Ursodeoxycholic acid
Synonym(s):3α,7β-Dihydroxy-5β-cholan-24-oic acid;5β-Cholan-24-oic acid-3α,7β-diol;7β-Hydroxylithocholic acid;UDCS;Ursodeoxycholic acid
- CAS NO.:128-13-2
- Empirical Formula: C24H40O4
- Molecular Weight: 392.57
- MDL number: MFCD00003680
- EINECS: 204-879-3
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-12-12 15:32:36
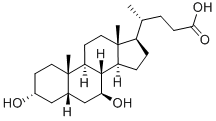
What is Ursodeoxycholic acid?
Absorption
Normally, endogenous ursodeoxycholic acid constitutes a minor fraction (about 5%) of the total human bile acid pool. Following oral administration, the majority of ursodiol is absorbed by passive diffusion, and its absorption is incomplete. Once absorbed, ursodiol undergoes hepatic extraction to about 50% in the absence of liver disease. As the severity of liver disease increases, the extent of extraction decreases. During chronic administration of ursodiol, it becomes a major biliary and plasma bile acid. At a chronic dose of 13 to 15 mg/kg/day, ursodiol constitutes 30-50% of biliary and plasma bile acids.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 in rats is >4600-5000 mg/kg. It is over 7500 mg/kg for mice.
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is associated with rare hepatotoxicities, such as jaundice, worsening pre-existing liver diseases, and hepatitis. There have been no reports of accidental or intentional overdosage with UDCA. A single oral dose of UDCA at 1.5 g/kg was lethal in hamsters. Single oral doses of UDCA at 10 g/kg in mice and dogs and 5 g/kg in rats were not lethal. Symptoms of acute toxicity were salivation and vomiting in dogs, while ataxia, dyspnea, ptosis, agonal convulsions and coma were observed in hamsters.
Description
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is a secondary bile acid, which means that it is a bacterial metabolite of primary bile acids produced in the liver. It is a C7 epimer of chenodeoxycholic acid, one of the two primary human bile acids. M. Shoda, a Japanese researcher, first isolated UDCA from bear bile in 1927. (UDCA takes its name from ursus, the Latin word for bear.) Two years later, K. Kaziro, also in Japan, determined its structure.
Chemical properties
WHITE CRYSTALLINE POWDER
Originator
Actigall,Novartis
The Uses of Ursodeoxycholic acid
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCS) is a cell protectant used extensively to mitigate hepatic and biliary diseases. Ursodeoxycholic acid may be used to study its specific activities that range from reduction of cholesterol absorpition, cholesterol gallstone dissolution to suppression of immune response. It is also used as an anticholelithogenic. Epimer with Chenodiol with respect to the hydroxyl group at C7.
Background
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA), also known as ursodiol, is a naturally-occurring bile acid that constitutes a minor fraction of the human bile acid pool. UDCA has been used to treat liver disease for decades: its first use in traditional medicine dates back more than a hundred years. UDCA was first characterized in the bile of the Chinese black bear and is formed by 7b-epimerization of chenodeoxycholic acid, which is a primary bile acid. Due to its hydrophilicity, UDCA is less toxic than cholic acid or chenodeoxycholic acid.
UDCA was first approved by the FDA in 1987 for dissolution of gallstones and for primary biliary cirrhosis in 1996. UDCA works by replacing the hydrophobic or more toxic bile acids from the bile acid pool.
Indications
Ursodeoxycholic acid is indicated for the treatment of patients with primary biliary cholangitis.
It is used for the short-term treatment of radiolucent, noncalcified gallbladder stones in patients selected for elective cholecystectomy. It is also used to prevent gallstone formation in obese patients experiencing rapid weight loss.
Definition
ChEBI: Ursodeoxycholic acid is a bile acid found in the bile of bears (Ursidae) as a conjugate with taurine. Used therapeutically, it prevents the synthesis and absorption of cholesterol and can lead to the dissolution of gallstones. It has a role as a human metabolite and a mouse metabolite. It is a bile acid, a dihydroxy-5beta-cholanic acid and a C24-steroid. It is a conjugate acid of an ursodeoxycholate.
Manufacturing Process
Chenodeoxycholanic acid was dissolved in acetic acid and to this solution
aqueous solution of CrO3 was added. As a result 3,7-diketodeoxycholanic acid
was obtained, yield 95%, melting point 145°C.
15.0 g of 3,7-diketodeoxycholanic acid were dissolved in 80 ml of toluene,
then petroleum ether 30 ml were added. 3,7-Diketodeoxycholanic acid as an
oil precipitate was obtained, melting point 152°-154°C.
10.0 g of 3,7-diketodeoxycholanic acid were dissolved in 300 ml butanol,
heated to 120°-130°C on bath and then sodium metallic 13.0 g were added.
After that to this mixture hydrochloric acid was added for neutralization.
Ursodeoxychlolanic acid was obtained, yield 9.4 g, melting point 193°C
(recrystallization from ethyl acetate).
brand name
Actigall (Watson); Urso (Axcan Scandipharm).
Therapeutic Function
Gallostone dissolving agent, Hepatoprotectant
General Description
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is a secondary bile acid that helps regulate cholesterol. Mass spectrometry-based analysis of UDCA is routinely performed in clinical diagnostic testing applications such as neonatal testing of inborn errors of bile acid synthesis, differentiating among types of familial intrahepatic cholestasis, and therapeutic monitoring of patient responses to UDCA therapy. This Certified Spiking Solution? is suitable as a starting material in preparation of linearity standards, calibrators, and controls for use in LC-MS/MS and GC/MS bile acid testing methods.
