Clofarabine
Synonym(s):(2R,3R,4S,5R)-5-(6-amino-2-chloropurin-9-yl)-4-fluoro-2-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-3-ol, 2-chloro-2′-arabino-fluoro-2′-deoxyadenosine
- CAS NO.:123318-82-1
- Empirical Formula: C10H11ClFN5O3
- Molecular Weight: 303.68
- MDL number: MFCD00871077
- EINECS: 631-422-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-23 13:58:55
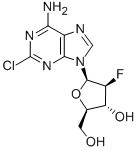
What is Clofarabine?
Toxicity
There were no known overdoses of clofarabine. The highest daily dose administered to a human to date (on a mg/m2 basis) has been 70 mg/m2/day × 5 days (2 pediatric ALL patients). The toxicities included in these 2 patients included grade 4 hyperbilirubinemia, grade 2 and 3 vomiting, and grade 3 maculopapular rash.
Description
Clofarabine is a new member of the purine nucleoside antimetabolite class of drugs, and it was launched as an intravenous infusion for treating pediatric patients (1–21 years old) with relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) after at least two prior regimens. Adenosine-related antimetabolites, such as cladribine and fludarabine have proven successful in treating low-grade lymphomas, chronic lymphocytic leukemia, and hairy-cell leukemia. Although structurally similar to cladribine and fludarabine, a key differentiator for clofarabine is the presence of a fluorine in the C-2′ position, which renders it less susceptible to phosphorolytic cleavage of the glycosydic bond and inactivation by purine nucleoside phosphorylases. In addition, the C-2′ fluoro group improves the acid stability relative to its predecessors. As seen with other purine nucleoside analogs, the mechanism of action of clofarabine involves intracellular phosphorylation to active triphosphate by 2′ -deoxycytidine kinase, and subsequent inhibition of RNA reductase and DNA polymerase a. Clofarabine is cytotoxic to rapidly proliferating and quiescent cancer cell types in vitro.The higher potency of clofarabine relative to other purine nucleoside analogs is attributed to the higher efficiency of its phosphorylation by deoxycytidine kinase, and the longer intracellular half-life of the triphosphate metabolite (>24 h).
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Southern Research Institute (US)
The Uses of Clofarabine
Clofarabine has been used in a cell viability assay to analyze the sensitivity of the isogenic cell lines towards clofarabine. It is also used to study the interaction of anticancer drug clofarabine with human serum albumin and human α-1 acid glycoprotein.
The Uses of Clofarabine
ISecond generation purine nucleoside analog; antimetabolite that inhibits DNA synthesis and resists deamination by adenosine deaminase. Antineoplastic
Indications
For the treatment of pediatric patients 1 to 21 years old with relapsed or refractory acute lymphocytic (lymphoblastic) leukemia after at least two prior regimens. It is designated as an orphan drug by the FDA for this use.
Background
Clofarabine is a purine nucleoside antimetabolite that is being studied in the treatment of cancer. It is marketed as Clolar in the U.S. and Canada, or Evoltra in Europe, Australia, and New Zealand. Clofarabine is used in paediatrics to treat a type of leukaemia called relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL), only after at least two other types of treatment have failed. It is not known if the drug extends life expectancy. Its potential use in acute myeloid leukaemia (AML) and juvenile myelomonocytic leukaemia (JMML) has been investigated.
Definition
ChEBI: A purine nucleoside analogue consisting of a 6-amino-2-chloropurin-9-yl group attached to the 1beta position of 2'-deoxy-2'-fluoro-D-arabinofuranose. It is metabolized intracellularly to the active 5'-triphosphate metaboli e, which inhibits DNA synthesisis and so stops the growth of cancer cells. Clofarabine is used as an antimetabolite antineoplastic agent in the treatment of relapsed or refractory acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.
