Capastat sulfate
Synonym(s):Capreomycin sulfate salt
- CAS NO.:1405-37-4
- Empirical Formula: C24H44N14O12S
- Molecular Weight: 752.76
- MDL number: MFCD00079032
- EINECS: 215-776-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2024-11-20 15:18:15
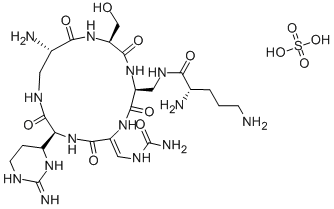
What is Capastat sulfate?
Description
Capreomycin is a polypeptide antibiotic first isolated from S. capreolus. It is cytotoxic to M. tuberculosis (MIC = 10 μg/ml). Capreomycin is more effective against M. tuberculosis when combined with aminoglycoside antibiotics.
Originator
Capastat,Lilly,UK,1966
The Uses of Capastat sulfate
antibacterial, tuberculostatic
The Uses of Capastat sulfate
Capreomycin sulfate is a salt of a complex of cyclic pentopeptides isolated from Streptomyces capreolus, first reported in 1962. The sulfate salt is the most commonly accessible formulation of capreomycin and is used for pharmaceutical applications. The complex has two major components, IA and IB, with an exocyclic lysine residue, and two minor delysinyl components, IIA and IIB. Capreomycin is a potent antibiotic with activity against mycobateria, and Gram positive and negative organisms. Capreomycin acts by binding to the 23S ribosomal subunit, disrupting protein synthesis.
The Uses of Capastat sulfate
Thought to inhibit protein synthesis by inhibiting normal ribosomal functions
What are the applications of Application
Capreomycin sulfate from Streptomyces capreolus is a cyclic peptide antibiotic that is often grouped with aminoglycosides
Manufacturing Process
A culture of NRRL 2773 is produced by growing the organism on a nutrient
agar slant having the following composition:
Oatmeal-Tomato Paste Agar
Tomato paste 20Grams
Precooked oatmeal 20Grams
Agar 15Grams
Tap water, added to make a final volume of 1 liter.
The slant is inoculated with spores of NRRL 2773 and is incubated for 10 days
at about 30°C. The culture growth on the slant is covered with 6 ml of
nutrient broth, and the slant is scraped gently to remove the organisms to
provide an aqueous suspension. Employing aseptic techniques, the inoculum
obtained from one 1-inch agar slant is used to inoculate a 2-liter Erlenmeyer
flask containing a 500-ml portion of a sterilized vegetative culture medium
having the following composition: soluble starch, 10 g; peptones, 5 g; beef
extract, 5 g; sodium chloride, 5 g; yeast extract, 2.5 g; and tap water, 1,100
ml. The incubation is carried on at 28°C for 48 hours with shaking at 250
cycles per minute on a rotary shaker having a 1-inch stroke.
To produce a larger quantity of vegetative inoculum, 500 ml of the vegetative
inoculum is added aseptically to a stainless steel 350-gallon fermentation tank
containing 250 gallons of sterile medium having the following composition
(weight/volume): glucose, 1.5%; yeast, 1.5%; and antifoam (Polyglycol No.
2000, Dow Chemical Co.), 0.02%. The inoculum is allowed to grow for about
22 hours at a temperature of 30°C. Throughout the growth period, the
medium is aerated with sterile air at the rate of 17 cfm and is agitated with
two 16-inch impellers rotating at 160 revolutions per minute. To a 1,700-
gallon stainless steel fermentor are added 1,100 gallons of a medium having
the following composition (weight/volume):
Peptone No. 159 Medium
Glucose 2.5%
Molasses 1.0%
Peptones 4.0%
Calcium carbonate 0.2%
Hydrolyzed casein 0.6%
Antifoam (Polyglycol No. 2000, Dow Chemical Co.) 0.005
The medium after sterilization is inoculated with 100 gallons of the inoculum
grown in the fermentation tank. The fermentation is carried on at 30°C for
about five days. The foam is controlled by the addition, when needed, of
Larex No. 1 (an antifoam product, Swift and Co.). Throughout the
fermentation, the medium is aerated by the addition of sterile air at the rate
of 96 cfm and is agitated with two 22-inch impellers operated at 140
revolutions per minute. At the end of the fermentation, 240 lb of Dicalite 476
(a perlite filter product, Great Lakes Carbon Corporation) are added to 1,000
gallons of the antibiotic broth, and the mixture is stirred and filtered. The filter
cake is washed with tap water and the wash water and the filtrate are
combined to provide a total volume of 1,000 gallons.
