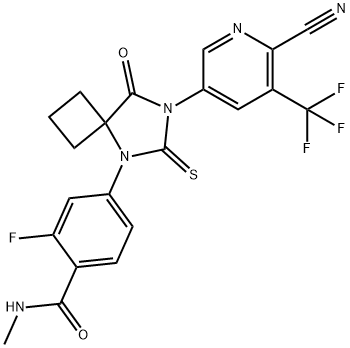
Enzalutamide
- CAS NO.:915087-33-1
- Empirical Formula: C21H16F4N4O2S
- Molecular Weight: 464.44
- MDL number: MFCD14155804
- EINECS: 805-022-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18

What is Enzalutamide?
Absorption
The median Tmax is 1 hour (0.5 to 3 hours) following a single 160 mg dose of capsules and 2 hours (0.5 to 6 hours) following a single 160 mg dose of tablets. Enzalutamide achieves steady-state by Day 28 and its AUC accumulates approximately 8.3-fold relative to a single dose. At steady-state, the mean (%CV) maximum concentration (Cmax) for enzalutamide and N-desmethyl enzalutamide is 16.6 μg/mL (23%) and 12.7 μg/mL (30%), respectively, and the mean (%CV) minimum concentrations (Cmin) are 11.4 μg/mL (26%) and 13.0 μg/mL (30%), respectively.
Toxicity
In an embryo-fetal developmental toxicity study in mice, enzalutamide caused developmental toxicity when administered at oral doses of 10 or 30 mg/kg/day throughout the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6-15). Findings included embryo-fetal lethality (increased post-implantation loss and resorptions) and decreased anogenital distance at ≥ 10 mg/kg/day, and cleft palate and absent palatine bone at 30 mg/kg/day. Doses of 30 mg/kg/day caused maternal toxicity. The doses tested in mice (1, 10, and 30 mg/kg/day) resulted in systemic exposures (AUC) of approximately 0.04, 0.4, and 1.1 times, respectively, the exposures in patients. Enzalutamide did not cause developmental toxicity in rabbits when administered throughout the period of organogenesis (gestational days 6-18) at dose levels up to 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.4 times the exposures in patients based on AUC).
In a pharmacokinetic study in pregnant rats with a single oral 30 mg/kg enzalutamide administration on gestation day 14,
enzalutamide and/or its metabolites were present in the fetus at a Cmax that was approximately 0.3 times the concentration
found in maternal plasma and occurred 4 hours after administration.
Based on animal studies, XTANDI may impair fertility in males of reproductive potential. Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment and for 3 months after the last dose of XTANDI.
The most common adverse reactions (≥ 5%) are asthenia/fatigue, back pain, diarrhea, arthralgia, hot flush, peripheral edema, musculoskeletal pain, headache, upper respiratory infection, muscular weakness, dizziness, insomnia, lower respiratory infection, spinal cord compression and cauda equina syndrome, hematuria, paresthesia, anxiety, and hypertension.
Description
In August 2012, the US FDA approved enzalutamide for the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) in patients who have previously been treated with docetaxel. Synthesis of enzalutamide was achieved by a triply convergent route that employed a Strecker condensation, followed by isothiocyanate condensation and hydrolysis to form the thiohydantoin moiety. In LNCaP/AR cells with high expression of AR, enzalutamide demonstrated potent inhibition of 16b-[18F]-5α-dihydrotestosterone binding (IC50=21 nM compared with bicalutamide IC50=160 nM), and inhibited AR translocation to the nucleus more potently than bicalutamide.The primary metabolite is the result of CYP2C8-mediated N-demethylation; enzalutamide is primarily eliminated by hepatic metabolism.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
University of California (United States)
The Uses of Enzalutamide
MDV3100, known as Enzalutamide, is a second-generation androgen receptor (AR) signaling inhibitor. It is able to inhibit binding of androgens to the AR, AR nuclear translocation, and the association of the AR with DNA.
Background
Enzalutamide is an androgen receptor (AR) inhibitor for the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), both metastatic and non-metastatic. It is a second-generation antiandrogen agent that the FDA approved on August 31, 2012. Although androgen deprivation therapy (ADT) is the first-line treatment of prostate cancer and remission can be achieved, arising resistance is inevitable, becoming castration-resistant prostate cancer. Until recently, docetaxel is the only treatment available for metastatic CRPC; however, AR inhibitors have been developed for more targeted therapy, although first-generation AR inhibitors like bicalutamide did not substantially increase the survival rate. Second-generation such as enzalutamide is more efficacious due to a higher affinity to AR and no partial agonist activity compared to bicalutamide.
Due to a favorable pharmacological profile, a phase 1 study of enzalutamide was initiated in July 2007. Compared to the average time of 10 to 15 years for a drug to go from pre-clinical to clinical studies, enzalutamide was developed relatively rapidly.
Indications
Enzalutamide is indicated for the treatment of castration-resistant prostate cancer and metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer (mCRPC). It is also used in combination with talazoparib for the treatment of adult patients with HRR gene-mutated mCRPC.
What are the applications of Application
MDV3100 is a non-steroidal androgen receptor inhibitor, applied against advanced cancers that depend on androgen receptor signaling.