Pharmacokinetics
Ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) is a secondary bile acid with cytoprotectant, immunomodulating, and choleretic effects. It reduces the cholesterol fraction of biliary lipids.
UDCA inhibits the absorption of cholesterol in the intestine and the secretion of cholesterol into bile, decreasing biliary cholesterol saturation. UDCA increases bile acid flow and promotes the secretion of bile acids.
Clinical Use
Dissolution of gallstones
Ursodeoxycholic acid or ursodiol is a naturally occurring bile acid that is used dissolve cholesterol gall stones and to treat cholestatic forms of liver diseases including primary biliary cirrhosis.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Ciclosporin: unpredictably increases the absorption
of ciclosporin in some patients.
Metabolism
Upon administration, ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) enters the portal vein and into the liver, where it undergoes conjugation with glycine or taurine. UDCA is also decreased into bile. Glycine or taurine conjugates are absorbed in the small intestine via passive and active mechanisms. The conjugates can also be deconjugated in the ileum by intestinal enzymes, leading to the formation of free UDCA that can be reabsorbed and re-conjugated in the liver.
Nonabsorbed UDCA passes into the colon, where it undergoes 7-dehydroxylation by intestinal bacteria to lithocholic acid. Some UDCA is epimerized to chenodeoxycholic acid via a 7-oxo intermediate. Chenodeoxycholic acid also undergoes 7-dehydroxylation to form lithocholic acid. These metabolites are poorly soluble and excreted in the feces. A small portion of lithocholic acid is reabsorbed, conjugated in the liver with glycine or taurine, and sulfated at the 3 position. The resulting sulfated lithocholic acid conjugates are excreted in bile and then lost in feces.
Metabolism
Ursodeoxycholic acid is absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and undergoes enterohepatic recycling. It is partly conjugated in the liver before being excreted into the bile. Under the influence of intestinal bacteria the free and conjugated forms undergo 7α-dehydroxylation to lithocholic acid, some of which is excreted directly in the faeces and the rest absorbed and mainly conjugated and sulphated by the liver before excretion in the faeces.
storage
+4°C
Purification Methods
Recrystallise ursodiol from wet Et2O, EtOH or EtOH/MeOH. [Iwasaki Hoppe Seyler's Z Physiol Chem 244 181, 183 1936, Beilstein 10 III 1635.]
Properties of Ursodeoxycholic acid
| Melting point: | 203-204 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 437.26°C (rough estimate) |
| alpha | 60 º (c=2, EtOH) |
| Density | 0.9985 (rough estimate) |
| refractive index | 60.5 ° (C=2, EtOH) |
| Flash point: | 9℃ |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | ethanol: 50 mg/mL, clear |
| form | Solid. Powder. |
| appearance | white crystals or powder |
| pka | pKa 5.04±0.04(H2O
t = 25.0±0.1
I = 0.00)(Approximate) |
| color | White - almost white. |
| Water Solubility | practically insoluble |
| Merck | 14,9889 |
| BRN | 3219888 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 128-13-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Ursodeoxycholic acid
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P332+P313:IF SKIN irritation occurs: Get medical advice/attention. P337+P313:IF eye irritation persists: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Ursodeoxycholic acid
| InChIKey | RUDATBOHQWOJDD-UZVSRGJWSA-N |
Ursodeoxycholic acid manufacturer
Honour Lab Limited
Shilpa Medicare Limited (SML)
IOL Chemicals And Pharmaceuticals Limited
Raichem Medicare
New Products
(S)-3-Aminobutanenitrile hydrochloride 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid S-2-CHLORO PROPIONIC ACID ETHYL ISOCYANOACETATE 2-Bromo-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 4-IODO BENZOIC ACID 3-NITRO-2-METHYL ANILINE 1-(2,4-DICHLOROPHENYL) ETHANAMINE (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![(2S)-2-[[[(1,1-Dimethylethyl)diphenylsilyl]oxy]methyl]-1,3-oxathiolan-5-ol 5-Acetate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/20180601/GIF/202532-88-5.gif)
You may like
-
 UDCA 99%View Details
UDCA 99%View Details -
 Ursodeoxycholic acid 98%View Details
Ursodeoxycholic acid 98%View Details
128-13-2 -
 Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCS) extrapure CAS 128-13-2View Details
Ursodeoxycholic Acid (UDCS) extrapure CAS 128-13-2View Details
128-13-2 -
 Ursodeoxycholic acid 98% CAS 128-13-2View Details
Ursodeoxycholic acid 98% CAS 128-13-2View Details
128-13-2 -
 Ursodeoxycholic Acid CAS 128-13-2View Details
Ursodeoxycholic Acid CAS 128-13-2View Details
128-13-2 -
 Ursodeoxycholic Acid CAS 128-13-2View Details
Ursodeoxycholic Acid CAS 128-13-2View Details
128-13-2 -
 Ursodeoxycholic acid 99% CAS 128-13-2View Details
Ursodeoxycholic acid 99% CAS 128-13-2View Details
128-13-2 -
 Ursodiol CAS 128-13-2View Details
Ursodiol CAS 128-13-2View Details
128-13-2