Azoxystrobin
- CAS NO.:131860-33-8
- Empirical Formula: C22H17N3O5
- Molecular Weight: 403.39
- MDL number: MFCD08277047
- EINECS: 204-037-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-12 11:51:25
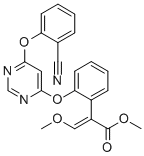
What is Azoxystrobin?
Description
Azoxystrobin is a second broad-spectrum strobilurin fungicide (28,29). It forms white solids with a mp = 116 ?C; vp = 1.1 × 10?7 mPa at 25 ?C; logP = 2.5 at 20?C; water solubility = 6 mg/L; and a half-life of 11 to 17 days for aqueous photolysis.
Chemical properties
White to beige crystalline solid or powder.
The Uses of Azoxystrobin
Azoxystrobin has a very broad spectrum of activity and is active against fungal pathogens from all four taxonomic groups, the Oomycetes, Ascomycetes, Deuteromycetes and Basidiomycetes. It controls diseases on cereals, rice, vines, apples, peaches, bananas, citrus, curcurbits, potatoes, tomatoes, peanuts, coffee and turf.
The Uses of Azoxystrobin
Strobilurin fungicide; inhibits mitochondrial respiration by blocking electron transfer between cytochromes b and c1. Agricultural fungicide.
The Uses of Azoxystrobin
Agricultural fungicide.
What are the applications of Application
Azoxystrobin is Azoxystrobin is a potent and commonly used fungicide.
Definition
ChEBI: An aryloxypyrimidine having a 4,6-diphenoxypyrimidine skeleton in which one of the phenyl rings is cyano-substituted at C-2 and the other carries a 2-methoxy-1-(methoxycarbonyl)vinyl substituent, also at C-2. An inhibitor of mitochondrial respiration by b ocking electron transfer between cytochromes b and c1, it is used widely as a fungicide in agriculture.
Hazard
Moderately toxic by inhalation.
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide: Azoxystrobin has been processed as a Reduced Risk pesticide for Turf uses. Azoxystrobin is a systemic, broad-spectrum fungicide that was first introduced in 1998. It inhibits spore germination and is used on grape vines, cereals, potatoes, apples, bananas, citrus, tomatoes and other crops. Largest crop uses in California are on almonds, rice, pistachios, wine grapes, raisins and garlic. Among the diseases it controls are rusts, downey and powdery mildew, rice blast and apple scab. A U.S. EPA restricted Use Pesticide (RUP)
Trade name
ABOUND®; AMISTAR®; AMISTAR OPTI; AMISTAR PRO; BANKIT®; HERITAGE®; ICIA5504 80WG®; OLYMPUS®; ORTIVA®; PROTEGE®; PROTEGE-ALLEGIANCE WP®;PROTEGE-FL SEED APPLIED FUNGICIDE®; QUADRIS OPTI®; QUILT®; SOYGARD WITH PROTEGE®
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by inhalation.When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors ofNOx.
Potential Exposure
A β-methyoxyacrylate, Strobilurin is an agricultural fungicide.
Metabolic pathway
Azoxystrobin is a recently developed fungicide with a novel mode of
action (see Overview for relevant references). It was first registered in
1996. It has been and is being subjected to the full range of studies to meet
current regulatory requirements for toxicology, metabolism and
environmental fate. Information on its metabolism and environmental
fate was presented as a lecture at the 9th International Congress of
Pesticide Chemistry (IUPAC) in 1998 and this will be published in the
Proceedings. The information presented below is derived from this source
(Joseph, 1998).
Azoxystrobin is a carboxylic acid methyl ester and one of its pathways
of metabolism is via hydrolysis to its carboxylic acid. The latter is not
biologically active (see Overview) and the favourable selective toxicity of
the fungicide is due to this and other metabolic reactions in non-target
species. Azoxystrobin is readily degraded in soil and ultimately mineralised
and it is metabolised in plants and animals. Metabolism is complex
because the molecule possesses several functional groups. Five different
pathways have been identified in plants and animals. Biotransformations
occurring on the parent molecule include hydrolysis, aromatic hydroxylation,
cleavage of both phenoxy linkages, nitrile to amide hydrolysis and
fragmentation of the acrylate double bond. Some photo-induced changes
also occur, including conversion to the (Z)-isomer.