Definition
ChEBI: A benzamide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-{3-[4-cyano-3-(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-5,5-dimethyl-4-oxo-2-thioxoimidazolidin-1-yl}-2-fluorobenzoic acid with methylamine. Used for the treatment of of metastatic castration-resistant p ostate cancer.
brand name
Xtandi
Pharmacokinetics
Enzalutamide is a second-generation antiandrogen that blocks the activity of androgen and androgen receptor (AR) in prostate cancer. AR activity and prostate cancer progression are closely related due to the normal physiology of prostate cells, providing the rationale for androgen deprivation therapy (ADT). However, resistance will eventually arise after the commencement of ADT in 2-3 years due to the accumulation of mutations, including constitutively active mutation, AR overexpression, and changes in AR splicing variants. Enzalutamide was therefore designed to exploit these mutations. In vitro experiments in human prostate cancer cell line VCaP showed that enzalutamide can suppress cell growth and induce apoptosis while other antiandrogens like bicalutamide did not.
Clinical trials on prostate cancer patients indicated that enzalutamide can lead to a decrease in serum PSA for at least 12 weeks, although this response can be short-lived and thus resulting in enzalutamide resistance. Patients receiving enzalutamide also had a 37% decreased in the risk of death compared to placebo.
Clinical Use
In August 2012, the FDA approved enzalutamide, marketed by Medivation and Astellas Pharma US for the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), specifically for those patients who had previously received docetaxel. Enzalutamide is an inhibitor of androgen receptors (AR)— whose increased expression has been closely linked with castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC),thus, AR inhibitors have seen increased recent attention from the medicinal chemistry community. Phase I/II trials were particularly promising for enzalutamide, as 43% of patients showed >50% sustained suppression of a key serum biomarker.
Synthesis
Of the several patents and papers describing synthetic approaches, a 2011 patent represents the most likely scale production route to enzalutamide, and this is described in the scheme.Commercially available carboxylic acid 70 was first converted to the corresponding acid chloride 71, followed by amide formation with methylamine to furnish benzamide 72 in 90% yield over two steps. Bromide 72 was then coupled with amine 73 using copper (I) catalysis to afford trisubstituted benzene 74 in 76% isolated yield. Esterification of 74 to 75 with iodomethane furnished one fragment for the key ring-forming event. Isothiocyanate 76, available in one step from the corresponding aniline 77, was then exposed to aminoester 75 in the presence of warm isopropyl acetate, resulting in construction of the lynchpin thiohydantoin and delivering enzalutamide (XI) in an impressive 78% yield. This 5-step process has successfully generated multi-gram quantities of the drug in 50.7% overall yield.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs Anticoagulants: possibly reduces concentration effect of coumarinsAnxiolytics: concentration of midazolam reduced.Cytotoxics: concentration of palbociclib possibly reduced - avoid. Lipid-regulating drugs: concentration increased by gemfibrozil - avoid or halve enzalutamide dose.
Metabolism
Enzalutamide is metabolized by CYP2C8 and CYP3A4. CYP2C8 is primarily responsible for the formation of the active metabolite (N-desmethyl enzalutamide). Carboxylesterase 1 metabolizes N-desmethyl enzalutamide and enzalutamide to the inactive carboxylic acid metabolite.
Metabolism
Clearance of enzalutamide is mainly via hepatic metabolism, producing an active metabolite that is equally as active as enzalutamide and circulates at approximately the same plasma concentration as enzalutamide. Under conditions of clinical use, enzalutamide is a strong inducer of CYP3A4, a moderate inducer of CYP2C9 and CYP2C19, and has no clinically relevant effect on CYP2C8Excreted mainly as metabolites 71% in urine and 14% via faeces.
References
Tran et al. (2009), Development of a Second-Generation Antiandrogen for Treatment of Advanced Prostate Cancer; Science 324 787 Jung et al. (2010), Structure-Activity Relationship for Thiohydantoin Androgen Receptor Antagonist for Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer (CRPC); J. Med. Chem. 53 2779
Properties of Enzalutamide
| Melting point: | 198 - 200°C |
| Density | 1.49 |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (>25 mg/ml) |
| form | solid |
| pka | 13.88±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| Stability: | Stable for 1 year as supplied. Solutions in DMSO may be stored at -20°C for up to 3 months. |
Safety information for Enzalutamide
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H227:Flammable liquids H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. P370+P378:In case of fire: Use … for extinction. P403+P235:Store in a well-ventilated place. Keep cool. |
Computed Descriptors for Enzalutamide
Enzalutamide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 915087-33-1 98%View Details
915087-33-1 98%View Details
915087-33-1 -
 Enzalutamide 97%View Details
Enzalutamide 97%View Details -
 Enzalutamide 99%View Details
Enzalutamide 99%View Details -
 915087-33-1 Enzalutamide 98%View Details
915087-33-1 Enzalutamide 98%View Details
915087-33-1 -
 915087-33-1 Enzalutamide 98%View Details
915087-33-1 Enzalutamide 98%View Details
915087-33-1 -
 Enzalutamide 98% (HPLC) CAS 915087-33-1View Details
Enzalutamide 98% (HPLC) CAS 915087-33-1View Details
915087-33-1 -
 Enzalutamide API CAS 915087-33-1View Details
Enzalutamide API CAS 915087-33-1View Details
915087-33-1 -
 Astellas Enzalutamide Xtandi 40 mg Capsules, Packaging Type: BoxView Details
Astellas Enzalutamide Xtandi 40 mg Capsules, Packaging Type: BoxView Details
915087-33-1