D-METHAMPHETAMINE
Synonym(s):(−)-2-(Methyl-amino)-1-phenylpropane;(−)-Deoxyephedrine;(−)-Methamphetamine;dextro-Methamphetamine
- CAS NO.:537-46-2
- Empirical Formula: C10H15N
- Molecular Weight: 149.24
- MDL number: MFCD00079140
- EINECS: 208-668-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2022-12-21 16:56:50
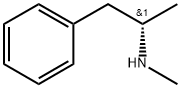
What is D-METHAMPHETAMINE?
Absorption
Methamphetamine is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with peak methamphetamine concentrations occurring in 3.13 to 6.3 hours post ingestion. Moreover, when administered intranasally or as an inhalation, methamphetamine also demonstrates a high degree of absorption. It is distributed to most parts of the body. Because methamphetamine has a high lipophilicity it is distributed across the blood brain barrier and crosses the placenta.
Toxicity
Manifestations of acute overdosage with methamphetamine include restlessness, tremor, hyperreflexia, rapid respiration, confusion, assaultiveness, hallucinations, panic states, hyperpyrexia, and rhabdomyolysis. Fatigue and depression usually follow the central stimulation. Cardiovascular effects include arrhythmias, hypertension or hypotension, and circulatory collapse. Gastrointestinal symptoms include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps. Fatal poisoning usually terminates in convulsions and coma.
Originator
Desoxyn ,Abbott Laboratories
The Uses of D-METHAMPHETAMINE
Nasal decongestant.
Background
Metamfetamine (methamphetamine) is a psychostimulant and sympathomimetic drug, and a member of the amphetamine group of sympathomimetic amines. Methamphetamine can induce effects such as euphoria, increased alertness and energy, and enhanced self-esteem. It is a scheduled drug in most countries due to its high potential for addiction and abuse.
The FDA withdrew its approval for the use of all parenteral drug products containing methamphetamine hydrochloride, a metamfetamine salt.
Indications
For the treatment of Attention Deficit Disorder with Hyperactivity (ADHD) and exogenous obesity.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of amphetamines in which the amino group of (S)-amphetamine carries a methyl substituent.
Manufacturing Process
2 Methods of prepearing of methamphetamine:
1. (-)-Ephedrin was reduced by hydrogenesation with hydrogen in the presence of Pt-C catalyst to give the (+)-N-α-dimethylphenethylamine (methamphetamine), melting point 172°-174°C.
2. Methamphetamine was obtained by the methylation of
phenylisopropylamine.
To give methamphetamine hydrochloride the base methamphetamine was
treated by eqimolar quantity of hydrochloric acid.
brand name
Amone;Desoxyn;Dexophrine;Dexoval;Doxyfed;Doxyn Drinalfa;Efroxine;Euphrodinal;Gardstat;Gerobit;Geronyl;Lemobese;Madrine;Mediatric;Meloda;Metamsustac;Methampex;Methedrinal;Neodrine-triple;Obedrin-la;Obelones;Obe-slim;Pervitin;Phedrisox;Phelantin;Philopon;Soxympamine;Syndrox;Tonedron;Uno.
Therapeutic Function
Sympathomimetic, Central stimulant
World Health Organization (WHO)
Metamfetamine, an amfetamine derivative, is controlled under Schedule II of the 1971 Convention on Psychotropic Substances. See WHO comment for amfetamine. (Reference: (UNCPS2) United Nations Convention on Psychotropic Substances (II), , , 1971)
Pharmacokinetics
Methamphetamine is a potent central nervous system stimulant which affects neurochemical mechanisms responsible for regulating heart rate, body temperature, blood pressure, appetite, attention, mood and responses associated with alertness or alarm conditions. The acute effects of the drug closely resemble the physiological and psychological effects of an epinephrine-provoked fight-or-flight response, including increased heart rate and blood pressure, vasoconstriction (constriction of the arterial walls), bronchodilation, and hyperglycemia (increased blood sugar). Users experience an increase in focus, increased mental alertness, and the elimination of fatigue, as well as a decrease in appetite.
Metabolism
Hepatic. The primary site of metabolism is in the liver by aromatic hydroxylation, N-dealkylation and deamination. At least seven metabolites have been identified in the urine, with the main metabolites being amphetamine (active) and 4-hydroxymethamphetamine. Other minor metabolites include 4-hydroxyamphetamine, norephedrine, and 4-hydroxynorephedrine.
Properties of D-METHAMPHETAMINE
| Melting point: | 143°C (estimate) |
| Boiling point: | 230.33°C (estimate) |
| Density | 0.9285 (estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5105 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| pka | 10.38±0.10(Predicted) |
Safety information for D-METHAMPHETAMINE
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P311:Call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. |
Computed Descriptors for D-METHAMPHETAMINE
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid Tropic acid 1-Bromo-3,5-Di-Tert-Butylbenzene S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID 98%View Details
42831-50-5 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1