Sodium sulfate
Synonym(s):Disodium Sulfate;Natrii sulfas anhydricus;Sodium sulfate;Sodium Sulfate Anhydrous
- CAS NO.:7757-82-6
- Empirical Formula: Na2SO4
- Molecular Weight: 142.04214
- MDL number: MFCD00003504
- EINECS: 231-820-9
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:43
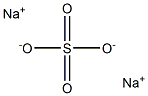
What is Sodium sulfate?
Absorption
Absorption of sodium sulfate after ingestion in rats was investigated. 35)S-Radioactivity excreted in urine during 24 hr indicated almost complete absorption from GI tract. Determination in serum 2 hr after admin revealed 3-fold increase in sulfate concentration rapid and almost complete absorption of inorganic sulfate occurs after oral admin in rats.
Description
Anhydrous sodium sulfate (Na2SO4) is typically used in organic chemistry as a drying agent. After aqueous extractions the organic layer always has a certain amount of water left in it. Adding anhydrous sodium sulfate removes this water by forming the sodium sulfate hydrate, which conveniently is also a solid allowing it to be filtered away. Magnesium sulfate (MgSO4) is a similar drying agent.
Chemical properties
Sodium sulfate, also known as thenardite and salt cake, is a crystalline compound that melts at 888°C (1632°C). Sodium sulfate is found in natural form(thenardite) in Chile and Spain. It is used in the manufacture of paperboard, glass,and freezing mixtures. It is used in dyeing,manufacturing glass,and in the preparation of sodium bisulfate.
Physical properties
Sodium sulfate is a white crystalline solid. It frequently is found as the decahydrate. orthorhombic or hexagonal structure; hygroscopic; refractive index 1.468; hardness 2.8 Mohs; density 2.664 g/cm3; melts at 884°C; soluble in water, insoluble in ethanol. The decahydrate consists of colorless monoclinic crystals; refractive index 1.394; hardness 1.8 Mohs; density 1.4 6g/cm3; decomposes at 32°C; soluble in water; insoluble in ethanol.
Occurrence
Sodium sulfate occurs in nature as the minerals mirabilite and thenardite. While thenardite is the anhydrous form of Na2SO4, mirabilite is a naturallyoccurring decahydrate, Na2SO4.10H2O.
Sodium sulfate is one of the most important sodium salts. The decahydrate,commonly known as the Glauber’s salt, was first prepared by Johann Glauber in the seventeenth century as a by-product in making hydrochloric acid from sulfuric acid and sodium chloride.
The Uses of Sodium sulfate
Sodium sulfate serves several functions in industrial and laboratory settings. In the manufacturing of synthetic detergents and soaps, it is primarily used as a filler. It is also a common laboratory reagent, where its principal application is as a drying agent to remove residual water from organic solvents and their extracts. Additionally, sodium sulfate is utilized as a starting material for the chemical synthesis of other sodium salts.
Background
Sodium Sulfate Anhydrous is the anhydrous, sodium salt form of sulfuric acid. Sodium sulfate anhydrous disassociates in water to provide sodium ions and sulfate ions. Sodium ion is the principal cation of the extracellular fluid and plays a large part in the therapy of fluid and electrolyte disturbances. Sodium sulfate anhydrous is an electrolyte replenisher and is used in isosmotic solutions so that administration does not disturb normal electrolyte balance and does not lead to absorption or excretion of water and ions.
Indications
indicated for bowel cleansing prior to colonoscopy or barium enema X-ray examination.
Production Methods
Sodium sulfate can be produced industrially through two primary methods. The first involves the reaction of magnesium sulfate with sodium chloride in solution, followed by crystallization. The second method is the reaction of concentrated sulfuric acid with solid sodium chloride. This latter process was integral to the historic Leblanc process for alkali production and is the origin of the term "salt cake" for impure, industrial-grade sodium sulfate. Industrially, sodium sulfate is used in the manufacturing of glass and soft glazes. In the dyeing industry, it is employed as a leveling agent to promote an even finish. It also has medicinal applications as a laxative and is a component of some commercial purgative salts.
Pharmacokinetics
Induces catharsis by the osmotic effects of the unabsorbed sulfate salts and polyethylene glycol (PEG) in the GI tract. Specifically, sulfate salts provide sulfate anions, which are poorly absorbed, and PEG, which is primarily unabsorbed, causes water to be retained in the GI tract resulting in watery diarrhea.
Toxicity
Moderately toxic by intravenous route. Mildly toxic by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic effects. Violent reaction with Al. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SOx and Na2O.
Potential Exposure
Sodium sulfate is used in the manufacture of glass; as a precipitating agent in the manufacture of silver emulsions; as an analytical reagent; in making ultramarine and paper pulp; in ceramic glazes and pharmaceuticals; as a food additive; and a filler in synthetic detergents.
Chemical property
Hygroscopic. Sodium sulfate reacts violently with magnesium. Also incompatible with aluminum, potassium, mercury, lead, calcium, silver, barium, ammonium ions, and strontium. Sulfates give precipitates with salts of lead, barium, strontium, and calcium. Silver and mercury form slightly soluble salts. Alcohol preciptates most sulfates out of solution.
Incompatibilities
Violent reaction with aluminum, magnesium. Attacks metals in the presence of moisture.
Waste Disposal
Do not discharge waste sodium sulfate directly into sewers or surface waters. Recovered sodium sulfate may be disposed of by burial in a landfill.
Properties of Sodium sulfate
| Melting point: | 884 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1700°C |
| Density | 2.68 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| refractive index | 1.484 |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | powder (fine) |
| appearance | White crystalline solid |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 2.68 |
| PH Range | 5.2 - 9.2 |
| Odor | wh. cryst. or powd., odorless, bitter saline taste |
| PH | 5.2-8.0 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 18.5 mg/L |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| λmax | λ: 260 nm Amax: 0.015 λ: 280 nm Amax: 0.015 |
| Merck | 14,8680 |
| Dielectric constant | 2.7(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, aluminium, magnesium, strong bases. Hygroscopic. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7757-82-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Sodium sulfate(7757-82-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium sulfate (7757-82-6) |
Safety information for Sodium sulfate
Computed Descriptors for Sodium sulfate
Sodium sulfate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Zama Chemical
Shree Ganesh Chemicals
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 SODIUM SULPHATE ANHYDROUS 99%View Details
SODIUM SULPHATE ANHYDROUS 99%View Details -
 Sodium sulphate 99%View Details
Sodium sulphate 99%View Details -
 Sodium Sulphate 99%View Details
Sodium Sulphate 99%View Details -
 Sodium Sulphate 99%View Details
Sodium Sulphate 99%View Details -
 Sodium sulfate 99%View Details
Sodium sulfate 99%View Details -
 Sodium sulfate 98%View Details
Sodium sulfate 98%View Details -
 Sodium Sulphate 99%View Details
Sodium Sulphate 99%View Details -
 Sodium sulfate, anhydrous 99%View Details
Sodium sulfate, anhydrous 99%View Details
