Epirubicin
- CAS NO.:56420-45-2
- Empirical Formula: C27H29NO11
- Molecular Weight: 543.52
- MDL number: MFCD01713214
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-19 15:53:33
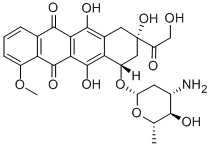
What is Epirubicin?
Absorption
100%
Toxicity
bone marrow aplasia, grade 4 mucositis, and gastrointestinal bleeding
Originator
Ellence,Pharmacia and Upjohn Co.
The Uses of Epirubicin
Epirubicin is a cell permeable Topo II inhibitor.
The Uses of Epirubicin
Antineoplastic.
Background
An anthracycline which is the 4'-epi-isomer of doxorubicin. The compound exerts its antitumor effects by interference with the synthesis and function of DNA.
Indications
For use as a component of adjuvant therapy in patients with evidence of axillary node tumor involvement following resection of primary breast cancer.
What are the applications of Application
Epirubicin is a cell permeable Topo II inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: An anthracycline that is the 4'-epi-isomer of doxorubicin.
Manufacturing Process
Conversion of daunorobicin hydrochloride to 4'-epi-doxorubicin hydrochloride
employing the trifluoroacetyl moiety for the 3'-amino group protection:
To a solution of 8 g (14 mmol) of daunorubicin hydrochloride in 500 ml of dry
MeOH, 5.9 ml (79 mmol, 5.6 eq.) of acetylchloride was added. After refluxing
for 1 h the solvents were evaporated in vacuo. Addition of CHCl3 to the
residue caused precipitation of daunosamine. After the aminosugar had been
filtered off, the filtrate was evaporated in vacuo. Diisopropylether was added
to the remaining solid and the mixture was sonicated for 15 min to yielddaunomycinone. In total, 2.55 g (91%) of daunosamine (4-amino-6-methoxy-
2-methyltetrahydropyran-3-ol hydrochloride) and 5.5 g (99%) of
daunomycinone were obtained, m.p. 209-233°C (dec.).
Under an argon atmosphere, a solution of 1.24 ml (2.5 eq.) of Br2 in 72.8 ml
CHCl3 was added to a solution of 3.90 g (9.8 mmol) of daunomycinone in 390
ml of CHCl3. After stirring the reaction mixture over night at room
temperature, the pure bromide 4 precipitated and was filtered out. Yield 4.1 g
(88%).The bromide was dissolved in 1.17 L of acetone, 16.7 g of AcOK was
added to the mixture which was then refluxed for 5 min. Thereafter the
solvents were evaporated in vacuo. The residue was dissolved in CHCl3 and
washed with water and brine. The combined organic extracts were dried over
Na2SO4, filtered and concentrated in vacuo. Diisopropylether was added and
the mixture was sonicated and filtrated to give doxorubicinone acetate, 3.8 g
(97%), m.p. 226-229°C (dec.).
Daunosamine modification:
To a solution of 2.55 g (12.9 mmol) of daunosamine in 64 ml of dry
diethylether under an argon atmosphere 5 ml (4.8 eq.) of pyridine was added.
The reaction mixture was cooled to -20°C and 3.63 ml of trifluoroacetic acid
anhydride was added. After stirring overnight at room temperature, the
mixture was filtered and the filtrate was washed with diethylether. The filtrate
was subsequently washed with 10% citric acid solution, saturated NaHCO3 and
brine. The combined extracts were dried over MgSO4, filtrated and evaporated
in vacuo. The residue was purified by flash column chromatography (5%
MeOH in CHCl3) to give 2.69 g (81%) of (3-hydroxy-6-methoxy-2-
methyltetrahydropyran-4-yl)carbamic acid trifluoromethyl ester, m.p. 137-
152°C.
To a solution of 2.5 g (9.7 mmol) of (3-hydroxy-6-methoxy-2-
methyltetrahydropyran-4-yl)carbamic acid trifluoromethyl ester in 100 ml of
CH2Cl2 2.45 g (11.4 mmol) of pyridinium chlorochromate (PCC) was added.
After 2 and after 4 hours of refluxing 1.08 g (5.0 mmol) of PCC was added.
Again after refluxing the reaction mixture for 8 hours 1.5 g (7.0 mmol) of PCC
was added and the mixture was stirred over night. The mixture was poured
into 436 ml of diethylether, filtered and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was
purified by flash column chromatography (2% acetone in CH2Cl2) to give 2.10
g (85%) of (6-methoxy-2-methyl-3-oxotetrahydropyran-4-yl)-carbamic acid
trifluoromethyl ester, m.p. 74-98°C.
