Cymoxanil
Synonym(s):1-(2-Cyano-2-methoxyiminoacetyl)-3-ethylurea
- CAS NO.:57966-95-7
- Empirical Formula: C7H10N4O3
- Molecular Weight: 198.18
- MDL number: MFCD00137381
- EINECS: 261-043-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-22 20:27:16
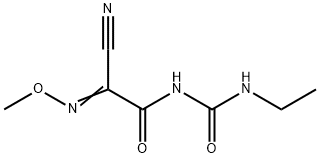
What is Cymoxanil?
Description
Cymoxanil is a cyanoacetamide fungicide. It inhibits the mycelial growth of 12 isolates of P. infestans with EC50 values of 0.27-0.57 μg/ml. Cymoxanil (5-100 mg/l) inhibits the growth of several strains of S. cerevisiae (IC50s = 8-25 mg/l) but not S. pombe, K. marxianus, P. anomala, or C. utilis. A spray application of cymoxanil (1 mg/mL) one day after inoculation of potato leaves with P. infestans and cucumber leaves with P. cubensis reduces blighted leaves by 79 and 60%, respectively. It is toxic to rats with an acute LD50 value of 3.8 mmol/kg. Formulations containing cymoxanil have been used to prevent fungal growth on crops and treat late potato blight in agriculture.
Chemical properties
A white to peach (pale pink) crystalline solid.
The Uses of Cymoxanil
Cymoxanil is a fungicide applied as a seed treatment or as a foliar application to the plants to control late blight.
The Uses of Cymoxanil
Agricultural fungicide.
The Uses of Cymoxanil
Cymoxanil is a foliar applied fungicide which provides preventive and curative control of pathogen species of the order Peronosporales (eg. Phytophthora, Plasmopara and Peronospora) in grapes, potatoes, tomatoes, hops, tobacco and cucurbits.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of ureas that is urea in which the two nitrogen atoms are substituted by an ethyl group and a 2-cyano-2-(methoxyimino)acetyl group respectively. A fungicide used to control Peronosporales on a range of crops including vin s, hops and potatoes.
Agricultural Uses
Fungicide: Cymoxanil is applied as a seed treatment to cut potato seed pieces or as a foliar to control late blight.
Trade name
CURZATE®; DPX 3217®; DPX 3217 M®; DPX-T3217®; EVOLVE®; MZ-CURZATE®; TANOS® Cymoxanil
Contact allergens
Cymoxanil, an urea derivative, is included (10%) with dithianone (25%) in Aktuan?. It is a fungicide agent, possibly sensitizing agricultural workers
Potential Exposure
Cymoxanil is a cyanoacetamide oxime fungicide applied as a seed treatment to cut potato seed pieces or as a foliar to control late blight.
Metabolic pathway
Cymoxanil is rapidly degraded in neutral to alkaline aqueous solutions and is metabolised extensively in soil, plants and animals. Cymoxanil degradation follows a series of cyclisation and /or hydrolysis reactions to form 5- and 6-membered ring compounds and shorter chain keto acids and amides. In plants and animals, cymoxanil is metabolised to form natural products, especially glycine.
Metabolism
Animals
Radiolabeled cymoxanil is metabolized in the goat to
natural products, including fatty acids, glycerol, glycerin,
and other amino acids, lactose, and acid-hydrolysable
formyl and acetyl groups.
Plants
Rapid degradation to naturally occurring amino acids,
particularly to glycine, with subsequent incorporation into
constituent sugars, starch, fatty acids, and lignin (6).
Soil
In laboratory soils, DT50 0.75–1.5 d (5 soils, pH range
5.7–7.8, o.m. 0.8–3.5%). In the field, DT50 (bare soil)
0.9–9 d.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous haz- ardous material, Technical Name Required.
Degradation
The hydrolysis of cymoxanil is pH dependent. It degraded rapidly in
alkaline solution at 25 °C with calculated DT50 values at pH 5,7 and 9, of
148 days, 34 hours and 31 minutes, respectively (PM). The principal
hydrolysis products at pH 9 were 1-ethyldihydro-dimino-2,4,5(3H)-
pyrimidinetrione 5-(O-methyloxime) (2), cyano(methoxyimino)acetic acid
(3) and [[(ethylamino)carbonyl]amino]oxoacetic acid (4). Oxalic(5) and
aminooxoacetic acid (6) were recovered as minor products. The principal
degradation products at pH 7 were compounds 2 and 4. No hydrolytic
products at pH 5 exceeded 10% of the applied radioactivity throughout
the 30-day incubation (Lawler, 1996).
