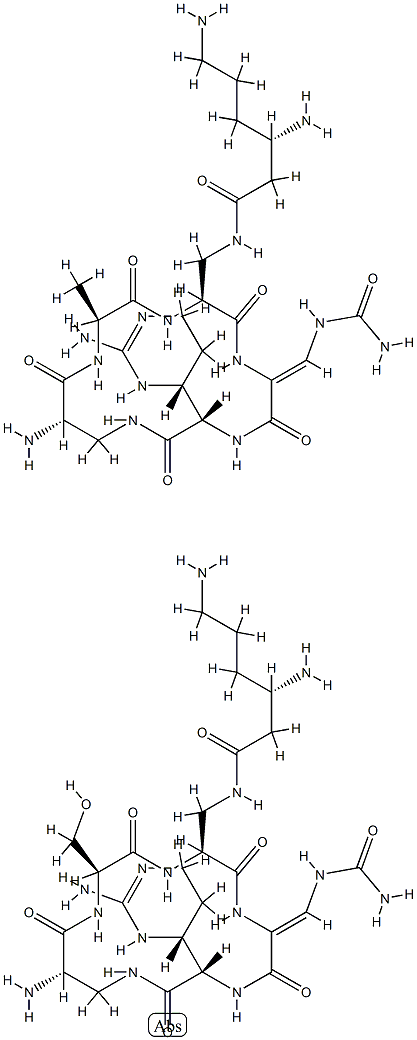
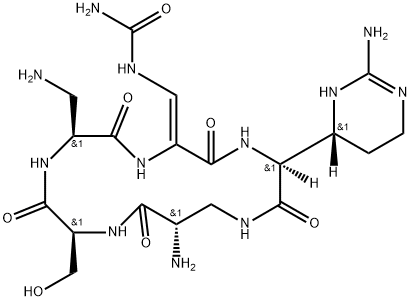
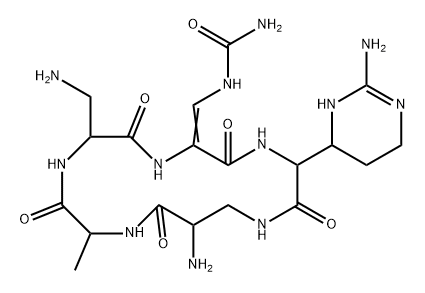
CAPREOMYCIN
- CAS NO.:11003-38-6
- Empirical Formula: C50H88N28O15
- Molecular Weight: 1321.41232
- MDL number: MFCD01770630
- Update Date: 2024-10-28 23:16:16
What is CAPREOMYCIN?
Absorption
Not absorbed in significant quantities from the gastrointestinal tract and must be administered parenterally.
Toxicity
Hypokalemia, hypocalcemia, hypomagnesemia, and an electrolyte disturbance resembling Bartter's syndrome have been reported to occur in patients with capreomycin toxicity. The subcutaneous median lethal dose (LD50) in mice was 514 mg/kg.
Description
Capreomycin is a semisynthetic antibiotic (34.1.21) that is isolated from
the cultural fluid of Streptomyces capreolus, and it is a complex of a minimum of four
microbiologically active ingredients that have only partially been characterized.
Capreomycin has a pronounced suppressive effect against Mycobacterium tuberculosis
and Mycobacterium bovis. Most strains of Mycobacterium kansasii are also sensitive to
kanamycin, while other, nontuberculous strains are not sensitive to it. It is often used upon
necessity of using parenternal therapy through deep intramuscular injections.
Capreomycin is less toxic than kanamycin and has somewhat more of a bacteriostatic
effect. Synonyms of this drug are capromycin, capastat, ogostal, and others.
Originator
Capastat,Dista
The Uses of CAPREOMYCIN
Capreomycin is a complex of cyclic pentopeptides isolated from Streptomyces capreolus, first reported in 1962. The complex has two major components, IA and IB, with an exocyclic lysine residue and two minor delysinyl components, IIA and IIB. Capreomycin is a potent antibiotic with activity against mycobateria, Gram positive and Gram negative organisms. Capreomycin acts by binding to the 23S ribosomal subunit, disrupting protein synthesis.
Background
Cyclic peptide antibiotic similar to viomycin. It is produced by Streptomyces capreolus.
Indications
Used in the treatment of tuberculosis in combination with other drugs.
Indications
Capreomycin (Capastat) is a polypeptide antibiotic derived from Streptomyces capreolus. It is bacteriostatic against most strains of M. tuberculosis, including the MDR strain. In addition, it is active against M. kansasii, M. avium, and in high concentrations, some grampositive and gram-negative bacteria. Like other antitubercular drugs, resistance to capreomycin occurs rapidly if the drug is used alone.There is no cross-resistance between streptomycin and capreomycin, but some isolates resistant to capreomycin are resistant to viomycin.
Manufacturing Process
Preparation of Capreomycin
A culture of NRRL 2773 is produced by growing the organism on a nutrient
agar slant having the following composition: Tomato paste 20 g, Pre-cooked
oatmeal 20 g, Agar 15 g and tap water up to 1 L. The slant is inoculated for
10 days at about 30°C. The culture growth on the slant is covered with 6 ml
of nutrient broth, and the slant is scraped gently to remove the organisms to
provide an aqueous suspension.
Employing aseptic techniques, the inocolum obtained is used to inoculate a 2
L Erlenmeyer flask containing a 500 ml portion of a sterilized vegetative
culture medium having the following composition: Soluble starch 10 g,
Peptones 5 g, Beef extract 5 g, Sodium chloride 5 g, Yeast extract 2.5 g and
tap water 1100 ml.
