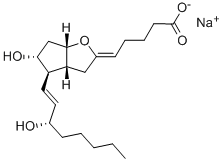
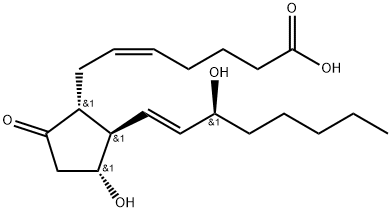
Bimatoprost
Synonym(s):Bimatoprost
- CAS NO.:155206-00-1
- Empirical Formula: C25H37NO4
- Molecular Weight: 415.57
- MDL number: MFCD03411999
- EINECS: 642-890-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-25 11:31:46
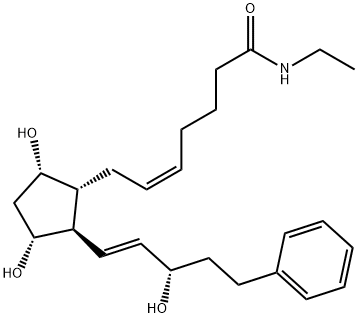
What is Bimatoprost?
Description
Bimatoprost was first introduced in the US and Brazil as Lumigan?, an ophthalmic solution (0.03%) for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure (IOP) in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension, a proven risk of glaucomatous visual field loss. Bitamoprost is a new agent belonging to the PGF2α analog class of prostamides launched in this indication after latanoprost, the most efficaceous topical medication currently available. This synthetic fatty acid amide can be prepared by esterification of 17- phenyl-18,19,20-trinorprostaglandin F2α followed by ethylamidation. Bimatoprost, as related prostamides, is devoid of typical activities associated with PGF2,, analogs; it exhibits a unique pharmacological profile in contracting the feline iris sphincter with an EC50 of 34 nM without interacting with any known prostanoid receptors. Thus it mimics the action of endogenous prostamides on specific receptors that lower IOP by increasing aqueous humor outflow through both pressure-insensitive and pressure-sensitive pathways without reducing humor formation. In a 3-month controlled clinical trial of efficacy and safety in patients with elevated IOP, bimatoprost demonstrated lower mean intraocular pressures at every time point throughout the study, as well as a good tolerance and systemic safety profile compared to latanoprost.
Chemical properties
Crystalline Solid
Originator
Allergan (US)
The Uses of Bimatoprost
Bimatoprost is a prostaglandin analog used topically (as eye drops) to control the progression of glaucoma and in the management of ocular hypertension. It reduces intraocular pressure (IOP) by increasing the outflow of aqueous fluid from the eyes.
The Uses of Bimatoprost
Antiglaucoma. Synthetic prostamide; structurally related to prostaglandin F2a.
The Uses of Bimatoprost
Bimatoprost is an antiglaucoma agent. Bimatoprost is an synthetic prostamide; structurally related to prostaglandin F2α.
The Uses of Bimatoprost
17-phenyl trinor Prostaglandin F2α ethyl amide (17-phenyl trinor PGF2α ethyl amide) is an F-series PG analog which has been approved for use as an ocular hypotensive drug. Investigations in our lab have shown that 17-phenyl trinor PGF2α ethyl amide is converted by an amidase enzymatic activity in the bovine and human cornea to yield the corresponding free acid, with a conversion rate of about 40 μg/g corneal tissue/24 hours. The free acid, 17-phenyl trinor PGF2α, is a potent FP receptor agonist. In human and animal models of glaucoma, FP receptor agonist activity corresponds very closely with intraocular hypotensive activity.[Cayman Chemical]
Indications
Bimatoprost is used for the reduction of elevated intraocular pressure in patients with open-angle glaucoma or ocular hypertension.
These patients must be intolerant to other intraocular pressure lowering medications or inadequately responsive to other treatments.
Bimatoprost is also indicated to treat eyelash hypotrichosis.
Background
Bimatoprost, also known as Latisse or Lumigan, belongs to a group of drugs called prostamides, which are synthetic structural analogs of prostaglandin. Bimatoprost, marketed by Allergan, is administered in both the ophthalmic solution and implant form. It has the ability to reduce ocular hypotension, proving effective in conditions such as ocular hypertension and glaucoma. Bimatoprost is also used to treat eyelash hypotrichosis, or sparse eyelash growth. It was initially approved by the FDA in 2001 for ocular hypertension and later approved for hypothrichosis in 2008, as eyelash growth became a desirable adverse effect for patients using this drug.
