Copper(I) Cyanide
Synonym(s):Copper(I) cyanide;Cupricin;Cuprous cyanide
- CAS NO.:544-92-3
- Empirical Formula: CCuN
- Molecular Weight: 89.56
- MDL number: MFCD00010975
- EINECS: 208-883-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-10 11:56:18
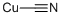
What is Copper(I) Cyanide?
Description
off-white to green powder. Insoluble in water,soluble in HCI, Nl40H, and potassium cyanide. Used in Sandmeyer's reaction to synthesize aryl cyanides. Toxic by skin absorption, through open wounds, by ingestion, and by inhalation of hydrogen cyanide that arises from slight decomposition. Produces toxic oxides of nitrogen in fires.
Chemical properties
Cuprous cyanide is a white crystalline substance.
Physical properties
Cream-colored powder or green orthorhombic or red monoclinic crystals; density 2.90 g/cm3; melts at 474°C; decomposes at higher temperatures; practically insoluble in water, ethanol, and cold dilute acids; dissolves in ammonium hydroxide and potassium cyanide solutions.
The Uses of Copper(I) Cyanide
Copper(I) cyanide is commonly used as a polymerization catalyst. The compound is useful in organic synthesis, as a catalyst, reagent in the preparation of nitriles(sandmeyer reaction). It is also used in electroplating copper and iron, silver plating, brass plating, and copper-tin alloy plating. It is used to make phthalocyanine dyes and pigments.
The Uses of Copper(I) Cyanide

A mixture of the SM (150 mg, 0.36 mmol), TBAF (281 mg, 1.08 mmol), and TMSCN (107 mg, 1.08 mmol) in DMF (3 mL) was stirred at 100 C for 1 h. After cooling to RT, the mixture was purified by Prep HPLC (5-95% MeOH/H2O with 0.05% NH4OH) to provide the product as a white solid. [50 mg, 38%]
The Uses of Copper(I) Cyanide
In electroplating Cu or Fe; as insecticide, fungicide; as antifouling agent in marine paints; as polymerization catalyst.
The Uses of Copper(I) Cyanide
Cuprous cyanide is used in electroplating; as an insecticide and fungicide; and as a catalyst for polymerization.
Reactivity Profile
Copper(I) Cyanide is decomposed by acids to give off hydrogen cyanide, a flammable poisonous gas. Tends to explosive instability. Capable of violent oxidation under certain condition: fusion with metal chlorates, perchlorates, nitrates or nitrites can cause explosions [Bretherick, 1979 p. 101]. Reacts with incandescence with magnesium [Mellor, 1940, Vol. 4, 271].
Hazard
Poison.
Health Hazard
Cuprous cyanide is a highly toxic substance. The toxic routes are inhalation of dust, ingestion, and skin contact. Toxicology and LD50 values for this compound are not reported. Because it is slightly soluble in water, its dissociation to cuprous and cyanide ions in the body may not be significant. The role of cyanide ion in the toxicity of cuprous cyanide is not established. The inhalation hazard, however, is attributable to copper. It is a skin irritant.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Toxic hydrogen cyanide gas may form in fires.
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
A poison. Reacts violently with magnesium. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic CNand NOx. See also CYANIDE and COPPER COMPOUNDS.
Potential Exposure
Copper cyanide is used in electroplating copper on iron; and as an insecticide and a catalyst.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least30 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit. Speedin removing material from skin is of extreme importance.Remove and isolate contaminated clothing and shoes at thesite. Keep victim quiet and maintain normal body temperature. Effects may be delayed. Keep victim underobservation.
Storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area away from strong oxidizers.
Shipping
UN1587 Copper cyanide, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials
Purification Methods
Wash the cyanide thoroughly with boiling H2O, then with EtOH. Dry it at 100o to a fine soft powder. It dissolves in excess alkali cyanide solutions to form the very soluble complex ion Cu(CN)43-. [Bassett & Corbett J Chem Soc 125 1660 1924, Barber J Chem Soc 79 1943.]
Incompatibilities
Contact with heat, strong acids (HCl, H2SO4, HNO3) forms deadly hydrogen cyanide gas. May release hydrogen cyanide on contact with moisture. Incompatible with strong oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides, acetylene gas, and chemically active metals, such as potassium, sodium, magnesium, and zinc.
Waste Disposal
Copper-containing soluble wastes can be concentrated through the use of ion exchange, reverse osmosis, or evaporators to the point where copper can be electrolytically removed and sent to a reclaiming firm. If recovery is not feasible, the copper can be precipitated through the use of caustics and the sludge deposited in a chemical waste landfill. Copper-containing wastes can be concentrated to the point where copper can be electrolytically removed and reclaimed. If recovery is not feasible, the copper can be precipitated by alkali; the cyanide destroyed by alkaline oxidation yielding a sludge which can be sent to a chemical waste landfill. In accordance with 40CFR165, follow recommendations for the disposal of pesticides and pesticide containers. Must be disposed properly by following package label directions or by contacting your local or federal environmental control agency, or by contacting your regional EPA office.
Properties of Copper(I) Cyanide
| Melting point: | 474 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | decomposes [STR93] |
| Density | 2.92 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| storage temp. | Poison room |
| solubility | insoluble in H2O, ethanol; soluble in KCN solution |
| appearance | Off-white to pale yellow powder |
| form | Powder |
| color | White-beige to greenish |
| Specific Gravity | 2.92 |
| Water Solubility | Practically insoluble in water and alcohol. Soluble in ammonium hydroxide, aqueous ammonia, pyridine and N-methylpyrrolidone. |
| Sensitive | air sensitive |
| Merck | 14,2661 |
| BRN | 3587244 |
| Solubility Product Constant (Ksp) | pKsp: 19.46 |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 1 mg Cu/m3 (ACGIH). |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with acids, bases, magnesium. Reacts violently with oxidizing agents, nitrates. Reaction with acid releases highly toxic gas (HCN). |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 544-92-3(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Copper(I) cyanide (544-92-3) |
Safety information for Copper(I) Cyanide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P262:Do not get in eyes, on skin, or on clothing. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Copper(I) Cyanide
Copper(I) Cyanide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 544-92-23 Copper Cyanide 99%View Details
544-92-23 Copper Cyanide 99%View Details
544-92-23 -
 Copper(I) cyanide CAS 544-92-3View Details
Copper(I) cyanide CAS 544-92-3View Details
544-92-3 -
 Copper(I) cyanide CAS 544-92-3View Details
Copper(I) cyanide CAS 544-92-3View Details
544-92-3 -
 Copper(I) cyanide CAS 544-92-3View Details
Copper(I) cyanide CAS 544-92-3View Details
544-92-3 -
 Copper Cyanide CASView Details
Copper Cyanide CASView Details -
 Cuprous Cyanide CASView Details
Cuprous Cyanide CASView Details -
 Copper Cyanide CASView Details
Copper Cyanide CASView Details -
 Copper Cyanide CASView Details
Copper Cyanide CASView Details
