Dronedarone
- CAS NO.:141626-36-0
- Empirical Formula: C31H44N2O5S
- Molecular Weight: 556.76
- MDL number: MFCD00910331
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-07-02 08:54:59
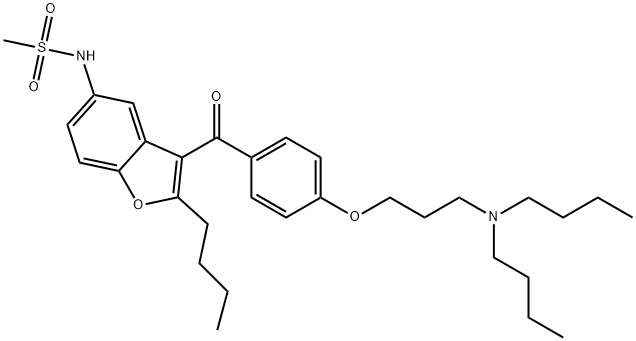
What is Dronedarone?
Absorption
Dronedarone is well absorbed after oral administration (>70%). It displays low systemic bioavailability due to extensive first-pass metabolism. The absolute bioavailability of dronedarone without and with a high-fat meal is 4% and 15%, respectively. The peak plasma concentrations of dronedarone and its main circulating N-debutyl metabolite are reached within 3 to 6 hours after administration with food.
Following repeated administration of 400 mg dronedarone twice daily, the steady-state was reached within 4 to 8 days of initial treatment. The steady-state Cmax and systemic exposure to the N-debutyl metabolite are similar to that of the parent compound.
Toxicity
In an acute toxicity study, the oral LD50 in rat was >2,000 mg/kg.
In oral studies, dronedarone showed a limited potential for toxicity in humans in acute overdose situations. However, it is recommended that the patient's cardiac rhythm and blood pressure is monitored in the event of overdose. Symptomatic and supportive treatments should be initiated.
Description
AF is the most common form of sustained cardiac arrhythmia, with
an increasing prevalence in the aging population. AF accounts for
34.5% of arrhythmia-related hospital admissions in the United States.
The most significant consequences of AF include congestive heart failure, a 5-fold increased risk of stroke, and increased rate of mortality.
Although a 90% conversion rate from AF to normal sinus rhythm (NSR)
can be achieved with electrical cardioversion, up to 70% of these
patients require additional therapy with antiarrhythmic drugs in order
to maintain NSR.
Dronedarone, a close
analog of amiodarone, is structurally modified to provide improved
safety and pharmacokinetic profile. With the introduction of a sulfonamide group, dronedarone is less lipophilic, has lower tissue accumulation, and has a much shorter serum half-life (~24 h) compared with
amiodarone. Additionally, dronedarone lacks the iodine moieties that
are responsible for thyroid dysfunctions associated with amiodarone.
Dronedarone is specifically indicated to reduce the risk of cardiovascular hospitalization in patients with paroxysmal or persistent AF or AFL,
with a recent episode of AF/AFL and associated cardiovascular risk
factors, who are in sinus rhythm or who will be cardioverted. Similar to
amiodarone, dronedarone is a potent blocker of multiple ion currents
(including the rapidly activating delayed-rectifier potassium current,
the slowly activating delayed-rectifier potassium current, the inward rectifier potassium current, the acetylcholine-activated potassium current, peak sodium current, and L-type calcium current) and exhibits
antiadrenergic effects. Overall, dronedarone was well tolerated. The
most common side effects were gastrointestinal in nature and
included nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
Originator
Sanofi-Aventis (US)
The Uses of Dronedarone
Dronedarone-d9 is an isotopic labeled form of Dronedarone(D679445). Dronedarone is a drug used for the treatment of atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter in patients who have suffered cardiac arrhythmias.
Background
Dronedarone is a Class III antiarrhythmic drug that works to restore the normal sinus rhythm in patients with paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation. Atrial fibrillation is a common sustained arrhythmia where the treatment primarily focuses on stroke prevention and symptom management. It is managed by rate control, rhythm control, prevention of thromboembolic events, and treatment of the underlying disease. Similar to amiodarone, dronedarone is a multichannel blocker that works to control rhythm and rate in atrial fibrillation. It meets criteria of all four Vaughan Williams antiarrhythmic drug classes by blocking sodium, potassium, and calcium ion channels and inhibiting β-adrenergic receptors.
Dronedarone is a related benzofuran compound to amiodarone but its chemical structure lacks iodine moieties which are associated with amiodarone-induced thyroid problems. Additionally, the methyl sulfonyl group in its structure renders dronedarone to be more lipophilic with a shorter half-life than amiodarone. This ultimately leads to reduced tissue accumulation of the drug and decreased risk for organ toxicities, such as thyroid and pulmonary toxicities. Commonly marketed as Multaq?, dronedarone was approved by the FDA in July 2009 and Health Canada in August 2009. A safety concern for the risk of drug-induced hepatocellular injury has been issued following marketing of dronedarone.
Indications
Dronedarone is indicated for the management of atrial fibrillation (AF) in patients in sinus rhythm with a history of paroxysmal or persistent AF to reduce the risk of hospitalization.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of 1-benzofurans used for the treatment of cardiac arrhythmias.
brand name
Multaq
Pharmacokinetics
Dronedarone is an antiarrhythmic agent that restores normal sinus rhythm and reduces heart rate in atrial fibrillation. In another model, it prevents ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation. Dronedarone moderately prolongs the QTc interval by about 10 ms on average. Dronedarone decreases arterial blood pressure and reduces oxygen consumption. It reduces myocardial contractility with no change in left ventricular ejection fraction. Dronedarone vasodilates coronary arteries through activation of the nitric oxide pathway. In clinical studies, dronedarone reduced incidence of hospitalizations for acute coronary syndromes and reduced incidence of stroke. Dronedarone exhibits antiadrenergic effects by reducing alpha-adrenergic blood pressure response to epinephrine and beta 1 and beta 2 responses to isoproterenol.