brand name
Clolar
Biological Activity
Deoxycytidine kinase (dCK) substrate. Phosphorylated to form clofarabine triphosphate, which competes with dATP for DNA polymerase- α and - ε and potently inhibits ribonucleotide reductase (IC 50 = 65 nM). Induces apoptosis by directly altering mitochondrial transmembrane potential. Demonstrates growth inhibition and cytotoxic activity in a variety of leukemias and solid tumors.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Clofarabine is a second-generation nucleoside analog, used in cancer treatments. Clofarabine is metabolized to 5′-triphosphate and is known to block DNA synthesis. The human equilibrative nucleoside transporters (hENT1 and hENT2) and human concentrative nucleoside transporter (hCNT2 and hCNT3) mediates clofarabine transport into the cell. It also serves as a substrate for mitochondrial deoxyguanosine kinase. Clofarabine is an inhibitor of ribonucleotide reductase. It resists the phosphorolytic cleavage catalyzed by purine nucleoside phosphorylase of bacterias. Clofarabine also withstands deamination by adenosine deaminase.
Pharmacokinetics
Clofarabine is a purine nucleoside antimetabolite that differs from other puring nucleoside analogs by the presence of a chlorine in the purine ring and a flourine in the ribose moiety. Clofarabine seems to interfere with the growth of cancer cells, which are eventually destroyed. Since the growth of normal body cells may also be affected by clofarabine, other effects also occur. Clofarabine prevents cells from making DNA and RNA by interfering with the synthesis of nucleic acids, thus stopping the growth of cancer cells.
Synthesis
The drug was discovered by Ilex oncology (now Genzyme) and currently marketed by Genzyme [3,6]. Several routes to the synthesis of clofarabine have been published, including a process scale-up chemistry as shown in the Scheme. Treatment of commercially available 2-deoxy-2-|?-fluoro-1,3,5-tri- O-benzoyl-1-R-D-arabinofuranose (6) with 33%HBr in acetic acid provided the bromo sugar 7 in 88% yield. The bromide 7 was reacted with 2-chloroadenine (8) in optimized mixed solvent system in the presence of calcium hydride and potassium t-butoxide to give the desired |?-anomeric product 9 in 50:1 ratio. Deprotection of the benzoyl groups with sodium methoxide then provided clofarabine (II).

Adverse reactions
Adverse events associated with clofarabine were similar to other chemotherapy agents, including vomiting, nausea, febrile neutropenia, and diarrhea.
Metabolism
Clofarabine is sequentially metabolized intracellularly to the 5’-monophosphate metabolite by deoxycytidine kinase and mono- and di-phosphokinases to the active 5’-triphosphate metabolite. Clofarabine has high affinity for the activating phosphorylating enzyme, deoxycytidine kinase, equal to or greater than that of the natural substrate, deoxycytidine.
Storage
Store at +4°C
Properties of Clofarabine
| Melting point: | 228-2310C |
| Boiling point: | 550.0±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.4804 (estimate) |
| RTECS | UD7473000 |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: >10mg/mL |
| form | Powder |
| pka | 12.56±0.70(Predicted) |
| color | white |
| λmax | 263nm(EtOH)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,2372 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 123318-82-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Clofarabine
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H351:Carcinogenicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Clofarabine
| InChIKey | INHHKRVRRUIAPA-KJHIFWANSA-N |
Clofarabine manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 123318-82-1 99%View Details
123318-82-1 99%View Details
123318-82-1 -
 Clofarabine 98%View Details
Clofarabine 98%View Details
123318-82-1 -
 Clofarabine 123318-82-1 98%View Details
Clofarabine 123318-82-1 98%View Details
123318-82-1 -
 Clofarabine 123318-82-1 98%View Details
Clofarabine 123318-82-1 98%View Details
123318-82-1 -
 Clofarabine CAS 123318-82-1View Details
Clofarabine CAS 123318-82-1View Details
123318-82-1 -
 Clofarabine 95% CAS 123318-82-1View Details
Clofarabine 95% CAS 123318-82-1View Details
123318-82-1 -
 Clofarabine CAS 123318-82-1View Details
Clofarabine CAS 123318-82-1View Details
123318-82-1 -
 Clofarabine Bulk CAS NO.123318-82, CHEMLAND IND, 5View Details
Clofarabine Bulk CAS NO.123318-82, CHEMLAND IND, 5View Details
123318-82-1
