Glasdegib
- CAS NO.:1095173-27-5
- Empirical Formula: C21H22N6O
- Molecular Weight: 374.44
- MDL number: MFCD25976839
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 11:34:44
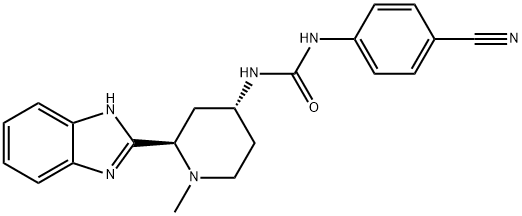
What is Glasdegib?
Absorption
Glasdegib presents a dose-proportional pharmacokinetic profile which is observed by the presence of a broad dose-proportional maximum plasma concentration. In this study and on a dose of 50 mg, the median time to reach a maximum concentration of 321 ng/ml was of 4 hours with an AUC of 9587 ng.h/ml. The oral bioavailability of glasdegib is reported to be of 55%.
In a multiple dose study of 50 mg, the Cmax, tmax and AUC was reported to be 542 ng/ml, 4 h and 9310 ng.h/ml respectively. In this same study, the average concentration at a steady state was of 388 ng/ml.
The absorption rates of glasdegib can be modified by the concomitant consumption of a high-fat, high-calorie meal.
Toxicity
Based on its mechanism of action and findings in animal embryo-fetal developmental toxicity studies, glasdegib can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no clinical data on the use of glasdegib in pregnant women to inform of a drug-associated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage. Glasdegib is not recommended for use during pregnancy. Conduct pregnancy testing in female patients of reproductive potential prior to initiating treatment with glasdegib. Report pregnancy exposures to Pfizer at 1-800-438-1985.
In animal embryo-fetal developmental toxicity studies, repeat-dose oral administration of glasdegib during organogenesis at maternal exposures that were less than the human exposure at the recommended dose resulted in embryotoxicity, fetotoxicity, and teratogenicity in rats and rabbits. Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus.
Carcinogenicity studies have not been performed with glasdegib. Glasdegib was not mutagenic in vitro in the bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay and was not clastogenic in the in vitro chromosome aberration assay in human lymphocytes. Glasdegib was not clastogenic or aneugenic in the rat micronucleus assay.
Based on nonclinical safety findings, glasdegib has the potential to impair reproductive function in males. Men should seek advice on effective fertility preservation before treatment. In repeat-dose toxicity studies in rats, findings observed in the male reproductive tract included adverse testicular changes with glasdegib at doses ≥50 mg/kg/day and consisted of minimal to severe hypospermatogenesis characterized by partial to complete loss of spermatogonia, spermatocytes and spermatids and testicular degeneration. Hypospermatogenesis did not recover whereas testicular degeneration did recover. The dose at which testicular effects were observed in male rats was identified as 50 mg/kg/day with corresponding systemic exposures that were approximately 6.6 times (based on AUC) those associated with the observed human exposure at the 100 mg once daily dose.
There is no specific antidote for DAURISMO. Management of DAURISMO overdose should include symptomatic treatment and ECG monitoring. Glasdegib has been administered in clinical studies up to a dose of 640 mg/day. At the highest dosage, the adverse reactions that were dose-limiting were nausea, vomiting, dehydration, hypotension, fatigue, and dizziness.
The Uses of Glasdegib
Glasdegib acts as a potent, orally biovailablesmoothened (Smo) inhibitor used in the treatment of cancer.
Background
Glasdegib, also known as PF-04449913, is a small-molecule hedgehog signaling inhibitor selected under the group of benzimidazoles. In early research, benzimidazoles attracted large interest as they represented a class of inhibitors with low molecular weight, potent inhibitory activity, and lacking unstable functionality. The great lipophilicity of this group of compounds brought interest to further modification. This analysis concluded that the presence of p-cyano ureas presented good physicochemical and pharmacokinetic properties from which glasdegib was developed.
Glasdegib was developed by Pfizer Inc and approved on November 21, 2018 by the FDA for the treatment of Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). Glasdegib targets cancerous cells by inhibiting the sonic hedgehog receptor smoothened (SMO), a transmembrane protein involved in the Hedgehog (Hh) signaling cascade. Aberrant of Hh signaling is one of the main pathophysiologies of AML, with observed overexpression or constitutive activation of SMO. Although the efficacy of glasdegib monotherapy is limited, the landmark Phase 2 Bright AML 1003 trial showed a superior overall survival and complete response when glasdegib is combined with low dose cytarabine. Currently, the current gold standard of AML in older patients is still venetoclax with hypomethylation agents, new clinical combinations of glasdegib are being tested in hope of replacing venetoclax due to glasdegib's more favorable side effects profile.
Indications
Glasdegib, in combination with cytarabine, is indicated for the treatment of newly diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia in adult patients who are over 75 years old or that have co-morbidities that preclude intensive induction chemotherapy.
