Zinc sulphate
- CAS NO.:7733-02-0
- Empirical Formula: ZnSO4
- Molecular Weight: 161.45
- MDL number: MFCD00011302
- EINECS: 231-793-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-11 14:08:43
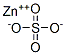
What is Zinc sulphate?
Absorption
Approximately 20 to 30% of dietary zinc is absorbed, primarily from the duodenum and ileum. The amount absorbed is dependent on the bioavailability from food. Zinc is the most bioavailable from red meat and oysters. Phytates may impair absorption by chelation and formation of insoluble complexes at an alkaline pH. After absorption, zinc is bound in the intestine to the protein metallothionein. Endogenous zinc can be reabsorbed in the ileum and colon, creating an enteropancreatic circulation of zinc.
Toxicity
Human : TDLo ( Oral) 45mg/kg/7D-C : Normocytic anemia, pulse rate increase without fall inBP Human: TDLo (oral) 106mg/kg : Hypermotylity, diarrhea Mouse ; LD50 Oral : 245mg/kg Mouse : LD50 : subcutaneous : 781mg/kg
Chemical properties
used in zinc plating and as a mordant [KIR84]
Physical properties
The anhydrous sulfate is a colorless rhombohedral crystalline solid; refractive index 1.658; density 3.54 g/cm3; decomposes at 600°C; soluble in water, methanol, and glycerol.
The heptahydrate, ZnSO4?7H2O, is a colorless crystalline solid; metallic taste; rhombohedral crystals; effloresces; refractive index 1.457; density 1.957 g/cm3 at 25°C; melts at 100°C; loses all its water molecules at 280°C; decomposes above 500°C; very soluble in water, 96.5 g/100mL at 20°C; soluble in glycerol, 40 g/100 mL; insoluble in alcohol
The hexahydrate, ZnSO4?6H2O constitutes colorless monoclinic or tetragonal crystals; density 2.072 g/cm3at 15°C; loses five water molecules at 70°C; soluble in water.
The Uses of Zinc sulphate
The principal commercial preparation of zinc sulfate is the monohydrate granular (36% of zinc) used as a fertilizer. It is also a component of spinning bath in the production of rayon, carbamate fungicides, zinc plating baths, and ophthalmic solutions. Zinc sulfate is used as an accelerating agent in dental impression material, froth flotation agent, and animal feed additive.
What are the applications of Application
Zinc sulfate solution can be used:
(1) Used as a component of spinning baths for the production of rayon, carbamate fungicides, galvanising baths and ophthalmic solutions.
(2) Used as an accelerator for dental impression materials, as a froth flotation agent and as an animal feed additive.
(3) Used as a component of in vitro mycelial growth test media. It is also used as a supplement to the medium together with isopropyl β-D-1 thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG) in the expression of zinc-containing proteins.
Background
Zinc sulfate is the inorganic compound with the formula ZnSO4 and historically known as "white vitriol". It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, a list of the most important medication needed in a basic health system.
Definition
zinc sulphate: A white crystalline water-soluble compound made by heating zinc sulphide ore in air and dissolving out and recrystallizing the sulphate. The common form is the heptahydrate, ZnSO4.7H2O; r.d. 1.9. This loses water above 30°C to give the hexahydrate and more water is lost above 70°C to form the monohydrate. The anhydrous salt forms at 280°C and this decomposes above 500°C. The compound, which was formerly called white vitriol, is used as a mordant and as a styptic (to check bleeding).
Definition
ChEBI: Zinc sulfate is a metal sulfate compound having zinc(2+) as the counterion. It has a role as a fertilizer. It is a metal sulfate and a zinc molecular entity. It contains a zinc(2+).
Indications
This medication is a mineral used to treat or prevent low levels of zinc alone and together with oral rehydration therapy (ORT). It is also used as a topical astringent. Zinc Sulfate Injection, USP is indicated for use as a supplement to intravenous solutions given for TPN.
Production Methods
Zinc sulfate is produced from side streams of electrolytic zinc manufacture. The main source of secondary zinc for zinc sulfate production is galvanizer residues. ZnSO4 is available as the mono-, hexa- and heptahydrates with zinc contents of 36%, 24%, and 22%, respectively.
General Description
Anhydrous Zinc sulphate is a colorless crystalline solid. Zinc sulphate is also obtained as a hexahydrate, ZnSO4.6H2O, and as a heptahydrate ZnSO4.7H2O. All forms are soluble in water. All are noncombustible. The primary hazard is the threat posed to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Zinc sulphate is used in the production of rayon, as a feed supplement, used to obtaine lectrolyte zinc, in printing textiles and to make lithopone, to impregnate wood and hides,as an additive to spinning baths for production of synthetic silks, in electroplating, and in animal feeds.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble. Efflorescent in air. Aqueous solutions are acidic.
