Ethacrynic acid
Synonym(s):Ethacrynic acid;ECA;Etacrynic acid;(2,3-Dichloro-4-[2-methylenebutyryl]phenoxy)acetic acid;[2,3-Dichloro-4-(2-ethylacryloyl)phenoxy]acetic acid
- CAS NO.:58-54-8
- Empirical Formula: C13H12Cl2O4
- Molecular Weight: 303.14
- MDL number: MFCD00056693
- EINECS: 200-384-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-18 14:15:32
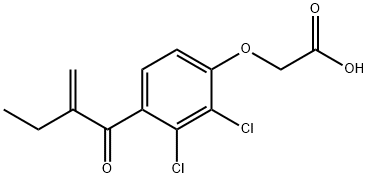
What is Ethacrynic acid?
Absorption
Onset of action is rapid, usually within 30 minutes after an oral dose of ethacrynic acid or within 5 minutes after an intravenous injection of ethacrynic acid.
Toxicity
Overdosage may lead to excessive diuresis with electrolyte depletion.
Description
Ethacrynic acid is a loop diuretic with anticancer activity., It inhibits the Na-K-2Cl (NKCC) cotransporter in duck erythrocytes (IC50 = 0.18 mM) and ATP-dependent chloride uptake in rat renal plasma membrane vesicles when used at a concentration of 0.3 mM., Ethacrynic acid also inhibits glutathione S-transferase P1-1 (GSTP1-1) and GSTA3-3 (IC50s = 4.9 and ~0.4 μM, respectively), and inhibits Wnt/β-catenin signaling in a cell-based reporter assay. It is cytotoxic to primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells (IC50 = 8.56 μM), as well as MCF-7, MDA-MB-231, and 4T1 cancer cells (IC50s = 45.53, 39.64, and 25.23 μM, respectively). Ethacrynic acid (250 μg per day) increases tumor growth reduction induced by the EGFR family inhibitors afatinib (Item Nos. 11492 | 21567) or neratinib in a 4T1 murine breast cancer model. Formulations containing ethacrynic acid have been used in the treatment of edema.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Hydromedin,MSD,W. Germany,1966
The Uses of Ethacrynic acid
Ethacrynic acid is a powerful diuretic prescribed for edema associated with cardiac insufficiency, renal edema that does not respond to other diuretics, and edema of the brain and lungs.
The Uses of Ethacrynic acid
A diuretic used to treat high blood pressure and swelling caused by congestive heart failure, liver failure and kidney failure.
The Uses of Ethacrynic acid
Ethacrynic acid is used to inhibits symport of sodium, potassium, and chloride primarily in the ascending limb of Henle, but also in the proximal and distal tubules. This pharmacological action results in excretion of these ions, increased urinary output, and reduction in extracellular fluid. This compound has been classified as a loop or high ceiling diuretic.
Background
A compound that inhibits symport of sodium, potassium, and chloride primarily in the ascending limb of Henle, but also in the proximal and distal tubules. This pharmacological action results in excretion of these ions, increased urinary output, and reduction in extracellular fluid. This compound has been classified as a loop or high ceiling diuretic.
Indications
For the treatment of high blood pressure and edema caused by diseases like congestive heart failure, liver failure, and kidney failure.
What are the applications of Application
Ethacrynic acid is a high ceiling loop diuretic with anticancer activity, cytotoxic to primary chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells.
Definition
ChEBI: An aromatic ether that is phenoxyacetic acid in which the phenyl ring is substituted by chlorines at positions 2 and 3, and by a 2-methylidenebutanoyl group at position 4. It is a loop diuretic used to treat high blood pressure resulting from diseases such as congestive heart failure, liver failure, and kidney failure. It is also a glutathione S-transferase (EC 2.5.1.18) inhibitor.
Manufacturing Process
Step A: Preparation of 2,3-Dichloro-4-Butyrylphenoxy Acid - The product is
prepared using the following ingredients: 22.1 grams (0.1 mol) 2,3-
dichlorophenoxyacetic acid; 21.3 grams (0.2 mol) n-butyryl chloride; and 53.3
grams (0.4 mol) powdered aluminum chloride.
