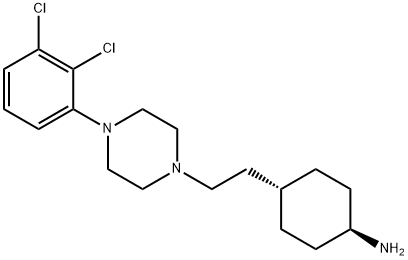
Cariprazine
- CAS NO.:839712-12-8
- Empirical Formula: C21H32Cl2N4O
- Molecular Weight: 427.41
- EINECS: 1592732-453-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 23:02:33
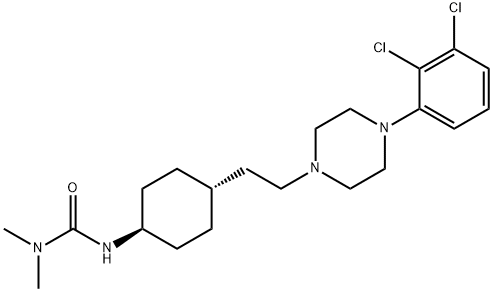
What is Cariprazine?
Absorption
The most clinically relevant drug concentration equates to the combined systemic concentration of cariprazine plus desmethyl cariprazine (DCAR) and didesmethyl cariprazine (DDCAR), the two main pharmacologically active metabolites of cariprazine. After single dose administration of cariprazine, the peak plasma cariprazine concentration occurred in approximately three to six hours. In healthy volunteers, the Tmax following oral administration was 3.6 hours for cariprazine, 6.5 hours for DCAR, and 18.1 hours for DDCAR. The steady-state was reached dose-proportionally within three weeks for cariprazine, DCAR, and DDCAR in patients with schizophrenia.
Administration of a single dose of 1.5 mg cariprazine capsule with a high-fat meal did not significantly affect the Cmax and AUC of cariprazine or its metabolite, desmethyl cariprazine (DCAR).
Toxicity
In pre-marketing clinical trials, an accidental acute overdosage (48 mg/day) was reported in one patient who experienced orthostasis and sedation. The patient fully recovered the same day. As there are no specific antidotes for cariprazine, supportive care, including close medical supervision and monitoring, is advised to manage overdose. The possibility of multiple drug involvement should also be considered.
The Uses of Cariprazine
Cariprazine is an orally active D2/D3 dopamine receptor antagonist. Cariprazine is an antipsychotic drug candidate for the potential treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar mania and depression
The Uses of Cariprazine
Cariprazine is an orally active D2/D3 dopamine receptor antagonist (1,2,3). Cariprazine is an antipsychotic drug candidate for the potential treatment of schizophrenia, bipolar mania and depression.
Indications
Cariprazine is indicated for the treatment of schizophrenia in adults to manage both positive and negative symptoms. It is also indicated to monotherapy for acute management of manic or mixed episodes associated with bipolar I disorder (bipolar mania) in adults, and acute management of depressive episodes associated with bipolar I disorder (bipolar depression) in adults.
Background
Cariprazine is an atypical antipsychotic agent and a piperazine derivative that was first developed in Hungary. It works as a partial agonist at central dopamine D2, dopamine D3, and serotonin 5-HT1A receptors and as an antagonist at serotonin 5-HT2A receptors. Cariprazine has been investigated in a variety of psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia, bipolar disorders, and major depressive disorder. Cariprazine gained its first global approval in the US in September 2015 and was later approved by Health Canada in April 2022. It is currently used to treat schizophrenia, and manic or mixed episodes and depressive episodes associated with bipolar I disorder.
Definition
ChEBI: An N-alkylpiperazine that is N,N-dimethyl-N'-{trans-4-[2-(piperazin-1-yl)ethyl]cyclohexyl}urea substituted at position 4 on the piperazine ring by a 2,3-dichloroph nyl group. Used (as the hydrochloride salt) for treatment of schizophrenia and bipolar disorder.
Pharmacokinetics
Cariprazine is an antipsychotic agent. In clinical trials, it reduced positive and negative symptoms in patients with schizophrenia and acute mania in patients with bipolar I disorder. In animal models, cariprazine showed therapeutic benefits against cognitive deficits, mania, and catalepsy. In a meta-analysis study, cariprazine was shown to improve anxiety and depressed mood in patients with psychosis.
As cariprazine is a partial agonist at dopamine D2 and D3 receptors, it produces an apparent lower blockade level than other antipsychotic agents that block dopamine receptors. This receptor binding profile is advantageous as dopamine receptor blockade is associated with extrapyramidal symptoms as side effects. Partial agonism would allow the dopamine receptor to be stimulated even at maximal receptor occupancy by the drug. Antagonism at 5-HT1A and 5-HT2A receptors by cariprazine can increase dopaminergic neurotransmission in the nigrostriatal pathway, thereby further reducing the risk of extrapyramidal symptoms. However, cariprazine is still associated with a risk of akathisia, extrapyramidal disorder, restlessness, and tremor.
Metabolism
Cariprazine is extensively metabolized by CYP3A4 and, to a lesser extent, by CYP2D6 to form two major metabolites, desmethyl cariprazine (DCAR) and didesmethyl cariprazine (DDCAR). DCAR and DDCAR are pharmacologically active metabolites with in vitro receptor binding profiles similar to the parent drug. DCAR is further metabolized into DDCAR by CYP3A4 and CYP2D6. DDCAR can be metabolized by CYP3A4 to form a hydroxylated metabolite.
Properties of Cariprazine
| Melting point: | >180°C (dec.) |
| Density | 1.24 |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer, Under inert atmosphere |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| color | Off-White to Light Beige |
Safety information for Cariprazine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Cariprazine
Cariprazine manufacturer
Exemed Pharmaceuticals (Oneiro Chemicals Pvt Ltd)
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 839712-12-8 Cariprazine 98%View Details
839712-12-8 Cariprazine 98%View Details
839712-12-8 -
 Cariprazine 95% CAS 839712-12-8View Details
Cariprazine 95% CAS 839712-12-8View Details
839712-12-8 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8