Ferric sulfate
- CAS NO.:10028-22-5
- Empirical Formula: Fe2O12S3
- Molecular Weight: 399.88
- MDL number: MFCD00011007
- EINECS: 233-072-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:40
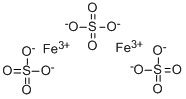
What is Ferric sulfate ?
Absorption
Pharmacokinetic studies related to the absorption of ferric sulfate have not been performed.
Toxicity
Ferric sulfate has been proven to be an irritating substance into the eye, throat, gastrointestinal and respiratory tract.
Description
§184.1307(a) Ferric sulfate (iron(HI)sulfate, Fe2(S04)3), a yellow substance that may be prepared by oxidizing iron(II)sulfate or by treating ferric oxide or ferric hydroxide with sulfuric acid.
Chemical properties
Yellow crystals or grayish-white powder.(1) slightly soluble in water, (2) very soluble in water. Keep well closed and protected from light. Noncombustible.
Chemical properties
Ferric Sulfate is a grayish-white powder or yellow lumpy crystals.
Physical properties
The anhydrous salt constitutes grayish-white rhombic crystals; hygroscopic; density 3.10 g/cm3; slightly soluble in cold water; decomposes in hot water. The nonahydrate is a yellow hexagonal crystalline substance; refractive index 1.54; density 2.10 g/cm3; hardness 2.5 Mohs; decomposes at 400°C; very soluble in water.
The Uses of Ferric sulfate
Ferric Sulfate is a nutrient and dietary supplement that is a source of iron.
The Uses of Ferric sulfate
In preparation of iron alums, other iron salts and pigments; as coagulant in water purification and sewage treatment; in etching aluminum; in pickling stainless steel and copper; as mordant in textile dyeing and calico printing; in soil conditioners; as polymerization catalyst.
The Uses of Ferric sulfate
Iron(III) Sulfate can be used for water treatment system.
Indications
Ferric sulfate was first used in dermatology as part of the Monsel's solution. This solution is an antihemorrhagic agent used in skin and mucosal biopsies. The use of ferric sulfate in dermatology is under review as ferric sulfate is corrosive and injurious and it can cause degenerative changes that are not observed with other alternatives like collagen.
Ferric sulfate is also used as a coagulative and hemostatic agent. It is a mechanic hemostatic agent used directly on the damaged tissue.
In dentistry, ferric sulfate is used as a pulpotomy medicament to control pulpal bleeding, as an antibacterial agent and as a hemostatic reagent for restorative dentistry, for postextraction hemorrhage and for periradicular and endodontic surgery.
Background
Ferric sulfate has the molecular formula of Fe2SO4, and it is a dark brown or yellow chemical agent with acidic properties. It is produced by the reaction of sulfuric acid and an oxidizing agent. It is used in different fields such as dermatology, dentistry and it is thought to present hemostatic properties by interacting chemically with blood proteins. By the FDA, ferric sulfate is a direct food substance affirmed in the GRAS category (Generally Recognized As Safe).
What are the applications of Application
Iron(III) sulfate is an inorganic compound for proteomics research
Definition
Ferrous sulfate,also known as ferrisulpas, green copperas, green vitriol, iron sulfate, and melanterite, is composed of blue green monoclinic crystals. It is soluble in water and is used as a mordant for dyeing wool in the textile industry. Ferrous sulfate is also used as a disinfectant and in the manufacture of ink.
Preparation
Iron(III) sulfate may be prepared by oxidation of iron(II) sulfate by hydrogen peroxide, nitric acid or any other suitable oxidizing agent. The reaction is carried out in sulfuric acid. Balanced molecular equations for the reactions with hydrogen peroxide and nitric acid are as follows:
2FeSO4 + H2SO4 + H2O2 → Fe2(SO4)3 + 2H2O
6FeSO4 + 3H2SO4 + 2HNO3 → 3Fe2(SO4)3 + 2NO + 4H2O
Even in the absence of an oxidizing agent, concentrated sulfuric acid alone can1 convert iron(II) sulfate to iron(III) sulfate: 2FeSO4 + 2H2SO4→ Fe2(SO4)3 + SO2 + 2H2O It also may be prepared by treating iron(III) oxide with sulfuric acid:
Fe2O3 + 3H2SO4 → Fe2(SO4)3 + 3H2O
.
General Description
A yellow crystalline solid or a grayish-white powder. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Ferric sulfate is used for water purification, and as a soil conditioner.