10 ml of 1 M BH3·THF was added dropwise to a solution of 2.6 g (10 mmol) of
(6-methoxy-2-methyl-3-oxotetrahydropyran-4-yl)carbamic acid trifluoromethyl
ester dissolved in a mixture of 200 ml of dry THF and 125 ml of dry MeOH
under an argon atmosphere at 0°C. After stirring for 10 min, 1 ml of H2O was
added and the solvents were evaporated in vacuo. The remaining oil was
purified by flash column chromatography (3% MeOH in CH2Cl2) to give 2.08 g
(80%) of 4'-epidaunosamine derivative as a white solid, m.p. 165-167°C. A
solution of 2.08 g (8.1 mmol) of 4'-epidaunosamine derivative in 20% of
AcOH was refluxed for 3 hours at 90°C. The solution was freeze-dried and
purified by flash column chromatography (10% MeOH in CH2Cl2) to give 1.38
g (70%) of hemiacetal, m.p. 180-185°C.
3.3 ml (23.5 mmol) of trifluoroacetic anhydride was added to a stirred
suspension of 272 mg (1.12 mmol) of hemiacetal in 10 ml of dry diethylether
under an argon atmosphere at 0°C. After the suspension had become clear,
stirring was continued for 1 hour at room temperature, after that the solvent
was cautiously removed in vacuo. To this residue 50 ml of dry CH2Cl2 and 10
g of 4 ANG molsieves and 0.27 ml (1.39 mmol) of trimethylsilyl
trifluoromethanesulfonate were added under an argon atmosphere at 0°C. The
reaction mixture was stirred at 0°C for 1 h and a solution of 0.50 g (1.11
mmol) of doxorubicinone acetate in 100 ml of dry CH2Cl2 was added. After
stirring for 2 hours at room temperature, the red suspension was poured into
a vigoriously stirred solution of saturated NaHCO3 and the aqueous layer was
extracted with CH2Cl2. The combined organic extracts were washed with brine
and dried over Na2SO4, filtered and the solvents were evaporated in vacuo.
The remaining red solid was stirred overnight in a mixture of 20 ml of CH2Cl2
and 175 ml of MeOH under an argon atmosphere and the solvents were
evaporated in vacuo. The remaining red solid was purified by flash column
chromatography (4% MeOH in CH2Cl2) to give 345 mg (47%) of 4'-
epidoxorubicin derivative, [122 mg (24%) of unreacted doxorubicinone
acetate was also obtained; m.p. 114-126°C].
225 ml of saturated NaHCO3 was added to a solution of 784 mg (1.15 mmol)
of 4'-epidoxorubicin in a mixture of 150 ml of acetone and 75 ml of methanol
under an argon atmosphere. After stirring for 3 hours at room temperature,
the purple suspension was poured into 600 ml of H2O and was extracted 3
times with CHCl2. The combined organic extracts were washed with brine,
dried over Na2SO2, filtered and taken to dryness in vacuo to give 526 mg
(72%) of deacetylated compound, m.p. 147-162°C (dec.).
5.1 ml (42 mmol) of 2,2-dimethoxypropane and 1 mg p-toluene sulfonic acid
were added to a solution of 107 mg (0.17 mmol) of deacetylated compound in
a mixture of 1 ml of dioxane and 20 ml of CHCl3 under an argon atmosphere.
After stirring for 24 hours at room temperature, 10 mg of NaHCO2 was added
and the solution was stirred for 5 min. The red reaction mixture was washed
with water until neutral pH. The organic layer was washed with brine, dried
over Na2SO4, filtered and evaporated in vacuo. The remaining red solid was
purified by flash column chromatography (5% MeOH in CH2Cl2) to give 86 mg
(72%) of compound with protected carbonyl group (a mixture of
diastereomers), m.p.146-164°C.
A solution of 325 mg (0.46 mmol) of above compound in a mixture of 50 ml
of 0.1 M NaOH and 10 ml of acetone was stirred for 30 min at room
temperature under an argon atmosphere. The pH of the reaction mixture was
adjusted to 8.4 with a 0.1 M HCl solution and extracted with CHCl3 until the
organic layer was colourless. The combined organic extracts were dried over
Na2SO4, filtered and the solvent was evaporated in vacuo. The residue was
dissolved in 20 ml of 0.1 M HCl and stirred for 39 hours at room temperature,
the solution was then washed with CHCl3 (to extract the aglycone). The pH of
the combined aqueous layer was adjusted to 8.5 with 0.1 M NaOH and
extracted with CHCl2 until the organic extract was colourless. The combined
organic extracts were dried over Na2SO4, filtered and the solution was
concentrated. Diethylether and 0.76 ml of 0.6 M HCl in MeOH were added, 4'-epidoxorubicin hydrochloride precipitated and was filtrated to obtain 118 mg
(45%), m.p. 176-185°C (dec.).
brand name
Ellence(Pfizer).