Metabolism
Metabolites are also rapidly degraded in soil. Photolysis studies show a DT50 of 11 days. Due to the rapid degradation and low soil mobility, no leaching is found in field studies.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required. UN3082 Environmentally hazardous substances, liquid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Degradation
Azoxystrobin is degraded under conditions of aqueous photolysis with a
DT50 of 11-17 days (PM).
Soil surface photolysis of azoxystrobin (14C-labelled separately in each
of the three rings) was studied on a sandy loam for a period of 30 days.
The fungicide was degraded with a DT50 measured as a mean of the three
radiolabels, of 11 days in natural summer sunlight. The degradation was
complex, affording many initial products, all at 40% of the applied
radiocarbon. These products were themselves readily photolysed and no
product accumulated during the course of the experiment. The yield of
14CO2 in 30 days was between 17% (phenylacrylate label) and 29%
(cyanophenyl label). Thus soil surface photodegradation is likely to
be an important mechanism for the removal of azoxystrobin from the
environment.
Toxicity evaluation
Azoxystrobin has an acute oral LD50 > 5,000 and an acute dermal LD50 > 2,000 mg/kg in rats. Azoxystrobin gives only slight skin and eye irritation and is nonmutagenic and nonteratogenic. Its NOEL is 18 mg/kg bw/day. It has no toxicity to birds in acute studies (LD50 > 2,000 mg/kg). It is harmless to other nontarget organisms (honey bees, earthworms, beneficial arthropods) due to low toxicity and rapid degradation in the environment, which minimizes exposure.
Incompatibilities
Combustible; dust may form explosive with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Waste Disposal
Recycle any unused portion of the material for its approved use or return it to the manufacturer or supplier. Dispose of contents and container to an approved waste disposal plant. Use a licensed professional waste disposal service to dispose of this material. Ultimate disposal of the chemical, product, and waste containers must consider: the material’s impact on air quality; potential migration in soil or water; effects on animal and plant life; and conformance with public health, local, state, and federal health and environmental regulations. Never reuse or recycle used product containers unless the recycling program specifically accepts pesticide containers and you follow the program’s instructions for preparing the empty containers for collection
Properties of Azoxystrobin
| Melting point: | 118-119° |
| Boiling point: | 581.3±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.33 |
| vapor pressure | 1.1 x 10-10 Pa (25 °C) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Room Temperature |
| solubility | Chloroform: Slightly Soluble |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 6 mg l-1 (20 °C) |
| pka | -0.93±0.18(Predicted) |
| Colour Index | 23860 |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to yellow |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C22H17N3O5/c1-27-13-17(22(26)28-2)16-8-4-6-10-19(16)30-21-11-20(24-14-25-21)29-18-9-5-3-7-15(18)12-23/h3-11,13-14H,1-2H3/b17-13+ |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 131860-33-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Azoxystrobin(131860-33-8) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Azoxystrobin (131860-33-8) |
Safety information for Azoxystrobin
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H331:Acute toxicity,inhalation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P391:Collect spillage. Hazardous to the aquatic environment P403+P233:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep container tightly closed. |
Computed Descriptors for Azoxystrobin
| InChIKey | WFDXOXNFNRHQEC-GHRIWEEISA-N |
| SMILES | C1(=CC=CC=C1OC1N=CN=C(OC2=CC=CC=C2C#N)C=1)/C(=C\OC)/C(=O)OC |
Azoxystrobin manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Azoxystrobin 98% (HPLC) CAS 131860-33-8View Details
Azoxystrobin 98% (HPLC) CAS 131860-33-8View Details
131860-33-8 -
 Azoxystrobin CAS 131860-33-8View Details
Azoxystrobin CAS 131860-33-8View Details
131860-33-8 -
 Azoxystrobin CAS 131860-33-8View Details
Azoxystrobin CAS 131860-33-8View Details
131860-33-8 -
 Azoxystrobin 23% SCView Details
Azoxystrobin 23% SCView Details
131860-33-8 -
 Azoxystrobin Technical Fungicides, C22H17N3O5, 25KGView Details
Azoxystrobin Technical Fungicides, C22H17N3O5, 25KGView Details
131860-33-8 -
 Azoxystrobin 23 ScView Details
Azoxystrobin 23 ScView Details
131860-33-8 -
 Form: Liquid Azoxystrobin 23 ScView Details
Form: Liquid Azoxystrobin 23 ScView Details
131860-33-8 -
 Form: Liquid Azoxystrobin 23% ScView Details
Form: Liquid Azoxystrobin 23% ScView Details
131860-33-8
