Cupferron
Synonym(s):N-Nitroso-N-phenylhydroxylamine ammonium salt
- CAS NO.:135-20-6
- Empirical Formula: C6H9N3O2
- Molecular Weight: 155.15
- MDL number: MFCD00078422
- EINECS: 205-183-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 10:05:35

What is Cupferron?
Description
Cupferron is a creamy-white crystalline compound. Molecular weight=156.21; Freezing/Melting point=163℃. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704M Rating System): Health 2, Flammability 2, Reactivity 1.Soluble in water
Chemical properties
white to light yellow crystalline powder
Chemical properties
Cupferron is a creamy-white crystalline compound
The Uses of Cupferron
The reagent used to be considered as specific for iron(II) and copper(II). However,
in the course of later analytical studies it turned out that cupferron forms
complexes with several other metals too, even in acidic medium. It is used today
primarily for the determination of copper(II), but it has proved suitable for the
determination of aluminium(III), bismuth(III), iron(III), mercury(II), thorium(IV),
tin(IV), titanium(III), vanadium(IV) and zirconium(IV) as well. Of these, the
zirconium(IV) complex is the most stable. Cupferron precipitates zirconium(IV)
quantitatively from aqueous media containing sulfuric acid.
The reagent gives a precipitate with most of the above metal ions even in strong
mineral acidic medium. Only the aluminium(III) complex does not precipitate in
the presence of mineral acids.
By means of cupferron many metal ions can be separated: thus, for instance,
iron(III) can be separated from aluminium(III) and manganese(II) and titanium
(IV), zirconium(IV) and hafnium(IV) from many other metal ions, etc. Though
the reagent makes possible several separations, the precipitates are not exactly of
stoichiometric composition (they almost always contain some excess of the ligand).
Hence instead of being directly weighed, the precipitates are usually ignited and
the metal oxide residues weighed.
The Uses of Cupferron
As a reagent for separating Sn from Zn, and Cu and Fe from other metals. Ppts iron quantitatively from strongly acid solution; as a quantitative reagent for vanadates with which it gives a dark-red ppt soluble in alkali solution, and for Ti with which it forms a yellow ppt; also suitable for the colorimetric estimation of Al.
The Uses of Cupferron
Cupferron is a reagent for determination of Ce, Cu, Fe, Sn, and Ti.
What are the applications of Application
Cupferron is a reagent for determination of Ce, Cu, Fe, Sn, and Ti
General Description
Light yellow or cream-colored crystals or a brown crystalline solid. As a reagent in the separation of copper and iron.
Air & Water Reactions
Hygroscopic. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Cupferron may be sensitive to prolonged exposure to air. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids and strong bases. Forms unstable solutions with thorium, titanium and zirconium salts.
Fire Hazard
Flash point data for Cupferron are not available; however, Cupferron is probably combustible.
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental carcinogenic and tumorigenic data. Poison by intravenous route. An eye irritant. Solutions with thorium salts are unstable explosives above 15°C. Solutions with titanium or zirconium salts are unstable explosives above 40℃. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic NH3 and NOx. See also N-NITROSO COMPOUNDS and AMINES
Potential Exposure
Cupferron is used to separate tin from zinc, and copper and iron from other metals in the laboratory. Cupferron also finds application as a quantitative reagent for vanadates and titanium; and for the colorimetric determination of aluminum. The potential for exposure appears to be greatest for those engaged in analytical or research studies involving use of the chemical. Workers may also be exposed to the compound during manufacturing processes.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Medical observation is recommended for 24-48 h afterbreathing overexposure, as pulmonary edema may bedelayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor orauthorized paramedic may consider administering a corticosteroid spray.
Carcinogenicity
Cupferron is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Storage
Color Code—Green: General storage may be used.Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Store in a securepoison location. Prior to working with cupferron you shouldbe trained on its proper handling and storage. A regulated,marked area should be established where this chemical ishandled, used, or stored in compliance with OSHAStandard 1910.1045. Cupferron should be stored in a refrigerator or in a cool dry place and protected from exposure tomoisture.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Recrystallise it twice from EtOH after treatment with Norite and finally once with EtOH. The crystals are washed with diethyl ether and air dried, then stored in the dark over solid ammonium carbonate. A standard solution (ca 0.05M prepared in air-free H2O) is prepared daily from this material for analytical work and is essentially 100% pure. [Olsen & Elving Anal Chem 26 1747 1954.] It can also be washed with Et2O, dried and stored as stated. In a sealed, dark container it can be stored for at least 12 months without deterioration. 260nm (CHCl3). max [Marvel Org Synth Coll Vol I 177 1941, Elving & Olson J Am Chem Soc 78 4206 1956, Beilstein 16 IV 891.] Possible CARCINOGEN.
Incompatibilities
Forms unstable and possibly explosive compounds with thorium salts; titanium, zirconium.
Properties of Cupferron
| Melting point: | 150-155 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 278.95°C (rough estimate) |
| Density | 1.3092 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.6500 (estimate) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | well soluble in water and ethanol. |
| form | Powder |
| color | Needles from water |
| Water Solubility | <0.1 g/100 mL at 18.5 ºC |
| Merck | 14,2622 |
| BRN | 3919107 |
| Stability: | Stable, but may be moisture sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong bases, strong acids. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 135-20-6(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 127) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Cupferron(135-20-6) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Cupferron (135-20-6) |
Safety information for Cupferron
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Cupferron
| InChIKey | GDEBSAWXIHEMNF-UHFFFAOYSA-O |
Cupferron manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
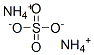
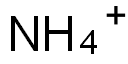

You may like
-
 Cupferron 98%View Details
Cupferron 98%View Details
135-20-6 -
 Cupferron 135-20-6 98%View Details
Cupferron 135-20-6 98%View Details
135-20-6 -
 135-20-6 99%View Details
135-20-6 99%View Details
135-20-6 -
 Cupferron CAS 135-20-6View Details
Cupferron CAS 135-20-6View Details
135-20-6 -
 N-Nitroso-N-phenylhydroxyamine ammonium salt 98.00% CAS 135-20-6View Details
N-Nitroso-N-phenylhydroxyamine ammonium salt 98.00% CAS 135-20-6View Details
135-20-6 -
 CUPFERRON AR CAS 135-20-6View Details
CUPFERRON AR CAS 135-20-6View Details
135-20-6 -
 Cupferron CAS 135-20-6View Details
Cupferron CAS 135-20-6View Details
135-20-6 -
 CupferronView Details
CupferronView Details
135-20-6
