6-Aminocaproic acid
Synonym(s):ε-Aminocaproic acid;6-Aminocaproic acid;6-Aminohexanoic acid;EACA
- CAS NO.:60-32-2
- Empirical Formula: C6H13NO2
- Molecular Weight: 131.17
- MDL number: MFCD00008238
- EINECS: 200-469-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:51
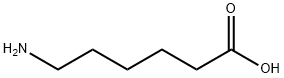
What is 6-Aminocaproic acid?
Absorption
Absorbed rapidly following oral administration. In adults, oral absorption appears to be a zero-order process with an absorption rate of 5.2 g/hr. The mean lag time in absorption is 10 minutes. After a single oral dose of 5 g, absorption was complete (F=1).
Toxicity
A few cases of acute overdosage with intravenous administration have been reported. The effects have ranged from no reaction to transient hypotension to severe acute renal failure leading to death. The intravenous and oral LD50 were 3.0 and 12.0 g/kg respectively in the mouse and 3.2 and 16.4 g/kg respectively in the rat. An intravenous infusion dose of 2.3 g/kg was lethal in the dog.
Chemical properties
white crystalline powder. Leaf crystals were obtained from ether. Odorless, bitter taste. Melting point 202 ~ 207 ℃ (decomposition). Soluble in water, slightly soluble in methanol, insoluble in ethanol, ether and chloroform.
Originator
Epsilon,Roche,W. Germany,1962
The Uses of 6-Aminocaproic acid
6-Aminohexanoic Acid is a reagent commonly used for the extraction of aldehydes from reaction mixtures. 6-Aminohexanoic Acid has also been shown to improve solubilization of membrane proteins in elect rophoresis. Studies suggest that 6-Aminohexanoic Acid inhibits the activation of the first component of the complement system.
The Uses of 6-Aminocaproic acid
EACA is directly soluble in water at 25 mg/ml. As an inhibitor of plasmin it is has been utilized in the clotting buffer for fibrinogen assays. This buffer is 10 mM potassium and sodium phosphate, pH 6.4, with 0.20 g CaCl2, 5 g 6-Aminohexanoic acid, 1 g sodium azide, and 9 g NaCl in 1 liter. The buffer is stable indefinitely at room temperature.
What are the applications of Application
e-Amino-n-caproic Acid is an antifibrinolytic lysine analog shown to inhibit streptokinase and basic carboxypeptidases
Background
An antifibrinolytic agent that acts by inhibiting plasminogen activators which have fibrinolytic properties.
Indications
For use in the treatment of excessive postoperative bleeding.
Definition
ChEBI: 6-aminohexanoic acid is an epsilon-amino acid comprising hexanoic acid carrying an amino substituent at position C-6. Used to control postoperative bleeding, and to treat overdose effects of the thrombolytic agents streptokinase and tissue plasminogen activator. It has a role as an antifibrinolytic drug, a hematologic agent and a metabolite. It is an epsilon-amino acid and an omega-amino fatty acid. It derives from a hexanoic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a 6-aminohexanoate. It is a tautomer of a 6-aminohexanoic acid zwitterion.
What are the applications of Application
6-Aminohexanoic acid was used as a biochemical reagent. It is also used as a hemostatic agent. 6-aminocaproic acid has a significant effect on some severe bleeding caused by increased fibrinolytic activity. It is suitable for oozing or local bleeding during various surgical operations. 6-aminocaproic acid is used for hemoptysis, gastrointestinal bleeding and bleeding disorders in obstetrics and gynecology.
6-Aminocaproic acid is an anti-fibrinolytic drug with a similar chemical structure to lysine. It can qualitatively inhibit the binding of plasminogen to fibrin and prevent its activation, thereby inhibiting fibrinolysis and achieving hemostasis. Aminocaproic acid is a monoaminocarboxylic acid, which can inhibit the conversion of plasminogen into plasmin and its binding to fibrin. For severe bleeding caused by hyperfibrinolysis caused by increased activation of plasminogen, can have therapeutic effect.
Preparation
6-aminocaproic acid is obtained by hydrolysis of 6-(N-benzoylamino)capronitrile in the presence of hydrochloric acid, or by hydrolysis of caprolactam in the presence of hydrochloric acid, and then treated with ammonium hydroxide.
Manufacturing Process
5 kg of caprolactam were heated with 40 liters of water in a pressure vessel at 250°C for a period of four hours. These quantities of reactants correspond to a water:lactam molecular ratio of 50:1. After cooling, the small quantity of the nonsoluble substance that is formed is filtered off, and the filtrate is evaporated as far as possible. The resulting concentrate is mixed with three times its volume of strong alcohol, thereby causing the desired product, epsilon-aminocaproic acid (6-aminohexanoic acid), to crystallize out. After separating the crystalline product thus obtained, a further quantity of epsilonaminocaproic acid can be obtained from the mother liquid if desired.
brand name
Amicar (Xanodyne).
Therapeutic Function
Antifibrinolytic
General Description
6-Aminocaproic acid is a synthetic inhibitor of fibrinolysis and is utilized for the control of excessive bleeding in patients with amegakaryocytic thrombocytopenia. It also is a protease inhibitor that displays anticancer activity but is limited by cytotoxicity.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Lysine analog. Promotes rapid dissociation of plasmin, thereby inhibiting the activation of plasminogen and subsequent fibrinolysis. Reported to inhibit plasminogen binding to activated platelets. An early report indicated that it inhibits the activation of the first component of the complement system. Binds and inactivates Carboxypeptidase B.
Mechanism of action
Because binding of plasminogen or plasmin to fibrinogen or fibrin is mediated by lysine groups that are part of the structures of fibrin and fibrinogen, aminocaproic acid, which is a structural analog of lysine that only differs in that it has one less amino group, acts as a competitive inhibitor for binding of plasmin(ogen) to fibrin. Aminocaproic acid shifts the homeostatic balance on the side of coagulation, thus restoring fibrinolytic mechanism activity. Aminocaproic acid, which is not a procoagulant, such as those used during surgical intervention and various pathological conditions, is accompanied by an elevation in fibrinolytic activity of blood and tissue. It is used to stop bleeding.
Pharmacokinetics
Aminocaproic acid works as an antifibrinolytic. It is a derivative of the amino acid lysine. The fibrinolysis-inhibitory effects of aminocaproic acid appear to be exerted principally via inhibition of plasminogen activators and to a lesser degree through antiplasmin activity. Aminocaproic acid may be a possible prophylactic for vascular disease, as it may prevent formation of lipoprotein (a), a risk factor for vascular disease.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by intravenous route. Human systemic effects by ingestion: changes in tubules (includmg acute renal failure, acute tubular necrosis), hematuria, and increased body temperature. Experimental reproductive effects. An eye irritant. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes such as NOx,.
Synthesis
Aminocaproic acid (24.4.1) is synthesized by hydrolyzing |? -caprolactam at high temperature.