Reactivity Profile
Acidic salts, such as Zinc sulphate, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydrogen ions and have pH's of less than 7.0. They react as acids to neutralize bases. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of inorganic acids, inorganic oxoacids, and carboxylic acid. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. Many of these compounds catalyze organic reactions.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust causes irritation of nose and throat. Ingestion can cause irritation or corrosion of the alimentary tract. Contact with eyes or skin causes irritation.
Agricultural Uses
White vitriol is another name for zinc sulphate heptahydrate, and is a commonly used zinc salt. It is widely used as a fertilizer for overcoming zinc deficiency.
Agricultural Uses
Zinc sulphate is a white, crystalline, water-soluble
compound made by heating zinc sulphide ore
in air and dissolving the sulphate formed, and
crystallizing it.
Zinc sulphate is the most common zinc salt (about
35% of zinc) used for preventing zinc deficiency in
plants. It is sprayed on the foliage as a water solution or
added in large quantities directly to the soil.
Industrial uses
Ferro sulfate (FeSO4·7H2O) is a crystalline substance greenish in color, with a specific gravity of 1.899. Ferro sulfate is obtained from various solutions using a vacuum crystallization method. Ferro sulfate has been used as a depressant and co-depressant in the following applications: (a) depression of sphalerite together with cyanide , (b) depression of fine molybdenite also with cyanide, and (c) in copper/lead separation using a method, based on copper depression by cyanide.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Zinc sulfate?solution is as potent as formalin. This chemical is mainly used to treat footrot. It may also be used to treat acute bronchiolitis.
Pharmacokinetics
Zinc has been identified as a cofactor for over 70 different enzymes, including alkaline phosphatase, lactic dehydrogenase and both RNA and DNA polymerase. Zinc facilitates wound healing, helps maintain normal growth rates, normal skin hydration and the senses of taste and smell.
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intraperitoneal, subcutaneous, and intravenous routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: acute pulmonary edema, agranulocytosis, blood pressure decrease, diarrhea and other gastrointestinal changes, hypermotility, increased pulse rate without blood pressure decrease, level changes for metals other than Na/K/Fe/Ca/P/Cl, microcytosis with or without anemia, normocytic anemia. Experimental teratogenic and reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Human mutation data reported. An eye irritant. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx and ZnO. See also SULFATES and ZINC COMPOUNDS.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from aqueous EtOH or dilute H2SO4 below 39o when it forms the heptahydrate, and between 39o and 70o it forms the hexahydrate, and above 70o the monohydrate is stable. The anhydrous salt is obtained from the hydrates by heating at 280o or lower temperatures in a current of dry air. It decomposes to ZnO and SO2 at 767o. The solubility of the heptahydrate in H2O is 5.88% at 0o, 61.92% at 30o, 66.61% at 35o and 70.05% at 39o.
Properties of Zinc sulphate
| Melting point: | 100°C |
| Boiling point: | 105°C (estimate) |
| Density | 1.31 g/mL at 20 °C |
| storage temp. | Store at +15°C to +25°C. |
| solubility | H2O: soluble |
| form | Liquid |
| color | Colorless |
| PH | 4.0±0.5 |
| Water Solubility | Soluble |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: <0.02 λ: 280 nm Amax: <0.02 |
| Merck | 14,10159 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7733-02-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Zinc sulfate(7733-02-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Zinc sulfate (7733-02-0) |
Safety information for Zinc sulphate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H401:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard H411:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Zinc sulphate
Abamectin manufacturer
UNILOSA INTERNATINAL PRIVATE LIMITED
Positive Chemicals Private Limited
Arihant Purechem Pvt Ltd
Snow White Products
New Products
4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium SODIUM AAS SOLUTION ZINC AAS SOLUTION BUFFER SOLUTION PH 10.0(BORATE) GOOCH CRUCIBLE SINTERED AQUANIL 5 BERYLLIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
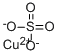
You may like
-
 ZINC SULPHATE 21% 99%View Details
ZINC SULPHATE 21% 99%View Details -
 Zinc Sulphate 7733-02-0 99%View Details
Zinc Sulphate 7733-02-0 99%View Details
7733-02-0 -
 zinc sulphate CASView Details
zinc sulphate CASView Details -
 Zinc sulfate 98%View Details
Zinc sulfate 98%View Details
7733-02-0 -
 7733-02-0 98%View Details
7733-02-0 98%View Details
7733-02-0 -
 ZINC SULPHATE 98%View Details
ZINC SULPHATE 98%View Details -
 Zinc sulfate solution CASView Details
Zinc sulfate solution CASView Details -
 Zinc sulfate solution CASView Details
Zinc sulfate solution CASView Details