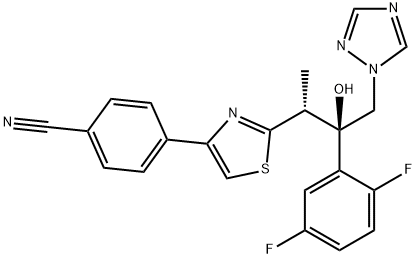
Isavuconazole
Synonym(s):(2R,3R)-3-[4-(4-Cyanophenyl)thiazol-2-yl]-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-1-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)butan-2-ol;1-[(2R,3R)-3-[4-(4-Cyanophenyl)thiazol-2-yl]-2-(2,5-difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxybutyl]-1,2,4-triazole;4-[2-[(1R,2R)-2-(2,5-Difluorophenyl)-2-hydroxy-1-methyl-3-(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)propyl]-4-thiazolyl]benzonitrile;BAL 4815;RO 0094815
- CAS NO.:241479-67-4
- Empirical Formula: C22H17F2N5OS
- Molecular Weight: 437.47
- EINECS: 1592732-453-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
What is Isavuconazole?
Absorption
Following oral administration of 200 mg isavuconazole, the mean peak plasma concentration (Cmax) at steady state was 7499 ng/mL. Cmax following oral administration of 600 mg isavuconazole was 20028 ng/mL . It is proposed that the Cmax at steady state is reached approximately 2–3 hours after single and multiple dosing of isavuconazole . Administration of 400 mg of oral and intravenous isavuconazole resulted in mean AUC of 189462.8 hng/mL and 193906.8 hng/mL, respectively . While isavuconazole can be administered with or without food, concurrent consumption of a high-fat meal reduced oral isavuconazole Cmax by 9% and increased AUC by 9% . The absolute bioavailability of isavuconazole following oral administration of a single dose of isavuconazole is 98% .
Toxicity
At three times the recommended maintenance dose of isavuconazole, treatment-emergent adverse reactions included headache, dizziness, paresthesia, somnolence, disturbance in attention, dysgeusia, dry mouth, diarrhea, oral hypoesthesia, vomiting, hot flush, anxiety, restlessness, palpitations, tachycardia, photophobia and arthralgia. As there is no specific antidote or effective method of hemodialysis for isavuconazole, supportive treatment with appropriate monitoring is recommended in case of overdose .
No mutagenic or clastogenic effects were detected in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation assay and the in vivo bone marrow micronucleus assay in rats . However, isavuconazole was weakly clastogenic at cytotoxic concentrations in the L5178Y tk+/- mouse lymphoma chromosome aberration assay without any significant evidence of increased frequency of micronuclei in an in vivo rat micronucleus test . While carcinogenicity studies isavuconazole have not been performed, other drugs in the azole class at near human recommended doses were associated with the development of hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas in mice and rat carcinogenicity studies . At doses up to 90 mg/kg/day, oral isavuconazole did not affect the fertility in male or female rats. Isavuconazole at systemic exposures of subtherapeutic levels was associated with dose-related increases in the incidence of skeletal anomalies in rat and rabbit offsprings . In rats, a dose-related increase in the incidence of zygomatic arch fusion was also noted in offspring .
Description
BAL-8557 (isavuconazonium) is the water-soluble pro-drug of BAL-4815 (isavuconazole). The conversion to isavuconazole is rapid and complete with very little cleavage product detectable – thus this chapter will focus entirely on isavuconazole. Isavuconazole is produced and developed by Basilea Pharmaceutica and, in common with the other azoles, works by inhibition of ergosterol synthesis. Isavuconazole is a water-soluble compound (the only broad-spectrum water soluble triazole) with oral and intravenous formulations and excellent bioavailability. Its long elimination half-life allows up to once-weekly dosing.
The Uses of Isavuconazole
Isavuconazole is a new triazole currently undergoing phase III clinical trials. This compound has shown in vitro activity against a large number of clinical important yeasts and molds including Asperg illus spp., Fusarium spp., Scedosporium spp., Candida spp., the Zygomycetes and Cryptococcus spp.
The Uses of Isavuconazole
Isavuconazole is a new triazole currently undergoing phase III clinical trials. This compound has shown in vitro activity against a large number of clinical important yeasts and molds including Aspergillus spp., Fusarium spp., Scedosporium spp., Candida spp., the Zygomycetes and Cryptococcus spp.