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Aminocaproic acid has been used as a treatment to degenerative myelopathy (seen primarily in German shepherds), but no controlled studies documenting its efficacy were located. There is interest in evaluating aminocaproic acid for adjunctive treatment of thrombocytopenia in dogs, but efficacy and safety for this purpose remains to be investigated. In humans, it is primarily used for treating hyperfibrinolysis-induced hemorrhage.
Metabolism
Sixty-five percent of the dose is recovered in the urine as unchanged drug and 11% of the dose appears as the metabolite adipic acid.
Properties of 6-Aminocaproic acid
| Melting point: | 207-209 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 242.49°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.042 g/cm3 |
| vapor pressure | <0.1 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.4870 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 207-209°C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 50 mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 4.373(at 25℃) |
| color | white |
| PH | 7.0-7.5 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | SOLUBLE |
| Merck | 14,432 |
| BRN | 906872 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 60-32-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Hexanoic acid, 6-amino-(60-32-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Hexanoic acid, 6-amino- (60-32-2) |
Safety information for 6-Aminocaproic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H320:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P304+P340:IF INHALED: Remove victim to fresh air and Keep at rest in a position comfortable for breathing. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P405:Store locked up. |
Computed Descriptors for 6-Aminocaproic acid
| InChIKey | SLXKOJJOQWFEFD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
6-Aminocaproic acid manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

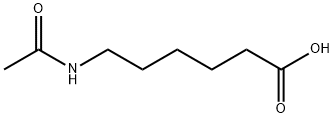

You may like
-
 60-32-2 98%View Details
60-32-2 98%View Details
60-32-2 -
 6-amino Caproic acid 95-99%View Details
6-amino Caproic acid 95-99%View Details
60-32-2 -
 Aminocaproic Acid BP CAS 60-32-2View Details
Aminocaproic Acid BP CAS 60-32-2View Details
60-32-2 -
 Aminocaproic Acid IP CAS 60-32-2View Details
Aminocaproic Acid IP CAS 60-32-2View Details
60-32-2 -
 6-Aminocaproic Acid extrapure CAS 60-32-2View Details
6-Aminocaproic Acid extrapure CAS 60-32-2View Details
60-32-2 -
 Aminocaproic Acid USP CAS 60-32-2View Details
Aminocaproic Acid USP CAS 60-32-2View Details
60-32-2 -
 6-Aminocaproic acid, 99% CAS 60-32-2View Details
6-Aminocaproic acid, 99% CAS 60-32-2View Details
60-32-2 -
 6-Aminocaproic Acid CAS: 60-32-2, For IndustrialView Details
6-Aminocaproic Acid CAS: 60-32-2, For IndustrialView Details
60-32-2