The 2,3-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid and n-butyryl chloride are placed in the
reaction vessel and stirred while the aluminum chloride is added portionwise
over a 45-minute period. The mixture then is heated on the steam bath for 3
hours and allowed to cool to room temperature. The gummy product obtained
is added to a mixture of 300 ml of crushed ice and 30 ml concentrated
hydrochloric acid. The resulting mixture is extracted with ether and the extract
evaporated at reduced pressure. The residue is suspended in boiling water
and dissolved by addition of a minimum quantity of 40% sodium hydroxide.
After treatment with decolorizing charcoal and filtering, the hot filtrate is
made acid to Congo red paper and chilled in ice.
The oil that separates is extracted with ether, the extract dried over
anhydrous sodium sulfate and then evaporated at reduced pressure. The
residue is dissolved in boiling benzene (75 ml) treated with decolorizing
charcoal, filtered, treated with boiling cyclohexane (275 milliliters) and cooled
to give 22.3 grams of 2,3-dichloro-4-butyrylphenoxyacetic acid. After several
recrystallizations from a mixture of benzene and cyclohexane, then from
methyl cyclohexane, next from a mixture of acetic acid and water, and finally
from methylcyclohexane, the product melts at 110° to 111°C (corr).
Step B: Preparation of 2,3-Dichloro-4-[2-(Dimethylaminomethyl)
Butyryl]Phenoxyacetic Acid Hydrochloride - In a 100 ml round flask equipped
with an outlet tube suitable for application of intermittent suction, an intimate
mixture of 5.20 grams (0.0179 mol) 2,3-dichloro-4-butyrylphenoxyacetic acid;
0.63 gram (0.0209 mol) paraformaldehyde; 1.59 grams (0.0195 mol) dry
dimethylamine hydrochloride; and 4 drops acetic acid is heated on the steam bath for about 1.5 hours during which period suction is applied for about 1
minute intervals five or six times. Upon cooling, a solid is obtained, The crude
reaction product is triturated with ether to give 5.8 grams (85%) of 2.3-
dichloro-4-[2-dimethylaminomethyl)butyryl]phenoxyacetic acid hydrochloride
in the form of a white solid. After two recrystallizations from a mixture of
methanol and ether, the product melts at 165° to 167°C.
Step C: Preparation of 2,3-Dichloro-4-(2-Methylenebutyryl) Phenoxyacetic
Acid - The Mannich compound obtained as described above is treated with
aqueous sodium bicarbonate to form 2,3-dichloro-4-(2-
methylenebutyryl)phenoxyacetic acid, MP 115° to 118°C. Two
recrystallizations from a mixture of benzene and cyclohexane give white solid
material melting at 118.5° to 120.5°C.
brand name
Edecrin (Merck).
Therapeutic Function
Diuretic, Cardiotonic, Smooth muscle relaxant, Respiratory stimulant
General Description
White solid.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Ethacrynic acid may react vigorously with strong oxidizing agents. Can react exothermically with reducing agents (such as alkali metals and hydrides) to release gaseous hydrogen. May react exothermically with acids. Reacts exothermically with all bases both organic (for example, the amines) and inorganic.
Fire Hazard
Ethacrynic acid is probably combustible.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Ethacrynic acid is non sulfonamide loop diuretic that is used to treat high blood pressure and the swelling caused by diseases like congestive heart failure. Ethacrynic acid blocks sodium-potassium-chloride cotransport. Also, Ethacrynic acid potently inhibits glutathione S-transferase family members. Studies show that ethacrynic acid potently inhibits Tgase-2 (transglutaminase-2) dependent metastasis of cancer cells including lung and pancreatic cancers.
Mechanism of action
The mechanism of action of ethacrynic acid appears to be more complex than the simple addition of sulfhydryl groups of the enzyme to
the drug molecule. When the double bond of ethacrynic acid is reduced, the resultant compound is still active, although the diuretic activity is diminished. The sulfhydryl
groups of the enzyme would not be expected to add to the drug molecule in the absence of the α,β-unsaturated ketone.
