Lithium nitrate
Synonym(s):Lithium nitrate
- CAS NO.:7790-69-4
- Empirical Formula: LiNO3
- Molecular Weight: 68.95
- MDL number: MFCD00011094
- EINECS: 232-218-9
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
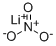
What is Lithium nitrate?
Description
Lithium nitrate is a colorless deliquescentpowder. Specific gravity (H2O:1)=2.38; Freezing/Meltingpoint = 264℃. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704M Rating System): Health 2, Flammability 1, Reactivity 2(Oxidizer). Soluble in water.
Chemical properties
Lithium nitrate is a colorless deliquescent powder, enthalpy of fusion 24.90 kJ/mol; can be prepared by reaction of HNO3 with LiOH or Li2CO3, followed by evaporation to dryness and then heating at ~200°C in vacuum; used in ceramics, pyrotechnics, molten salt baths, rocket propellants, refrigerators. [HAW93] [CRC10] [MER06] [KIR81] [FMC93]
The Uses of Lithium nitrate
Lithium nitrate can be used in special pyrotechnic devices to give a red flame. Lithium nitrate may also be used in combination with other salts, particularly nitrates, to produce low-melting fused salt mixtures.
Used in ceramics, heat-exchange media, refrigeration systems.
The Uses of Lithium nitrate
Lithium nitrate is used in ceramics, pyrotechnics, salt baths, heat-exchange media, refrigeration systems, rocket propellant and in solar batteries. It acts as an oxidizing agent used in the production of red-colored fireworks and flares, as a catalyst to accelerate the breakdown of nitrogen oxides and as a medium to store heat received from sun for cooking. It is applied to concrete-pavement to withstand weathering effects.
Definition
ChEBI: The inorganic nitrate salt of lithium.
Preparation
Lithium nitrate is readily prepared industrially or in the laboratory by the reaction of lithium hydroxide or lithium carbonate with nitric acid. The resulting solution is evaporated and the solid is dried to obtain anhydrous lithium nitrate. Lithium nitrate is very soluble in water. The compound absorbs moisture from the air. Below about 30 °C it crystallizes from solution as lithium nitrate trihydrate; above that temperature the anhydrous material precipitates although the question of the existence of a half-hydrate is not entirely settled.
General Description
A white to light yellow colored crystalline solid. Denser than water. Contact with the material may cause irritation to skin, eyes, and mucous membranes. May be toxic by ingestion. May cause the acceleration of the burning of combustible materials. Prolonged exposure to heat or flames may result in an explosion.
Air & Water Reactions
Deliquescent. Soluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Lithium nitrate is an oxidizing agent. Mixtures with alkyl esters may explode owing to the formation of alkyl nitrates; mixtures with phosphorus, tin(II) chloride, or other reducing agents may react explosively [Bretherick 1979. p. 108-109].
Health Hazard
Inhalation, ingestion or contact (skin, eyes) with vapors or substance may cause severe injury, burns or death. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
These substances will accelerate burning when involved in a fire. Some may decompose explosively when heated or involved in a fire. May explode from heat or contamination. Some will react explosively with hydrocarbons (fuels). May ignite combustibles (wood, paper, oil, clothing, etc.). Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may create fire or explosion hazard.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Potential Exposure
Lithium nitrate is used in ceramics, pyrotechnics, salt baths; refrigeration systems; and rocket propellants
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.Medical observation is recommended for 24-48 h afterbreathing overexposure, as pulmonary edema may bedelayed. As first aid for pulmonary edema, a doctor orauthorized paramedic may consider administering a corticosteroid spray.
storage
Color Code—Yellow: Reactive Hazard; Store in alocation separate from other materials, especially flammables and combustibles. Prior to working with this chemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Lithium nitrate must be stored to avoid contactwith wood, paper, oil and heat, and oxidizers (such as perchlorates, peroxides, permanganates, chlorates, andnitrates), since violent reactions occur. Protect containersagainst physical damage, heat, shock, sparks. Store intightly closed containers in a cool, well-ventilated area.Sources of ignition, such as smoking and open flames, areprohibited where this chemical is used, handled, or stored ina manner that could create a potential fire or explosion hazard. Wherever this chemical is used, handled, manufactured,or stored, use explosion-proof electrical equipment and fittings. See OSHA Standard 1910.104 and NFPA 43A Codefor the Storage of Liquid and Solid Oxidizers for detailedhandling and storage regulations.