Acute myeloid leukemia is characterized by abnormal production of myeloblasts, red cells, or platelets. It is considered a cancer of blood and bone marrow and it is the most common type of acute leukemia in adults.
Definition
ChEBI: Glasdegib is a member of the class of benzimidazoles that is 1H-benzimidazole which is substituted by a (2R,4S)-4-{[(4-cyanophenyl)carbamoyl]amino}-1-methylpiperidin-2-yl group at position 2. It is a hedgehog signalling pathway inhibitor that acts by binding to Smoothened (SMO) receptors and blocking signal transduction (IC50 = 5 nM). It is used in combination with low-dose cytarabine, for the treatment of newly-diagnosed acute myeloid leukemia (AML) in adult patients (aged >= 75 years), or who have medical conditions that prevent the use of standard chemotherapy. It has a role as a SMO receptor antagonist, a Hedgehog signaling pathway inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It is a member of benzimidazoles, a member of piperidines, a member of phenylureas and a nitrile.
Biological Activity
pf-04449913 is an orally bioavailable inhibitor of smoothened with ic50 value of 5nm [1].in the hedgehog (hh) signaling pathway, the combination of hh ligands and their receptor patched leads to the activation of smoothened and subsequently activation of three transcription factors gli1, gli2 and gli3. it then leads to the proliferation of cells. as an antagonist of smoothened, pf-04449913 is developed for treatment of cancer [1].pf-04449913 is found not to inhibit cytochrome p450 and is negative in ames and micronucleus assays suggesting it as a safe drug. in the preclinical studies, pf-04449913 shows a half-life of 30 h and an oral bioavailability of 55% in humans. it also has low plasma clearance of 1.03 ml/min/kg and moderate volume of distribution (2.7 l/kg) [1].
Biochem/physiol Actions
PF-04449913 maleate salt is also known as 1-((2R,4R)-2-(1H-benzo[d]imidazol-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-3-(4-cyanophenyl)urea. It increases the differentiation of blood cells from hematopoietic precursors of the lymph gland medullary zone. This human Smo inhibitor protein is now under clinical trials to treat myeloid malignancies.
PF-04449913 (Glasdegib) is an orally bioavailable Hedgehog pathway inhibitor. PF-04449913 acts by binidng Smoothened (Smo) and blocking signal transduction. PF-04449913 has an IC50 of 5 nM in the Gli-Luciferase assay. In a Phase I clinical trial in patients with advanced solid tumors, PF-04449913 caused disease stabilization in 34% of patients.
Pharmacokinetics
In preclinical studies, glasdegib achieved a significant reduction in leukemic stem cell burden in xenograft models and a reduction in cell population expressing leukemic stem cell markers.
In clinical trials, glasdegib demonstrated a marked downregulation of more than 80% of the expression of glioma-associated transcriptional regulator GL11 in skin. In this same study 8% of the studied individuals with acute myeloid leukemia achieved morphological complete remission while 31% achieved stable disease state.
The latest clinical trial proved glasdegib to generate an overall survival of 8.3 months which was almost double to what has been observed in patients under low-dose cytarabine treatment. As well, there have been reports of dose-dependent QTc prolongation in patients administered with glasdegib.
Metabolism
After oral administration, glasdegib was primarily metabolized by CYP3A4 with minor contributions of CYP2C8 and UGT1A9. The amount of unchanged glasdegib in plasma accounts only for 69% of the administered dose.
References
[1] munchhof mj, li q, shavnya a, borzillo gv, boyden tl, jones cs, lagreca sd, martinez-alsina l, patel n, pelletier k, reiter la, robbins md, tkalcevic gt. discovery of pf-04449913, a potent and orally bioavailable inhibitor of smoothened. acs med chem lett. 2011 dec 21;3(2):106-11.
Properties of Glasdegib
| Melting point: | >214°C (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 633.4±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.33±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C Freezer |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 11.93±0.10(Predicted) |
| color | Off-White |
Safety information for Glasdegib
Computed Descriptors for Glasdegib
| InChIKey | SFNSLLSYNZWZQG-VQIMIIECSA-N |
| SMILES | N([C@@H]1CCN(C)[C@@H](C2NC3=CC=CC=C3N=2)C1)C(NC1=CC=C(C#N)C=C1)=O |
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 PF-04449913 maleate salt CAS 1095173-27-5View Details
PF-04449913 maleate salt CAS 1095173-27-5View Details
1095173-27-5 -
 3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-amino-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)-1-methylpiperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 98%View Details
614-19-7 -
 3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 Methyl phenyl sulfone 98%View Details
3112-85-4 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 -
 3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details
3-(4-(hydroxyamino)-1-oxoisoindolin-2-yl)piperidine-2,6-dione 98%View Details -
 57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 2-bromo-4-chlorobenzonitrile 98%View Details
57381-49-4 -
 4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
4,6-dichloropyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde 98%View Details
5305-40-8