To 500 gallons of the combined liquids are added 132 lb of Darco G-60. The
mixture is stirred thoroughly and filtered, and the filtrate is discarded, The
carbon filter cake is washed with 200 liters of tap water, the wash water being
discarded. The washed carbon cake on which the capreomycin is adsorbed is
further washed with 200 liters of 0.05 N aqueous hydrochloric acid. The acid
wash is discarded. The washed carbon cake is eluted during a one-hour period
with 400 liters of an aqueous acetone mixture containing 1.65 liters of 11.7 N
hydrochloric acid and 80 liters of acetone. The filter cake is further eluted by
washing the cake with 200 liters of an aqueous acetone mixture containing
825 ml of 11.7 N hydrochloric acid and 40 liters of acetone during a 15-
minute period. The combined eluates, having a total volume of 575 liters, are
concentrated in vacuo to 52.5 liters.
The concentrate is added with stirring to 525 liters of acetone and the acetone
mixture is permitted to stand overnight at room temperature, during which
time an oily precipitate of capreomycin separates. The supernatant is
decanted and discarded, and the oily precipitate which remains is dissolved in
20 liters of distilled water. The aqueous solution is concentrated in vacuo to 12
liters to remove any residual acetone. The aqueous concentrate containing
capreomycin is filtered to remove a small amount of a precipitate, which is
discarded.
The filtrate containing the capreomycin is added to 240 liters of methanol with
stirring. The methanolic solution of capreomycin is acidified by the addition of
one liter of 10 N sulfuric acid, whereupon the precipitation of the sulfuric acid
addition salt of capreomycin commences. The mixture is permitted to stand
overnight for more complete precipitation. The supernatant is removed by
decanting and filtering. The precipitate, consisting of the capreomycin
disulfate, is washed with 10 liters of methanol and is dried in vacuo. Yield:
2,510 grams.
brand name
Capastat Sulfate (Lilly).
Therapeutic Function
Antitubercular
General Description
Capreomycin was found as an antituberculotic antibiotic by Herr et al. of Eli Lilly & Co. in the culture broth of Streptomyces capreolus NRRL2773 in 1962. It shows no cross-resistance with streptomycin and is used against tuberculosis caused by streptomycinresistant Mycobacterium or for patients with adverse side effects caused by streptomycin.
Properties of Capastat sulfate
| Melting point: | >220oC (dec.) |
| Boiling point: | 1377℃ |
| Flash point: | >110°(230°F) |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | H2O: soluble50mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| color | White to Off-White |
| Water Solubility | Freely soluble in water |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
Safety information for Capastat sulfate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H360:Reproductive toxicity |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Capastat sulfate
| InChIKey | LFFNIXQXRKNZCE-XYHGUWSSSA-N |
Abamectin manufacturer
New Products
4-AMINO-TETRAHYDRO-PYRAN-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID HCL 4-(Dimethylamino)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-4-carbonitrile 4-Aminotetrahydropyran-4-carbonitrile Hydrochloride (R)-3-Aminobutanenitrile Hydrochloride 3-((Dimethylamino)methyl)-5-methylhexan-2-one oxalate 1,4-Dioxa-8-azaspiro[4.5]decane 5-Bromo-2-nitropyridine Nimesulide BP Aceclofenac IP/BP/EP Diclofenac Sodium IP/BP/EP/USP Mefenamic Acid IP/BP/EP/USP Ornidazole IP Diclofenac Potassium THOMAIND PAPER PH 2.0 TO 4.5 1 BOX BUFFER CAPSULE PH 9.2 - 10 CAP SODIUM CHLORIDE 0.1N CVS ALLOXAN MONOHYDRATE 98% PLATINUM 0.5% ON 3 MM ALUMINA PELLETS (TYPE 73) LITHIUM AAS SOLUTION 2-Bromo-1-(bromomethyl)-3-chloro-5-nitrobenzene 2-Bromo-3-nitroaniline N-(3-Hydroxypropyl)-N-methylacetamide 3-Bromo-6-chloropyridazine 4-ethyl-3-nitrobenzoic acidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Capreomycin sulfate from streptomyces capreolus CAS 1405-37-4View Details
Capreomycin sulfate from streptomyces capreolus CAS 1405-37-4View Details
1405-37-4 -
 Capreomycin sulfate CAS 1405-37-4View Details
Capreomycin sulfate CAS 1405-37-4View Details
1405-37-4 -
 1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 98%View Details
1823368-42-8 -
 2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
2-(3-(tert-butyl)phenoxy)-2-methylpropanoic acid 1307449-08-6 98%View Details
1307449-08-6 -
 Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
Ethyl 3-(furan-2-yl)-3-hydroxypropanoate 25408-95-1 98%View Details
25408-95-1 -
 2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
2-Chloro-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-3-methylbenzene 98%View Details
1805639-70-6 -
 1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 98%View Details
1784294-80-9 -
 Lithium ClavulanateView Details
Lithium ClavulanateView Details
61177-44-4