Photolysis of cymoxanil occurred rapidly at pH 5 when irradiated
under a xenon arc light source. The DT50 values of cymoxanil at 25 °C were 1.8 and 148 days, light exposed vs. dark control, respectively. 3-Ethyl-4-
(methoxyamino)-2,5-dioxo-4-imidazolidinecarbonitrile(7) and 1-ethyl-imidazolidinetrione
5-(O-methyloxime) (8) were the major degradation
products. Compounds 2, 4, 6 and ethylimidazolidinetrione (9) were
also present as minor products (Anderson et al., 1993). The hydrolytic
degradation and photolytic degradation pathways of cymoxanil are presented
in Scheme 1.
Environmental considerations
Oral LD50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >2,250 mg/kg. Eight-day dietary LC50 for bobwhite quail and mallard ducks >5,620 mg/kg diet. Fish LC50 (in mg/L at 96 h): rainbow trout 61, bluegill sunfish 29, common carp 91, Zebra fish >47.5 mg/L. Earthworm LC50 (14 d) >2,208 mg/kg soil. Daphnia magna LC50 (48 h) 27 mg/L. Algal growth inhibition LC50 (72 h) 5.2 mg/L. Honeybee contact LD50 >25 μg/bee.
Toxicity evaluation
Rat oral LD50: 960 mg/kg, mouse oral LD50: 860 mg/kg. Rabbit dermal LD50: >2,000 mg/kg. Mild eye irritant to rabbit (clears at 48 h). Mild, transient dermal irritation to rabbit (clears at 48 h). Inhalation LC50 (4 h) for male and female rats >5.06 mg/L. Nononcogenic and nonteratogenic.
Incompatibilities
Slowly hydrolyzes in water, releasing ammonia and forming acetate salts. Light sensitive.
Waste Disposal
Do not discharge into drains or sewers. Burn in incinerator specifically designed for pes- ticide disposal or dispose as a Hazardous waste in a landfill approved and licensed for the disposal of pesticides. Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guid- ance on acceptable disposal practices. Ultimate disposal of the chemical must consider: the material’s impact on air quality; potential migration in soil or water; effects on ani- mal, aquatic, and plant life; and conformance with environ- mental and public health regulations.
Properties of Cymoxanil
| Melting point: | 160-161° |
| Boiling point: | 335.48°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3841 (rough estimate) |
| vapor pressure | 1.5 x 10-4 Pa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.6700 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 100 °C |
| storage temp. | 0-6°C |
| solubility | DMSO: 100 mg/mL (504.59 mM) |
| form | neat |
| Water Solubility | 890 mg l-1 (pH 5), 780 mg l-1 (pH 7),
unstable at pH 9 at 20 °C |
| pka | 9.7 |
| form | Solid |
| color | White to Light yellow to Light orange |
| Merck | 14,2765 |
| BRN | 2214018 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 57966-95-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetamide, 2-cyano-n-[(ethylamino)carbonyl]-2-(methoxyimino)-(57966-95-7) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cymoxanil (57966-95-7) |
Safety information for Cymoxanil
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Cymoxanil
Abamectin manufacturer
India Pesticides Limited
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 57966-95-7 Cymoxanil 99%View Details
57966-95-7 Cymoxanil 99%View Details
57966-95-7 -
 57966-95-7 99%View Details
57966-95-7 99%View Details
57966-95-7 -
 Cymoxanil 99%View Details
Cymoxanil 99%View Details
57966-95-7 -
 Cymoxanil CAS 57966-95-7View Details
Cymoxanil CAS 57966-95-7View Details
57966-95-7 -
 Cymoxanil 98% (HPLC) CAS 57966-95-7View Details
Cymoxanil 98% (HPLC) CAS 57966-95-7View Details
57966-95-7 -
 Cymoxanil CAS 57966-95-7View Details
Cymoxanil CAS 57966-95-7View Details
57966-95-7 -
 Cymoxanil CAS 57966-95-7View Details
Cymoxanil CAS 57966-95-7View Details
57966-95-7 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4