These compounds are potent high-ceiling diuretics that resemble ethacrynic acid in their mechanism of action. The ethyl ester group represents a pro-drug that can be
easily hydrolyzed to the free carboxyl group. As in ethacrynic acid, a 2,3-dichloro substitution is necessary. In addition, a para-hydroxyl group and an unsubstituted
aminomethyl group on the benzene ring are highly beneficial. The carbonyl group can be replaced with an ether or sulfide group. These compounds have no ability to add
the sulfhydryl groups of the kidney enzymes. The complete mechanism of action of these compounds remains in doubt.
Pharmacokinetics
Ethacrynic acid is a monosulfonamyl loop or high ceiling diuretic. Ethacrynic acid acts on the ascending limb of the loop of Henle and on the proximal and distal tubules. Urinary output is usually dose dependent and related to the magnitude of fluid accumulation. Water and electrolyte excretion may be increased several times over that observed with thiazide diuretics, since ethacrynic acid inhibits reabsorption of a much greater proportion of filtered sodium than most other diuretic agents. Therefore, ethacrynic acid is effective in many patients who have significant degrees of renal insufficiency. Ethacrynic acid has little or no effect on glomerular filtration or on renal blood flow, except following pronounced reductions in plasma volume when associated with rapid diuresis.
Synthesis
Ethacrynic acid?a[2,3-dichloro-4-(2-methylenbutyryl)phenoxy]acetic acid (21.4.9), is synthesized from 2,3-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid. This is acylated with butyroyl chloride, forming 4-butyroyl-2,3-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (21.4.7), which is further aminomethylated under Mannich reaction conditions using dimethylamine and formaldehyde. The resulting product (21.4.8) undergoes further thermal degredation, forming an unsaturated ketone?aethacrynic acid (21.4.9).

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Ethacrynic acid is a loop diuretic that shares the same indications
as furosemide (congestive cardiomyopathy, pulmonary edema, hypercalcuric
nephropathy, uremia, as adjunctive therapy in hyperkalemia
and, occasionally, as an antihypertensive agent). Its use has
been largely supplanted in the armamentarium by furosemide for
these indications.
Ethacrynic acid may be useful in the treatment of nephrogenic
diabetes insipidus as it may cause a paradoxical decrease in urine
volume. Other uses include the adjunctive treatment of hypercalcemia
and to increase the excretion of bromide in the treatment of
bromide toxicity.
Metabolism
Hepatic.
Properties of Ethacrynic acid
| Melting point: | 125 °C |
| Boiling point: | 480.0±45.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.3562 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: soluble20mg/mL, clear |
| form | powder |
| pka | 3.50(at 25℃) |
| color | white to beige |
| Water Solubility | Soluble in ethanol, chloroform, ether, ammonia, carbonates, and methanol. Insoluble in water. |
| Merck | 3717 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 58-54-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ethacrynic acid (58-54-8) |
Safety information for Ethacrynic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Ethacrynic acid
Ethacrynic acid manufacturer
Solara Active Pharma Sciences Ltd
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate (S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid Fmoc-Val-Cit-PAB DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
![58-54-8 Ethacrynic Acid
2-[2,3-Dichloro-4-(2-methylene-1-oxobutyl)phenoxy]acetic Acid 96%](https://img.chemicalbook.in//ProductImageIndia/2024-03/Raw/16325fc6-e3b8-416a-b033-c121395ed983.png) 58-54-8 Ethacrynic Acid 2-[2,3-Dichloro-4-(2-methylene-1-oxobutyl)phenoxy]acetic Acid 96%View Details
58-54-8 Ethacrynic Acid 2-[2,3-Dichloro-4-(2-methylene-1-oxobutyl)phenoxy]acetic Acid 96%View Details
58-54-8 -
 58-54-8 98%View Details
58-54-8 98%View Details
58-54-8 -
 58-54-8 Ethacrynic acid 98%View Details
58-54-8 Ethacrynic acid 98%View Details
58-54-8 -
 58-54-8 99%View Details
58-54-8 99%View Details
58-54-8 -
 Ethacrynic acid CAS 58-54-8View Details
Ethacrynic acid CAS 58-54-8View Details
58-54-8 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8