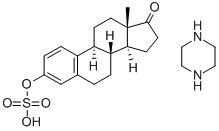
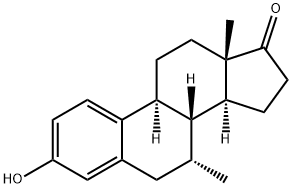
Estropipate
Synonym(s):3-(Sulfooxy)-estra-1,3,5(10)-trien-17-one : piperazine (1:1);Estrone sulfate piperazine salt;Estropipate;Harmogen;Ogen
- CAS NO.:7280-37-7
- Empirical Formula: C22H32N2O5S
- Molecular Weight: 436.56
- MDL number: MFCD00867399
- EINECS: 230-696-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 20:33:22
What is Estropipate?
Originator
Estropipate,ZYF Pharm Chemical
The Uses of Estropipate
Estropipate is used in post-menopausal women for hormonal replacement therapy, with benefits to improved cognition and prevention of osteoporosis.
The Uses of Estropipate
Estrogen.
What are the applications of Application
Estropipate is an ER agonist that inhibits OATP1B1
Definition
ChEBI: Estropipate is a steroid sulfate and a piperazinium salt. It is functionally related to an estrone.
Manufacturing Process
Step 1). A 100 L quantity of urine is adjusted by the addition of acid
(hydrochloric acid is preferred but not essential) to a pH of 4 and extracted
with a suitable solvent such as n-butyl alcohol, benzol, chloroform or ether in
a continuous extraction apparatus. By using the countercurrent principle we
find that this volume of urine may readily be extracted during one day's time
and the active fraction transferred completely to a 4 L volume of butyl alcohol.
This alcoholic solution is chilled and filtered from salts and other insoluble
matter.
Step 2). The butyl alcohol extract is distilled to dryness in vacuum and the
brown tarry residue (300 to 600 g). Residue is extracted with benzol using
successive volumes of 1.5, 1.0, and 0.75 L of hot benzol, which treatment
dissolves the active principle.
Step 3). The benzol solution is then chilled, poured from the insoluble matter
and distilled using a vacuum to complete removal of benzol. The residue from
the distillation is treated with e 200 mL of butyl alcohol to which solution or
suspension 4 L of petroleum ether (boiling point 60-80°C) are added. The
resultant solution and suspension then extracted five to eight times with 800
mL of water to each portion of which sufficient 10% NaOH is added to
maintain a reaction alkaline to phenolphthalein. In this manner the hormone
is transferred to the alkaline aqueous solution. This solution is chilled to 2°C
for a day and poured from tarry material which separates. Subsequent
purification of the hormone is based upon the fact that it possesses a
sufficient acidic property so that it can be removed from certain organic
solvents by means of alkali, and that it can be removed in turn from alkaline solutions by successive extractions with organic solvents.
Step 4). The slightly alkaline aqueous solution is extracted five times with
successive (800-1200 mL) portions of ether (peroxide-free). This combined
ether extract is then distilled and the active residue treated first with 80 mL
butyl alcohol and then with 1500 mL of petroleum ether as in Step 3.
Step 5). The petroleum ether solution is then extracted 4 to 6 times with 300
mL portions of dilute NaOH solution and filtered. The alkaline filtrate is then
extracted six times with 400 mL portions of sulfuric ether, thus again
transferring the hormone to ether solution. Up to this stage usually 60-75% of
the total activity is accounted for. For example in a typical experiment the
original crude material contained 300.000 units and the assay of the ether
solution obtained at the end of Step 5, assayed fully 200.000 units. In the
subsequent steps, however, a considerable amount of scattering of the active
material occurs and hence all by-products are worked back into the process.
Step 6). The ether solution is distilled to dryness and yields a yellowish oil.
The oil is leached with 200-240 mL of cold 0.2 N NaOH solution, repeating the
extraction 4 or 5 times, and combining and filtering the alkaline extract. This
aqueous alkaline solution is then extracted with six successive portions of
sulfuric ether using about 300 mL of peroxide-free ether extract.
Step 7). The ether solution resulting from Step 6 is distilled and the residue
crystallized from 25% aqueous ethyl alcohol or from 25% aqueous acetone.
As an alternative method of procedure, the following may be substituted for
Steps 4 to 7 inclusive of the above process. After distilling the benzol, the
tarry mass may be stirred directly with 2000 mL of hot 0.3 N NaOH with a
mechanical stirrer. The suspension is chilled and the supernatant Liquid
poured or siphoned off. Repetition of the extraction two or three times is
advisable. The alkaline aqueous solution is then extracted five or six times
with 400 mL portions of sulfuric ether, thus transferring the hormone to ether
solution. After distillation of the ether the residue is steam distilled as long as
a distillate other than water is obtained. The condensed water is removed by
vacuum distillation and the small amount of dark tarry residue leached 5
times with 50 mL of hot 0.3 N NaOH. This solution is filtered and the filtrate
extracted with sulfuric ether (100 mL, 6 times). The ether solution is distilled
and the residue leached with cold 0.3 N NaOH using 20 mL five times. This
alkaline solution is filtered and extracted with 50 mL of sulfuric ether five
times. Upon distillation of the ether and solution of the residue in a small
quantity of hot ethyl alcohol, the hormone separates in semi-crystalline balls
which may be filtered off. A further quantity is obtained by adding 3 volumes
of water to the alcoholic solution. It may be recrystallized from 25% aqueous
ethyl alcohol or from 25% aqueous acetone or from any of the following:
chloroform, benzol, ethyl acetate, ethyl ether or petroleum ether. The final
product consists of colorless crystals which, when crystallized from dilute
alcohol, possess a distinct rhomboid outline. The crystals melt at 242-243°C
(248-249°C corrected) with some decomposition.
Hormone was used with piperazine (1:1).
brand name
Ogen (Pharmacia & Upjohn); Ortho-EST (Sun).
Therapeutic Function
Estrogen
General Description
All the estrone 3-sulfate salts have the obvious pharmaceuticaladvantage of increased water solubility and better oralavailability. Acids convert the salts to the free 3-sulfate estersand cause some hydrolysis of the ester. This does not seem toaffect absorption adversely, but precipitation of the free sulfateesters in acidic pharmaceutical preparations should beavoided. The dibasic piperazine molecule acts as a buffer,giving it somewhat greater stability.
Biological Activity
Estrogen receptor agonist. Also inhibits organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1) (IC 50 = 70 nM).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Estropipate is the piperazine salt of the estrogen receptor agonist estrone-3-sulfate and a potent, specific inhibitor of the organic anion transporting polypeptide 1B1 (OATP1B1, IC50 = 60 nM).
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic vapors of SOx and NOx.
Properties of Estropipate
| Melting point: | 245 °C |
| alpha | D25 +87.8° (c = 1 in 0.4% NaOH) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥24mg/mL |
| pka | pKa 3.6/9.7(acetonitrile,80% v/v) (Uncertain) |
| form | powder |
| color | white to tan |
| optical activity | [α]/D 100 to 120°, c = 1 in DMSO |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7280-37-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Estropipate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H350:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Estropipate
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Estropipate CAS 7280-37-7View Details
Estropipate CAS 7280-37-7View Details
7280-37-7 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1