Definition
ChEBI: Bimatoprost is a monocarboxylic acid amide. It has a role as an antiglaucoma drug and an antihypertensive agent.
brand name
Lumigan (Allergan).
General Description
Bimatoprost (Lumigan) is supplied as a sterile 0.03%ophthalmic solution in 2.5- and 5.0-mL sizes. The recommendeddosage of bimatoprost is limited to one drop intothe affected eye once daily in the evening. Increased usagemay decrease its beneficial effect. If used concurrently withother IOP-lowering drugs, a waiting period of 5 minutesshould separate administrations.
Pharmacokinetics
High intraocular pressure is a major risk factor for glaucoma-related visual field loss. A linear relationship exists between intraocular pressure and the risk of damaging the optic nerve, which can lead to considerable visual impairment. Therefore, conditions such as ocular hypertension and glaucoma can cause dangerous elevations of intraocular pressure. Bimatoprost rapidly decreases intraocular pressure and reduces the risk for visual field loss from ocular hypertension due to various causes.
Other effects of this drug may include gradual changes in eyelid pigmentation, changes in iris pigmentation, changes in eyelash pigmentation, growth and thickness. Patients should be informed of these possible effects, especially if this drug is only administered to one eye, which may noticeably change in appearance with bimatoprost treatment.
Absorption
This drug is absorbed systemically when administered to the eye. A study was performed on 15 healthy volunteers and bimatoprost ophthalmic solution 0.03% was administered once daily for 14 days. The mean Cmax was approximately 0.08 ng/mL and AUC0-24hr was approximately 0.09 on days 7 and 14 of the study. By 10 minutes, peak blood concentration was achieved. Bimatoprost was not detectable at 1.5 hours after administration in most subjects. The maximum blood concentration in a study of 6 healthy volunteers was determined to be 12.2 ng/mL. Steady state was reached in the first week of dosing.
One drug label mentions that onset of decreased intraocular pressure occurs approximately 4 hours after the first administration and the peak effect occurs in the range of 8-12 hours. Bimatoprost effects may last up to 24 hours.
Metabolism
Bimatoprost is hydrolyzed to its active form, bimatoprost acid, in the eye. Bimatoprost undergoes oxidation, N-deethylation, and glucuronidation after it is systemically absorbed, and this leads to the production of various metabolites. In vitro studies show that CYP3A4 is an enzyme that participates in the metabolism of bimatoprost. Despite this, many enzymes and pathways metabolize bimatoprost, therefore, no significant drug-drug interactions are likely to occur. Glucuronidated metabolites comprise most of the excreted drug product in the blood, urine, and feces in rats.
Side Effects
Bimatoprost has several adverse side effects. The most frequent one is conjunctivitis, which occurs in more than 10% of patients. Others include blurred vision, redness, burning, and darkening of the iris. Eyelid infection and darkening can occur when the drug is used on eyelashes.
Properties of Bimatoprost
| Melting point: | 66-68°C |
| Boiling point: | 629.8±55.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.145±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Chloroform (Slightly), Dichloromethane (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly) |
| form | solid |
| appearance | white powder |
| pka | 14.25±0.20(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 155206-00-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Bimatoprost
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Bimatoprost
| InChIKey | AQOKCDNYWBIDND-FTOWTWDKSA-N |
| SMILES | C(NCC)(=O)CCC/C=C\C[C@H]1[C@@H](O)C[C@@H](O)[C@@H]1/C=C/[C@@H](O)CCC1=CC=CC=C1 |
Bimatoprost manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Bimatoprost 99%View Details
Bimatoprost 99%View Details -
 Bimatoprost 98% (HPLC) CAS 155206-00-1View Details
Bimatoprost 98% (HPLC) CAS 155206-00-1View Details
155206-00-1 -
 17-Phenyl-tri-norprostaglandin F2α-ethyl amide CAS 155206-00-1View Details
17-Phenyl-tri-norprostaglandin F2α-ethyl amide CAS 155206-00-1View Details
155206-00-1 -
 Bimatoprost Api, For Commerical, 155206-00-1View Details
Bimatoprost Api, For Commerical, 155206-00-1View Details
155206-00-1 -
 Bimatoprost Api Powder, 25kgView Details
Bimatoprost Api Powder, 25kgView Details
155206-00-1 -
 Bimatoprost Api PowderView Details
Bimatoprost Api PowderView Details
155206-00-1 -
 Bimatoprost Api Powder, USPView Details
Bimatoprost Api Powder, USPView Details
155206-00-1 -
 Bimatoprost APIView Details
Bimatoprost APIView Details
155206-00-1