Air & Water Reactions
Soluble in water. Hygroscopic in air. Forms acidic aqueous solutions.
Reactivity Profile
Ferric sulfate is acidic. Corrosive to copper, copper alloys, mild steel, and galvanized steel [USCG, 1999].
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust irritates nose and throat. Ingestion causes irritation of mouth and stomach. Dust irritates eyes and can irritate skin on prolonged contact.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Agricultural Uses
Herbicide, Molluscicide, Agricultural product constituent: Ferric sulfate is used on forage alfalfa, almonds, nurseries and structural pest control. This material is also used in pigments, textile dyeing, water treatment, and metal pickling
Trade name
GREENMASTER AUTUMN®; MAXICROP MOSS KILLER®; VITAX MICRO GRAN®; VITAX TURF TONIC®
Pharmacokinetics
The administration of ferric sulfate as a dermatologic agent has showed delayed reepithelialization and dyspigmentation. Some studies have reported the generation of inflammation in the sites of administration of ferric sulfate.
Safety Profile
A poison by intraperitoneal route. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx and Fe-. See also SULFATES and other ferric salts.
Potential Exposure
This material is used in pigments, textile dyeing, water treatment; and metal pickling.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. Thesymptoms of metal fume fever may be delayed for 4-12 hfollowing exposure: it may last less than 36 h.Note to physician: For severe poisoning do not use BAL[British Anti-Lewisite, dimercaprol, dithiopropanol(C3H8OS2)] as it is contraindicated or ineffective in poisoning from iron.
Metabolism
Pharmacokinetic studies related to the metabolism of ferric sulfate have not been performed.
Storage
Color Code—Green: General storage may be used.Prior to working with this chemical you should be trainedon its proper handling and storage. Store in tightly closedcontainers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from light,moisture, aluminum, magnesium, copper and its alloys,zinc, galvanized and mild steels.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous haz ardous material, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Dissolve the sulfate in the minimum volume of dilute aqueousH2SO4 and allow it to evaporate at room temperature until yellowish-white crystals start to form. Do not concentrate by boiling off the H2O as basic salts will be formed. Various hydrates are formed; the common ones are the dodeca and nona hydrates which are violet in colour. The anhydrous salt is colourless and is very hygroscopic, but it dissolves in H2O slowly unless ferrous sulfate is added. [Gmelin’s, Iron (8th edn) pp 439-462 1932.]
Incompatibilities
Hydrolyzed slowly in aqueous solution. Incompatible with magnesium, aluminum. Corrosive to copper and its alloys, mild and galvanized steel. Light sensitive.
Waste Disposal
Treat with soda ash or dilute NaOH. Separate any precipitate and landfill. Flush solution to sewer.
Properties of Ferric sulfate
| Melting point: | 480°C |
| Boiling point: | 101-118 °C |
| Density | 3.097 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 20℃ |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Inert atmosphere,Room temperature |
| solubility | slightly soluble in ethanol; insoluble in acetone |
| form | Powder |
| color | Yellow-gray |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in water. Sparingly soluble in alcohol. Almost insoluble in acetone and ethyl acetate. Insoluble in sulfuric acid and ammonia. |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,4032 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 1 mg/m3 NIOSH: TWA 1 mg/m3 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10028-22-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Ferric sulfate(10028-22-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ferric sulfate (10028-22-5) |
Safety information for Ferric sulfate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for Ferric sulfate
Ferric sulfate manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 FERRIC SULPHATE 99%View Details
FERRIC SULPHATE 99%View Details -
 Iron(III) sulfate 98%View Details
Iron(III) sulfate 98%View Details
10028-22-5 -
 Iron(III) sulfate 10028-22-5 98%View Details
Iron(III) sulfate 10028-22-5 98%View Details
10028-22-5 -
 10028-22-5 Iron(III) sulfate 98%View Details
10028-22-5 Iron(III) sulfate 98%View Details
10028-22-5 -
 Powder Ferric SulphateView Details
Powder Ferric SulphateView Details
10028-22-5 -
 Ferric Sulphate Technical/FCCView Details
Ferric Sulphate Technical/FCCView Details
10028-22-5 -
 Polymerized Ferrous Sulfate CAS 10028-22-5View Details
Polymerized Ferrous Sulfate CAS 10028-22-5View Details
10028-22-5 -
 20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0 (2,2-diethoxyethyl)methylamine 98%View Details
20677-73-0