Shipping
UN2722 Lithium nitrate, Hazard Class: 5.1; Labels: 5.1-Oxidizer
Purification Methods
It crystallises from water or EtOH. Dry it at 180o for several days by repeated melting under vacuum. If it is crystallised from water keeping the temperature above 70o, formation of trihydrate is avoided. The anhydrous salt is dried at 120o and stored in a vacuum desiccator over CaSO4. After the 99% pure salt was recrystallised 3times, it contained: metal (ppm) Ca (1.6), K (1.1), Mo (0.4), Na (2.2). [Donnan & Burt J Chem Soc 83 335 1903.]
Incompatibilities
May explode when exposed to sparks, shock and heat. Violent reactions with combustible materials; oxidizers, organic materials; reducing agents; strong acids
Properties of Lithium nitrate
| Melting point: | 264 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 600 °C |
| Density | 2.38 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| RTECS | QU9330000 |
| Flash point: | 600°C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 2.34[at 20 ℃] |
| Specific Gravity | 2.38 |
| color | White |
| PH | 7-9 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 90 g/L (28 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,5536 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 2 ppm; STEL 4 ppm OSHA: TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3) NIOSH: IDLH 25 ppm; TWA 2 ppm(5 mg/m3); STEL 4 ppm(10 mg/m3) |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with reducing agents, strong acids, organic materials, finely powdered metals. Oxidizer. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 7790-69-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Lithium nitrate (7790-69-4) |
Safety information for Lithium nitrate
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Over Circle Oxidizers GHS03  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H272:Oxidising liquids;Oxidising solids H302:Acute toxicity,oral H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Lithium nitrate
Lithium nitrate manufacturer
New Products
4-Piperidinemethanol Ethyl 2,4-Dihydroxy-6-methylnicotinate Ethyl isonicotinate 3-pyridine methanol N-Methyl 4-chloro-pyridine-2-carboxamide 2-Fluoro-6-iodobenzoic acid 2-((2,6-difluorobenzyl)(ethoxycarbonyl)amino)-4-((dimethylamino)methyl)-5-(4-nitrophenyl)thiophene-3-carboxylic acid Ethyl2-oxo-2,3,9,10-tetrahydro-1H-pyrido[3',4':4,5]pyrrolo[1,2,3-de]quinoxaline-8(7H)-carboxylate Elinzanetant tert-butyl 2-(4-amino-6-chloropyrimidin-5-yloxy)ethylmethylcarbamate Phenylazomalononitrile 5,6 Dimethoxy-1-indanone 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole N Ethylmethylamine Ethyl Methanesulfonate N N' DimethylEthylenediamine Lead II Bromide Variamine Blue B Diazonium salt N N N'Trimethyl ethylenediamineRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Lithium nitrate 99%View Details
Lithium nitrate 99%View Details -
 Lithium nitrate, Anhydrous CAS 7790-69-4View Details
Lithium nitrate, Anhydrous CAS 7790-69-4View Details
7790-69-4 -
 Lithium nitrate, Anhydrous CAS 7790-69-4View Details
Lithium nitrate, Anhydrous CAS 7790-69-4View Details
7790-69-4 -
 Lithium nitrate, Anhydrous CAS 7790-69-4View Details
Lithium nitrate, Anhydrous CAS 7790-69-4View Details
7790-69-4 -
 Lithium nitrate, Anhydrous CAS 7790-69-4View Details
Lithium nitrate, Anhydrous CAS 7790-69-4View Details
7790-69-4 -
 Lithium nitrate hydrate CAS 7790-69-4View Details
Lithium nitrate hydrate CAS 7790-69-4View Details
7790-69-4 -
 Lithium nitrate hydrate CAS 7790-69-4View Details
Lithium nitrate hydrate CAS 7790-69-4View Details
7790-69-4 -
 Lithium Standard for ICP CASView Details
Lithium Standard for ICP CASView Details