Background
Isavuconazole is an triazole antifungal with broad spectrum of activity and good safety profile . It is approved by the FDA and EMA for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis and mucormycosis. It works by inhibiting fungal cell membrane synthesis. Invasive fungal infections pose significant clinical challenges for patients, especially those who are immunocompromised. In vitro, most of the Candida species, most Aspergillus species, Mucorales, Cryptococcus spp., Fusarium species, dermatophytes and dimorphic fungi displayed susceptibility to isavuconzaole . Resistance to isavuconazole has been associated with the mutation in the target gene CYP51 . Cross-resistance between isavuconazole and other azoles was also proposed although the clinical relevance is unclear .
As isavuconazole displays low water solubility, it is found as an active ingredient of its prodrug, Isavuconazonium. The prodrug formulation of isavuconazole is FDA- and EMA-approved and is marketed under the trade name Cresemba for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis and mucormycosis as oral or intravenous administration. The intravenous formulation is cyclodextrin-free which gives isavuconazole an advantage over other azole antifungals that requires cyclodextrin for facilitating drug solubility; this is because cyclodextrin has a potential for nephrotoxicity . It is proposed that the intravenous and oral dosing can be used interchangeably , without the need for a repeat loading dose when transitioning from an IV to an oral formulation . Isavuconazonium displays excellent water solubility for intravenous formulations, good absorption, and enhanced oral bioavailability . Following administration, isavuconazonium undergoes biotransformation to form the active moiety, isavuconazole, for the antifungal actions.
Indications
Indicated for patients 18 years of age and older for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis . Indicated for patients 18 years of age and older for the treatment of invasive mucormycosis , including patients where treatment amphotericin B is inappropriate . Reduce drug development failure ratesBuild, train, & validate machine-learning modelswith evidence-based and structured datasets.See how Build, train, & validate predictive machine-learning models with structured datasets.See how
What are the applications of Application
Isavuconazole is a broad-spectrum antifungal
Definition
ChEBI: Isavuconazole is a 1,3-thiazole that is butan-2-ol which is substituted at positions 1, 2, and 3 by 1,2,4-triazol-1-yl, 2,5-difluorophenyl, and 4-(p-cyanophenyl)-1,3-thiazol-2-yl groups, respectively. It is an antifungal drug used for the treatment of invasive aspergillosis and invasive mucormycosis. It has a role as an ergosterol biosynthesis inhibitor, an EC 1.14.13.70 (sterol 14alpha-demethylase) inhibitor and an orphan drug. It is a member of 1,3-thiazoles, a nitrile, a difluorobenzene, a tertiary alcohol, a triazole antifungal drug and a conazole antifungal drug.
Antimicrobial activity
Isavuconazole is a new broad-spectrum triazole with activity against Candida, Cryptococcus, Aspergillus, Zygomycetes, Rhizopus, and Rhizomucor spp. and dimorphic fungi including Histoplasma capsulatum and Blastomyces dermatitidis and a range of dermatophytes. In animal models, isavuconazole is highly effective against systemic candidiasis and disseminated Aspergillus fumigatus and flavus infections.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Maximum plasma concentrations of BAL 4815 are observed 1.5–3 hours after oral doses or at the end of the 1-hour intravenous infusion. Mean elimination half-lives are remarkably long more than 50 and 70 hours after oral and intravenous doses, respectively, allowing for once-daily (or less frequent) dosing. The volume of distribution is large and systemic clearance low. The protein binding is 98%. Escalation in multiple dosing regimens results in a proportional increase in maximum plasma drug concentration.
Pharmacokinetics
Isavucoanzole exhibits antifungal activity against most strains of Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus fumigatus, Aspergillus niger, and Mucorales such as Rhizopus oryzae and Mucormycetes species in vivo and in vitro . In a cardiac electrophysiology study involving healthy subjects, isavuconazole induced dose-related shortening of the QTc interval but the additive effect of isavuconazole with other QTc-prolonging drug is unknown .