Therapeutic Function
Antineoplastic
Pharmacokinetics
Epirubicin is an antineoplastic in the anthracycline class. General properties of drugs in this class include: interaction with DNA in a variety of different ways including intercalation (squeezing between the base pairs), DNA strand breakage and inhibition with the enzyme topoisomerase II. Most of these compounds have been isolated from natural sources and antibiotics. However, they lack the specificity of the antimicrobial antibiotics and thus produce significant toxicity. The anthracyclines are among the most important antitumor drugs available. Doxorubicin is widely used for the treatment of several solid tumors while daunorubicin and idarubicin are used exclusively for the treatment of leukemia. Epirubicin may also inhibit polymerase activity, affect regulation of gene expression, and produce free radical damage to DNA. Epirubicin possesses an antitumor effect against a wide spectrum of tumors, either grafted or spontaneous. The anthracyclines are cell cycle-nonspecific.
Metabolism
Extensively and rapidly metabolized in the liver. Epirubicin is also metabolized by other organs and cells, including red blood cells. The four main metabolic routes are: (1) reduction of the C-13 keto-group with the formation of the 13(S)-dihydro derivative, epirubicinol; (2) conjugation of both the unchanged drug and epirubicinol with glucuronic acid; (3) loss of the amino sugar moiety through a hydrolytic process with the formation of the doxorubicin and doxorubicinol aglycones; and (4) loss of the amino sugar moiety through a redox process with the formation of the 7-deoxy-doxorubicin aglycone and 7-deoxy-doxorubicinol aglycone. Epirubicinol exhibits in vitro cytoxic activity (~10% that of epirubicin), but it is unlikely to reach sufficient concentrations in vivo to produce cytotoxic effects.
Properties of Epirubicin
| Boiling point: | 617.77°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3783 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6400 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | Store at -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| pka | 7.35±0.60(Predicted) |
Safety information for Epirubicin
Computed Descriptors for Epirubicin
Epirubicin manufacturer
New Products
Trans-methyl 4-aminocyclohexane- carboxylate HCl 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 3-Iodophenylacetic acid (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine Cyclohexane, (2-propynyloxy)- 3-Bromobenzaldehyde, 95% 2-Naphthol, 98% Cysteamine hydrochloride, 98% Copper(II) bromide, 98% 1-Chloro-2,4-difluorobenzene,98% Dodecylbenzenesulfonic acid, 95% L-Glycine methyl ester.HCl Fmoc-L-Tyr(tBu)-OH Calcium Alphaketoglutarate* H-Ser(t-Bu)-Ser(t-Bu)-Gly-OH Fmoc-Ser(tBu)-Ser(Ψ(Me,Me)pro-OH Triphosgene 5-Cyanophthalide 10-Methoxy-5H-dibenz[b,f]azepine L-Glutamic Acid Dimethyl Ester Hcl 2-AMINO-3,5-DIBROMO BENZALDEHYDE [ADBA] 4-(3,4-Dichlorophenyl)-3,4-Dihydro-N-Methyl-1-(2H)-Naphthalenimine (Schiff Base)Related products of tetrahydrofuran
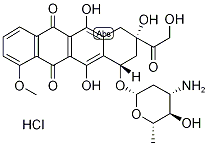


You may like
-
 56420-45-2 Epirubicin 98%View Details
56420-45-2 Epirubicin 98%View Details
56420-45-2 -
 Epirubicin 95% CAS 56420-45-2View Details
Epirubicin 95% CAS 56420-45-2View Details
56420-45-2 -
 15761-38-3 N-Boc-L-Alanine >98%View Details
15761-38-3 N-Boc-L-Alanine >98%View Details
15761-38-3 -
 873-74-5 4-Aminobenzonitrile 99%View Details
873-74-5 4-Aminobenzonitrile 99%View Details
873-74-5 -
 872-85-5 99%View Details
872-85-5 99%View Details
872-85-5 -
 N,N-Carbonyl diimidazole 99%View Details
N,N-Carbonyl diimidazole 99%View Details
530-62-1 -
 3- Pyridinecarboxaldehdye 500-22-1 99%View Details
3- Pyridinecarboxaldehdye 500-22-1 99%View Details
500-22-1 -
 80841-78-7 DMDO-Chloride 92%View Details
80841-78-7 DMDO-Chloride 92%View Details
80841-78-7
