Chlorine dioxide
- CAS NO.:10049-04-4
- Empirical Formula: ClO2
- Molecular Weight: 67.45
- MDL number: MFCD01732063
- EINECS: 233-162-8
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:51
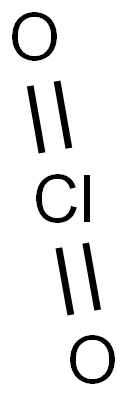
What is Chlorine dioxide ?
Description
Chlorine dioxide is a flammable, reddish-yellow gas or reddish-brown liquid (below 11℃/52°F) with anirritating odor like chlorine or nitric acid. Molecularweight=67.46; Specific gravity (H2O:1)=1.6 (liquid at0℃); Boiling point=11℃; Freezing/Meltingpoint=259℃; Relative vapor density (air=1)=2.3;Vapor pressure=.1 atm at 20℃. Explosive Limits in air:.10%. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA 704 MRating System): Health 3, Flammability 3, Reactivity 3(Shock; Oxidizer). Soluble in water (reactive);solubility=0.3% at 25℃.
Chemical properties
Chlorine dioxide,CI02, is a yellow-reddish gas.It is a very effective bleaching and water treatment agent. Chlorine dioxide is preparedby the reaction of chlorine and sodium chlorite. It is quite unstable and is commonly prepared immediately before use.
Chemical properties
Chlorine dioxide is a flammable, reddishyellow gas, or reddish-brown liquid (below 11C/52F) with an irritating odor like chlorine or nitric acid.
Physical properties
Yellow to red-yellow gas at room temperature; pungent chlorine-like odor; density 9.99 g/L at 11°C; liquefies to a reddish brown liquid at 11°C; liquid density 1.64 g/mL at 0°C; freezes at -59.5° C to red crystals (explodes); soluble in water, decomposes in hot water; soluble in alkalis and H2SO4.
The Uses of Chlorine dioxide
Chlorine Dioxide is a gas used in bleaching and aging flour. it acts on the flour almost instantly, resulting in improved color and dough properties. because usage levels are low, the bleaching action is limited.
The Uses of Chlorine dioxide
Bleaching cellulose, paper-pulp, flour, leather, fats and oils, textiles, beeswax; purification of water; taste and odor control of water; cleaning and detanning leather; manufacture of chlorite salts; oxidizing agent; bactericide, antiseptic and deodorizer.
The Uses of Chlorine dioxide
Chlorine dioxide is used for several purposes,including its applications as a bleachingagent to bleach fats, oils, textiles, cellulose,paper pulp, flour, and leather. It is also usedfor purifying water; as an oxidizing agent;as an antiseptic; and in the manufacture ofmany chlorite salts.
Definition
An orange gas formed by the action of concentrated sulfuric acid on potassium chlorate. It is a powerful oxidizing agent and its explosive properties in the presence of a reducing agent were used to make one of the first matches. It is widely used in the purification of water and as a bleach in the flour and wood-pulp industry. On an industrial scale an aqueous solution of chlorine dioxide is made by passing nitrogen dioxide up a tower packed with a fused mixture of aluminum oxide and clay, down which a solution of sodium chlorate flows.
Definition
chlorine dioxide: A yellowish-redexplosive gas, ClO2; d. 3.09 g dm–3;m.p. –59.5°C; b.p. 9.9°C. It is solublein cold water but decomposed by hotwater to give chloric(VII) acid, chlorine,and oxygen. Because of its highreactivity, chlorine dioxide is bestprepared by the reaction of sodiumchlorate and moist oxalic acid at90°–100°C, as the product is then dilutedby liberated carbon dioxide.Commercially the gas is produced bythe reaction of sulphuric acid containingchloride ions with sulphurdioxide. Chlorine dioxide is widelyused as a bleach in flour milling andin wood pulping and also finds applicationin water purification.
Production Methods
Chlorine dioxide is manufactured from the oxidation of chlorite or the reduction of chlorate. The latter method is used for large-volume production and is carried out in strongly acidic solution using reducing agents such as NaCl, HCl, sulfur dioxide, and methanol.
Preparation
Chlorine dioxide is prepared by passing nitrogen dioxide through sodium chlorate packed in a column:
NaClO3 + NO2 → NaNO3 + ClO2
Also, it may be prepared by the reaction of chlorine with sodium chlorite:
2NaClO2 + Cl2 → 2ClO2 + 2NaCl
Alternatively, it may be obtained by the treatment of sodium chlorate or potassium chlorate with sulfur dioxide and sulfuric acid:
2NaClO3 + SO2 + H2SO4 → 2ClO2 + 2 NaHSO4.
Hazard
Explodes when heated or by reaction with organic materials. Very irritating to skin and mucous membranes. Lower respiratory tract irritant. Broncitis.
Health Hazard
Chlorine dioxide is highly irritating to theeyes, nose, and throat. Inhalation can causecoughing, wheezing, respiratory distress, andcongestion in the lungs. Its toxicity inhumans is moderate to high. Its irritanteffects in humans can be intense at a con centration level of 5 ppm in air. A concen tration of 19 ppm of the gas inside a bleachtank caused the death of one worker (Elkins 1959). The chronic toxicity signs are mainlydyspnea and asthmatic bronchitis, and in cer tain cases irritation of the gastrointestinaltract. Ingestion of the liquid may cause som nolence and respiratory stimulation.