Clinical Use
Three regimens of isavuconazonium (BAL 8557) – single 200 mg dose followed by 50 mg daily, single 400 mg followed by 100 mg daily and single 400 mg followed by 400 mg weekly –were demonstrated to be as efficacious as fluconazole in a phase II study conducted on patients with uncomplicated esophageal candidiasis. The results of a phase II open-label dose-escalating trial of intravenous isavuconazonium as prophylaxis in AML (NCT00413439) are pending (NIH, 2008). Two phase III randomized double-blind studies to evaluate the safety and efficacy of isavuconazole are currently under way, versus caspofungin followed by voriconazole in the treatment of candidaemia and invasive candidiasis and versus voriconazole in primary treatment of invasive filamentous fungal infection . A phase III open-label study using isavuconazole in patients with aspergillosis and renal impairment and those with rare fungi is being planned NCT00634049.
Toxicology
In animals, isavuconazole has revealed no mutagenic, allergenic, phototoxic, or irritant potential. In 15 healthy volunteers, single doses of isavuconazole (up to 200 mg) were well tolerated, and no severe or serious adverse events occurred. In a multiple-dose pharmacokinetic study, 24 healthy males received isavuconazole for 21 days of oral or 14 days of intravenous dosing. The most frequent adverse events were headache, nasopharyngitis, and rhinitis, and all were mild or moderate; however one subject on oral high-dose BAL 8557 had mild transient abnormal liver function on day 14 of therapy, which resolved despite continuing the drug. No clinically relevant changes in vital signs or electrocardiogram were observed. In a double-blind randomized phase II trial for the treatment of esophageal candidiasis, BAL 8557 was safe and well tolerated, with an adverse event profile similar to that of fluconazole, the comparator drug.
Drug interactions
Rifampicin, a potent CYP3A4 inducer, decreases the Cmax and AUC of isavuconazole . Ketoconazole increases exposure to isavuconazole. Neither ciclosporin nor warfarin is affected by isavuconazole co-administration. Isavuconazole increases tacrolimus levels.
Metabolism
Following rapid conversion of the prodrug isavuconazonium to isavuconazole via esterase-mediated hydrolysis, a number of minor metabolites were identified in addition to the active moiety itself and the inactive cleavage product of isavuconazonium. However, no individual metabolite was observed with an AUC greater than 10% of total radio-labeled material . The main enzymes involved in the metabolism of isavuconazole are CYP3A4, CYP3A5, and subsequently uridine diphosphate- glucuronosyltransferases (UGT) according to the findings of in vivo and in vitro studies .
Mode of action
Isavuconzaole inhibits cytochrome P450-dependent lanosterol 14α-demethylase, which is essential for the synthesis of ergosterol, a component of the fungal membrane. This disruption leads to alterations in the structure and function of the fungal membrane leading to cell death. The isavuconazole structure includes a side arm that orients the molecule to engage the triazole ring to the binding pocket of the fungal CYP51 protein. This confers broader antifungal activity in comparison to other azoles.
PMC7712939
Properties of Isavuconazole
| Melting point: | 89 - 91oC |
| Boiling point: | 678.0±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.38 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 11.42±0.29(Predicted) |
| color | Off-White to Beige |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C22H17F2N5OS/c1-14(21-28-20(10-31-21)16-4-2-15(9-25)3-5-16)22(30,11-29-13-26-12-27-29)18-8-17(23)6-7-19(18)24/h2-8,10,12-14,30H,11H2,1H3/t14-,22+/m0/s1 |
Safety information for Isavuconazole
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Isavuconazole
| InChIKey | DDFOUSQFMYRUQK-RCDICMHDSA-N |
| SMILES | C(#N)C1=CC=C(C2=CSC([C@H](C)[C@](C3=CC(F)=CC=C3F)(O)CN3C=NC=N3)=N2)C=C1 |
Isavuconazole manufacturer
Virupaksha Organics Pvt Ltd
BDR Pharmaceuticals International Pvt Ltd
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Isavuconazole 98%View Details
Isavuconazole 98%View Details -
 241479-67-4 98%View Details
241479-67-4 98%View Details
241479-67-4 -
 Isavuconazole 98%View Details
Isavuconazole 98%View Details
241479-67-4 -
 Isavuconazole 95% CAS 241479-67-4View Details
Isavuconazole 95% CAS 241479-67-4View Details
241479-67-4 -
 Isavuconazole CAS 241479-67-4View Details
Isavuconazole CAS 241479-67-4View Details
241479-67-4 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1