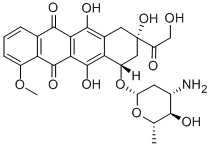
CHEMICAL AND PHYSICAL PROPERTIES
| Physical Description | Solid |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 344.53 °C |
| Solubility | 0.093 mg/ml |
| LogP | -0.5 |
| Stability/Shelf Life | Stable under recommended storage conditions. /Epirubicin hydrochloride/ |
| Decomposition | When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of /nitrogen oxides/. |
| Other Experimental Properties | The carbohydrate C-4 epimer of adriamycin, epirubicin is as potent as its parent molecule, but significantly less toxic. |
COMPUTED DESCRIPTORS
| Molecular Weight | 543.5 g/mol |
|---|---|
| XLogP3 | 1.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Exact Mass | 543.17406074 g/mol |
| Monoisotopic Mass | 543.17406074 g/mol |
| Topological Polar Surface Area | 206 Ų |
| Heavy Atom Count | 39 |
| Formal Charge | 0 |
| Complexity | 977 |
| Isotope Atom Count | 0 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 6 |
| Undefined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Defined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Undefined Bond Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| Covalently-Bonded Unit Count | 1 |
| Compound Is Canonicalized | Yes |
PRODUCT INTRODUCTION
description
4'-epidoxorubicin is an anthracycline that is the 4'-epi-isomer of doxorubicin. It has a role as an EC 5.99.1.3 [DNA topoisomerase (ATP-hydrolysing)] inhibitor, an antineoplastic agent and an antimicrobial agent. It is an anthracycline, a deoxy hexoside, an anthracycline antibiotic, an aminoglycoside, a monosaccharide derivative, a member of p-quinones, a primary alpha-hydroxy ketone and a tertiary alpha-hydroxy ketone. It is functionally related to a doxorubicin. It is a conjugate acid of a 4'-epidoxorubicinium.