Fire Hazard
Nonflammable gas; however, it is highly reactive and a strong oxidizing agent. Chlo rine dioxide explodes violently upon heating, exposure to sunlight, contact with dust, or when subjected to a spark. Detonation occurs at concentrations above 10% in air in the presence of an energy source or catalyst. It undergoes violent reactions with organic matter; explosion occurs when the mixture is subjected to shock or a spark. It reacts spon taneously with sulfur or phosphorus, caus ing ignition and/or explosion. Liquid chlorine dioxide may explode violently when mixed with mercury, caustic potash, caustic soda, or many metal hydrides. The gas reacts explo sively with fluorine and with difluoroamine (Lawless and Smith 1968).
Flammability and Explosibility
Not classified
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by inhalation. Experimental reproductive effects. Mutation data reported. An eye irritant. A powerful explosive sensitive to spark, impact, sunlight, or heating rapidly to 100℃. A powerful oxidzer. Concentrations of greater than 10% in air are explosive. Explodes on mixing with carbon monoxide, hydrocarbons (e.g., butadiene, ethane, ethylene, methane, propane), fluoramines (e.g., difluoramine, trifluoramine). Mtxtures with hydrogen explode with sparking or contact with platinum. Explodes on contact with mercury, potassium hydroxide, phosphorus pentachloride + chlorine. Ignites or explodes on contact with nonmetals (e.g., phosphorus, sulfur, sugar). Reacts violently with F2, NHF2. Reacts with water or steam to produce toxic and corrosive fumes of HCl. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Cl-. See also CHLORINE.
Potential Exposure
Chlorine dioxide is used in bleaching cellulose pulp; bleaching flour; water purification; as a liquid sterilizer in an ultrasonic cleaner.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Medical observation is recommended for 24-48 h afterbreathing overexposure, as pulmonary edema may bedelayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor orauthorized paramedic may consider administering a corticosteroid spray.
Storage
Color Code—Red Stripe: Flammability Hazard:Store separately from all other flammable materials. Prior toworking with chlorine dioxide you should be trained on itsproper handling and storage. This chemical is a powerful oxidizer, and is shock-, light- and heat-sensitive. It is violentlyexplosive in air at concentrations over 10%. Keep frozenwhen not in use. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool,dark, well-ventilated area at temperatures well below 130℃.Gas explosions may occur above 130℃. Use only nonsparking tools and equipment, especially when opening and closingcontainers of this chemical. Sources of ignition, such assmoking and open flames, are prohibited where this chemicalis used, handled, or stored in a manner that could create apotential fire or explosion hazard. Use explosion-proof electrical equipment and fittings in storage area. See OSHAStandard 1910.104 and NFPA 43A Code for the Storage ofLiquid and Solid Oxidizers for detailed handling and storageregulations.
Shipping
UN/NA 9191 Chlorine dioxide, hydrate, frozen, Hazard class: 5.1; Labels: 5.1-Oxidizer, 6.1-Poison Inhalation. Explosive: It may only be shipped in the frozen state and then only by private or contract motor carrier.
Incompatibilities
Unstable in light. A powerful oxidizer. Chlorine dioxide gas is explosive at concentrations over 10% and can be ignited by almost any form of energy, including sunlight, heat (explosions can occur in air in temperature above 130C), or sparks, shock, friction, or concussion. This chemical reacts violently with dust, combustible materials; and reducing agents. Reacts violently with mercury, phosphorus, sulfur, and many compounds, causing fire and explosion hazard. Contact with water forms perchloric and hydrochloric acid. Corrosive to metals.
Waste Disposal
Use large volume of concentrated solution of ferrous salt or bisulfite solution as reducing agent. Then neutralize and flush to sewer with abundant water.
Properties of Chlorine dioxide
| Melting point: | -59°C |
| Boiling point: | 11°C |
| Density | 3.09g/L |
| vapor pressure | 0-22900Pa at 20-25℃ |
| solubility | slightly soluble in H2O |
| form | orange-green gas |
| color | orange-green |
| Water Solubility | Soluble ºC |
| Dielectric constant | 1.7(77.0℃) |
| Exposure limits | TLV-TWA 0.1 ppm (0.3 mg/m3); (ACGIH,
MSHA, OSHA, and NIOSH); TLV-STEL
0.3 ppm (ACGIH); IDLH 10 ppm (NIOSH). |
| Stability: | May decompose explosively on shock, friction or concussion, or on heating rapidly. Strong oxidant - reacts violently with combustible and reducing materials, and with mercury, ammonia, sulphur and many organic compounds. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 10049-04-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Chlorine dioxide(10049-04-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Chlorine dioxide (10049-04-4) |
Safety information for Chlorine dioxide
Computed Descriptors for Chlorine dioxide
Chlorine dioxide manufacturer
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 10049-04-4 Chlorine dioxide 98%View Details
10049-04-4 Chlorine dioxide 98%View Details
10049-04-4 -
 1 Liter Liquid Chlorine DioxideView Details
1 Liter Liquid Chlorine DioxideView Details
10049-04-4 -
 Chlorine Dioxide For Surface Disinfection, Grade: Food GradeView Details
Chlorine Dioxide For Surface Disinfection, Grade: Food GradeView Details
10049-04-4 -
 Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
Pyridine 99.5% HPLC /UV SpectroscopyView Details
110-86-1 -
 Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
Piperazine Spot supply, best priceView Details
110-85-0 -
 Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
Dibutyl PhthalateView Details
84-74-2 -
 Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
Imidazole Spot supply, competitive priceView Details
288-32-4 -
 Thiourea 99% ARView Details
Thiourea 99% ARView Details
62-56-6