Dronedarone was shown to inhibit triiodothyronine (T3) signalling by binding to TRα1 but much less so to TRβ1. The treatment of dronedarone in patients with severe heart failure and left ventricular systolic dysfunction was associated with increased early mortality related to the worsening of heart failure. In animal studies, the use of dronedarone at doses equivalent to the recommended human doses was associated with fetal harm. In clinical studies and postmarketing reports, dronedarone was shown to cause hepatocellular liver injury and pulmonary toxicities, such as interstitial lung disease, pneumonitis, and pulmonary fibrosis. Compared to its related compound amiodarone, dronedarone has a faster onset and offset of actions with a shorter elimination half-life and low tissue accumulation.
Clinical Use
Anti-arrhythmic:
Maintenance of sinus rhythm after successful
cardioversion in adult clinically stable patients with
paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Anti-arrhythmics: increased risk of myocardial
depression with other anti-arrhythmics; increased
risk of ventricular arrhythmias with amiodarone or
disopyramide - avoid.
Antibacterials: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with clarithromycin, telithromycin and
erythromycin; concentration reduced by rifampicin
- avoid
Anticoagulants: increased anti-coagulant effect with
coumarins and phenindione; increased dabigatran
concentration - avoid; avoid with rivaroxaban;
concentration of edoxaban increased - reduce dose
of edoxaban.
Antidepressants: concentration possibly reduced by
St John’s wort - avoid; increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with tricyclic antidepressants,
citalopram and escitalopram - avoid.
Antiepileptics: concentration possibly reduced
by fosphenytoin, phenytoin, carbamazepine,
phenobarbital and primidone - avoid.
Antifungals: concentration increased by ketoconazole
- avoid; avoid with itraconazole, posaconazole and
voriconazole.
Antipsychotics: increased risk of ventricular
arrhythmias with antipsychotics that prolong the QT
interval; increased risk of ventricular arrhythmias
with phenothiazines - avoid.
Antivirals: avoid with ritonavir; increased risk of
ventricular arrhythmias with saquinavir - avoid.
Beta-blockers: increased risk of myocardial
depression; concentration of metoprolol and
propranolol possibly increased; increased risk of
ventricular arrhythmias with sotalol - avoid.
Calcium channel blockers: concentration increased
by nifedipine; increased risk of bradycardia and
myocardial depression with diltiazem and verapamil.
Cytotoxics: possibly increases bosutinib
concentration - avoid or consider reducing bosutinib
dose; possibly increases ibrutinib concentration -
reduce ibrutinib dose
Digoxin: increased concentration (halve digoxin
maintenance dose).
Fingolimod: possibly increased risk of bradycardia.
Grapefruit juice: concentration of dronedarone
increased - avoid.
Lipid-lowering drugs: concentration of atorvastatin
and rosuvastatin possibly increased; increased risk of myopathy with simvastatin; concentration of
lomitapide possibly increased - avoid.
Tacrolimus: manufacturer advises use with caution.
Metabolism
Dronedarone predominantly undergoes CYP3A-mediated hepatic metabolism. Initial metabolism of dronedarone involves N-debutylation to form the N-debutyl-dronedarone, which retains 1/10 to 1/3 of pharmacological activity of the parent compound. N-debutyl-dronedarone can be further metabolized to phenol-dronedarone via O-dealkylation and propanoic acid-dronedarone via oxidative deamination. Dronedarone can also be metabolized by CYP2D6 to form benzofuran-hydroxyl-dronedarone. Other detectable metabolites include C-dealkyl-dronedarone and dibutylamine-hydroxyl-dronedarone, along with other minor downstream metabolites with undetermined chemical structures.
Metabolism
Dronedarone is extensively metabolised in the liver,
mainly by the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4 to
a less active N-debutyl metabolite, and several inactive
metabolites
About 6% of an oral dose is excreted in the urine (entirely
metabolites) and 84% in the faeces (metabolites and
unchanged drug).
Properties of Dronedarone
| Melting point: | 65.3° |
| Boiling point: | 683.9±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.143±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ≥27.84 mg/mL in DMSO; insoluble in H2O; ≥49.8 mg/mL in EtOH |
| form | solid |
| pka | 7.40±0.30(Predicted) |
| color | White to off-white |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 141626-36-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Dronedarone
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H332:Acute toxicity,inhalation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Dronedarone
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Dronedarone 98%View Details
Dronedarone 98%View Details -
 141626-36-0 98%View Details
141626-36-0 98%View Details
141626-36-0 -
 Dronedarone 98%View Details
Dronedarone 98%View Details
141626-36-0 -
 Dronedarone 141626-36-0 98%View Details
Dronedarone 141626-36-0 98%View Details
141626-36-0 -
 Dronedarone 141626-36-0 99%View Details
Dronedarone 141626-36-0 99%View Details
141626-36-0 -
 Dronedarone CAS 141626-36-0View Details
Dronedarone CAS 141626-36-0View Details
141626-36-0 -
 Dronedarone 95% CAS 141626-36-0View Details
Dronedarone 95% CAS 141626-36-0View Details
141626-36-0 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
