hydrides, organophosphates form highly toxic and flammable phosphine gas. Contact with oxidizers can cause the release of toxic oxides of phosphorus.
Waste Disposal
Destruction by alkali hydrolysis or incineration. Containers must be disposed of properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Pirimiphos-methyl
| Melting point: | 15°C |
| Boiling point: | 386.5±52.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | d30 1.157 |
| vapor pressure | 1.5×10-2 Pa (30°C) |
| refractive index | nD25 1.527 |
| Flash point: | -18 °C |
| storage temp. | APPROX 4°C
|
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Ethyl Acetate (Slightly) |
| pka | 3.71 |
| Water Solubility | 9.9 mg l-1 (30 °C, pH 5.2) |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Light yellow to yellow |
| Merck | 13,7580 |
| BRN | 755726 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 29232-93-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Pirimiphos methyl(29232-93-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Pirimiphos-methyl (29232-93-7) |
Safety information for Pirimiphos-methyl
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure H372:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. |
Computed Descriptors for Pirimiphos-methyl
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran

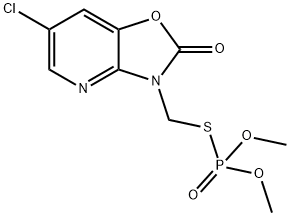
You may like
-
 Pirimiphos-methyl CAS 29232-93-7View Details
Pirimiphos-methyl CAS 29232-93-7View Details
29232-93-7 -
 Pirimiphos-methyl CAS 29232-93-7View Details
Pirimiphos-methyl CAS 29232-93-7View Details
29232-93-7 -
 17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 98+View Details
17604-74-9 -
 131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 98+View Details
131987-69-4 -
 Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 67967-07-1 98+View Details
67967-07-1 -
 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 98+View Details
5968-21-8 -
 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 1878-69-9 98+View Details
1878-69-9 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
