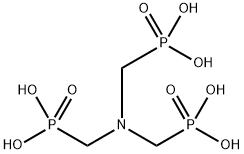
Ibandronic acid
- CAS NO.:114084-78-5
- Empirical Formula: C9H23NO7P2
- Molecular Weight: 319.23
- MDL number: MFCD00868772
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:08:52
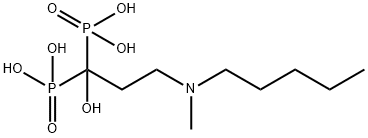
What is Ibandronic acid?
Absorption
Oral ibandronate is 0.63% bioavailable. In a study of healthy males, a 10mg oral dose had a Tmax of 1.1±0.6h and a Cmax of 4.1±2.6ng/mL. The Tmax is approximately 1 hour, while Cmax varies depending on dose.
A 2mg intravenous dose of ibandronate has an AUC of 316ng*h/mL, a 4mg intravenous dose of ibandronate has an AUC of 581ng*h/mL, and a 6mg intravenous dose of ibandronate has an AUC of 908ng*h/mL.
Toxicity
Patients experiencing an overdose may present with hypocalcemia, hypophosphatemia, upset stomach, dyspepsia, esophagitis, and uclers. Oral overdose can be managed by giving patients milk or antacids to bind excess unabsorbed ibandronate. Overdoses can be managed by providing intravenous electrolytes and dialysis is not expected to remove excess drug from serum.
Description
This third generation biphosphonate was launched in Austria and Germany for the treatment of bone disorders such as hypercalcemia in malignancy and ostedysis, Paget's disease and osteoporosis. It does not effect bone mineralization, therefore, the potential risk of osteomalacia is prevented. This was a problem with first generation derivatives. While the exact mode of action is not understood, they are inhibitors of osteroclast mediated bone resorption. These compounds strongly interact with hydroxyapatite crystals and have a half-life in the skeleton of several years. Despite this observation ibandronate was well tolerated and safe.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Boehringer Mannheim (Germany)
The Uses of Ibandronic acid
Labelled Ibandronic Acid (I120000). A bisphosphonate antiresorptive agent. Bone resorption inhibitor.
The Uses of Ibandronic acid
A biphosphonate bone resorption inhibitor.
The Uses of Ibandronic acid
A labeled biphosphonate bone resorption inhibitor.
The Uses of Ibandronic acid
A bisphosphonate antiresorptive agent. Bone resorption inhibitor.
Background
Ibandronate, or BM 21.0955, is a third generation, nitrogen containing bisphosphonate similar to zoledronic acid, minodronic acid, and risedronic acid. It is used to prevent and treat postmenopausal osteoporosis. Ibandronate was first described in the literature in 1993 as a treatment for bone loss in dogs.
Ibandronate was granted FDA approval on 16 May 2003.
Indications
For the treatment and prevention of osteoporosis in postmenopausal women.
What are the applications of Application
Ibandronic Acid is a biphosphonate bone resorption inhibitor
brand name
Bondronat
Pharmacokinetics
Ibandronate is a nitrogen containing bisphosphonate used to treat and prevent osteoporosis in postmenopausal women. The therapeutic index is wide as overdoses are not especially toxic, and the duration of action is long as the half life can be up to 157 hours. Patients should be counselled regarding the risk of upper GI adverse reactions, hypocalcemia, musculoskeletal pain, osteonecrosis of the jaw, atypical fractures of the femur, and severe renal impairment.
Clinical Use
Bisphosphonate:
Reduction of bone damage in bone metastases in
breast cancer
Hypercalcaemia of malignancy
Postmenopausal osteoporosis
Metabolism
Ibanronate is not metabolized in humans.
Metabolism
After initial systemic exposure, ibandronic acid rapidly binds to bone or is excreted into urine. There is no evidence that ibandronic acid is metabolised in animals or humans. The absorbed fraction of ibandronic acid is removed from the circulation via bone absorption (estimated to be 40-50% in postmenopausal women) and the remainder is eliminated unchanged by the kidney. The unabsorbed fraction of ibandronic acid is eliminated unchanged in the faeces. Renal clearance accounts for 50-60% of total clearance and is related to creatinine clearance. The difference between the apparent total and renal clearances is considered to reflect the uptake by bone.
Properties of Ibandronic acid
| Melting point: | 113-115°C |
| Boiling point: | 587.8±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.449±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | Aqueous Base (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly), Water (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 1.60±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 114084-78-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Phosphonic acid, P,P'-[1-hydroxy-3-(methylpentylamino)propylidene]bis- (114084-78-5) |
Safety information for Ibandronic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Ibandronic acid
Ibandronic acid manufacturer
Rivashaa Agrotech Biopharma Pvt. Ltd.
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 114084-78-5 Ibandronic acid 98%View Details
114084-78-5 Ibandronic acid 98%View Details
114084-78-5 -
 114084-78-5 98%View Details
114084-78-5 98%View Details
114084-78-5 -
 Ibandronic acid 95% CAS 114084-78-5View Details
Ibandronic acid 95% CAS 114084-78-5View Details
114084-78-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1