Cynarin
Synonym(s):Cynarin;1,3-Dicaffeoylquinic acid;1,5-Dicaffeoylquinic acid;Cynarine;1,5-DQA
- CAS NO.:30964-13-7
- Empirical Formula: C25H24O12
- Molecular Weight: 516.45
- MDL number: MFCD00867168
- EINECS: 214-655-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-28 13:16:12
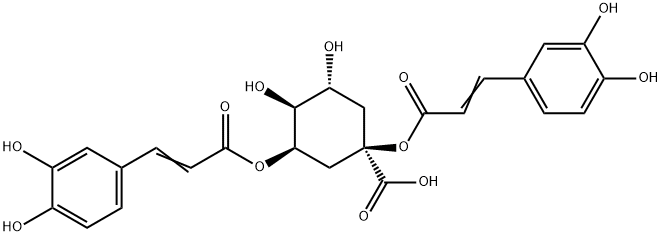
What is Cynarin?
Description
1,3-Dicaffeoylquinic acid is a polyphenol that has been found in C. scolymus. It decreases the expression and protein levels of inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) when used at a concentration of 10 μM in human coronary artery smooth muscle cells (HCASMCs) treated with a cytokine mixture. 1,3-Dicaffeoylquinic acid decreases protein levels of tyrosinase and microphthalmia-associated transcription factor (MITF) in B16F1 murine melanocytes. It inhibits melanogenesis in B16F1 cells and decreases tyrosinase activity in cell lysates when used at a concentration of 25 μM. 1,3-Dicaffeoylquinic acid (20 and 40 μM) reduces triglyceride levels in sodium oleate-induced hyperlipidemic HepG2 cells compared to hyperlipidemic control cells.
Originator
Anghirol,Biofarm
The Uses of Cynarin
Cynarin is used on MDR cells in anti-cancer therapy as an inhibitor of P-glycoprotein-mediated transport.
Definition
ChEBI: 1,3-dicaffeoylquinic acid is an alkyl caffeate ester obtained by the formal condensation of hydroxy groups at positions 1 and 3 of ()-quinic acid with two molecules of trans-caffeic acid. It has a role as a plant metabolite. It is a quinic acid and an alkyl caffeate ester. It is functionally related to a trans-caffeic acid and a (-)-quinic acid. It is a conjugate acid of a 1,3-dicaffeoylquinate.
Manufacturing Process
18.0 g of caffeic acid, suspended in 500 ml of water, are dissolved by adding sodium bicarbonate and stirring. The solution is cooled to 2°-3°C and then,
while stirring continuously, 20.0 g of phosgene dissolved in 200 ml of
chloroform are added in 4 to 5 portions. After acidifying by cautiously adding
iced hydrochloric acid (1:1), the solution is filtered and the collected
precipitate is washed with water. Upon crystallization from glacial acetic acid,
the carbonylcaffeic acid thus obtained melts at 238°-240°C (dec.).
5.0 g of carbonylcaffeic acid are suspended in 70 ml of ligroin (b. p. 120°-
140°C). After adding 6.0 g of phosphorus pentachloride and avoiding access
of moisture while frequently stirring, the suspension is refluxed by boiling
slowly and gently until everything is dissolved except a small amount of
reddish, resinous materials that adhere to the bottom. Then solution is rapidly
decanted into another flask containing 1.0 g of phosphorus pentachloride and
the whole is refluxed gently for about 15-30 min, after which time evolution of
hydrochloric acid ceases. This solution is left to cool on air for 1-2 h, and
then, the obtained carbonylcaffeic acid chloride rapidly is filtered, washed with
low-boiling ligroin and dried under vacuum at room temperature for about 1-
1.5 h. Melting point 118°-120°C.
5.0 g of carbonylcaffeic acid chloride are thoroughly mixed with 12.8 g of dry,
powdered quinide in a flask immersed in an oil bath. The flask is put under
vacuum and is heated to 120°C and then, slowly, to about 160°C, maintaining
this temperature for about 20-30 min. The molten mass is left to cool under
vacuum and then it is crushed in a mortar in the presence of water. This
material is washed with water several times. The residue is dissolved in
dioxin. 400 ml of cold, 3% barium hydroxide solution are added and cooled
with ice water and stirring vigorously in nitrogen atmosphere. The solution is
left standing insulated from contact with air for 20 h, whereupon the content
is rapidly acidified and concentrated in vacuum, on a water bath, to a volume
of about 80-100 ml. After cooling and standing, well protected from contact
with air, the brown material is filtered off and purified by crystallization from
50% acetic acid. 1,4-Dicaffeylquinic acid is obtained, melting point 226°-
228°C.
Therapeutic Function
Choleretic, Antihyperlipidemic
Properties of Cynarin
| Melting point: | 225-227° |
| alpha | D25 -59° (c = 2 in methanol) |
| Boiling point: | 819.9±65.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1?+-.0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| solubility | methanol: soluble5mg/mL, clear, light yellow to yellow |
| form | neat |
| pka | 2.58±0.50(Predicted) |
| form | Solid |
| color | faint yellow to yellow |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 30964-13-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Cynarin
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Cynarin
New Products
4-Fluorophenylacetic acid 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate (6-METHYL-[1,3]DITHIOLO[4,5-b]QUINOXALIN-2-ONE INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Cynarin CAS 30964-13-7View Details
Cynarin CAS 30964-13-7View Details
30964-13-7 -
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1