The incubation is carried out at 28°C for 48 hours; during which time the
flasks are shaken at the rate of 250 cycles per minute on a rotary shaker
having a 1-inch stroke. To produce a larger quantity of vegetative inocolum,
500 ml of the vegetative inocolum is added aseptically to a stainless steel
350-gallon fermentation tank containing 250 gallons of sterile medium having
following composition (weight/volume): Glucose 1.5%, Yeast 1.5%, Antifoam
("Polyglycol No 2000" sold by Dow Chemical Co) 0.02%.
The inoculum is allowed to grow for 22 hours at 30°C. Throughout the growth
period, the medium is aerated with sterile air at the rate of 17 cubic feet per
minute and is agitated with 16-inch impeller rotating at 160 revolution per
minute.
To a 1700-gallon stainless steel fermentor are added 1100 gallons of a
medium having following composition (weight/volume): Glucose 2.5%,
Molasses 1.0%, Peptones 4.0%, Calcium carbonate 0.2%, Hydrolyzed casein
0.6%, Antifoam ("Polyglycol No 2000" sold by Dow Chemical Co) 0.005%.
The medium after sterilization is inoculated with 100 gallons of the inoculum
grown in the fermentation tank. The fermentation is carried on at 30°C for 5
days. The foam is controlled by the addition, when needed, of "Larex No 1"
(an antifoam product sold by Swift and Co.). Throughout the fermentation,
the medium is aerated with sterile air at the rate of 17 cubic feet per minute
and is agitated with 22-inch impeller rotating at 140 revolution per minute. At
the end of the fermentation, 240 pounds of "Dicalite 476" (a perlite filler
product sold by Great Lakes Carbon Corporation) are added 1000 gallons or
the antibiotic broth, and the mixture is stirred and filtered. The filter cake is
washed with tap water and the filtrates are combined to provide a total
volume of 1000 gallons. To 500 gallons of the combined liquids are added 132
pounds of "Darco G-60". The mixture is filtered, and the filtrate is discarded.
The carbon filter cake is washed with 200 L of tap water, the wash water
being discarded.
The washed carbon cake on which the capreomycin is adsorbed is washed
with 200 L of 0.05 N aqueous hydrochloric acid. The acid wash is discarded.
The washed carbon cake is eluted during a one-hour period with 400 L of an
aqueous acetone containing 1.65 L of 11.7 N hydrochloric acid and 80 L of
acetone. The filter cake is further eluted by washing the cake with 200 L of an
aqueous acetone containing 825 ml of 11.7 N hydrochloric acid and 40 L of
acetone during a 15-minute period. The combined eluates, having a total
volume 575 L, are concentrated in vacuo to 52.5 L. The concentrate is added with stirring to 525 L of acetone and the acetone mixture is permitted to
stand overnight at room temperature, during which time an oily precipitate of
capreomycin separates. The supernatant is decanted and discarded, and the
oily precipitate which remains is dissolved in 20 L of distilled water. The
aqueous solution is filtered. The filtrate is added to 240 L of methanol. The
methanolic solution is acidified by the addition of 1 L of 10 N sulfuric acid,
whereupon the precipitation of the capreomycin disulfate commences. The
mixture is permitted to stand overnight. The supernant is removed by
decantation and filtering. The precipitate is washed with 10 L of methanol,
yield Capreomycin 2510 g.
brand name
Capastat Sulfate (Lilly).
Therapeutic Function
Antibacterial, Antitubercular
Pharmacokinetics
Capreomycin is a member of the aminoglycoside family of antibiotics. These antibiotics have the ability to kill a wide variety of bacteria, including bacteria responsible for causing tuberculosis (TB).
Pharmacology
Capreomycin is poorly absorbed from GI tract and so must be given parenterally. It is excreted mainly unchanged in the urine following glomerular filtration. Capreomycin is a used as a second-line agent in combination with other drugs. It appears to be particularly useful in multidrug regimens for the treatment of drugresistant tuberculosis, especially with streptomycin resistance. Capreomycin is associated with ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity, and these adverse effects can be severe in patients with preexisting renal insufficiency.
Clinical Use
Antibacterial agent in combination with other drugs:
Tuberculosis that is resistant to first-line drugs
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Increased risk of nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity with
aminoglycosides and vancomycin.
Metabolism
Not Available
Metabolism
Approximately 50% of a dose is excreted unchanged in the urine by glomerular filtration within 12 hours.
Properties of CAPREOMYCIN
| pka | pKa in 66% aq DMF: 6.2, 8.2, 10.1, 13.3(at 25℃) |
Safety information for CAPREOMYCIN
Computed Descriptors for CAPREOMYCIN
New Products
Tert-butyl bis(2-chloroethyl)carbamate 4-Methylphenylacetic acid N-Boc-D-alaninol N-BOC-D/L-ALANINOL N-octanoyl benzotriazole 3-Morpholino-1-(4-nitrophenyl)-5,6-dihydropyridin- 2(1H)-one Furan-2,5-Dicarboxylic Acid DIETHYL AMINOMALONATE HYDROCHLORIDE 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 4-Bromopyrazole 5-BROMO-2CYANO PYRIDINE 5,6-Dimethoxyindanone 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 2-(Cyanocyclohexyl)acetic acid 4-methoxy-3,5-dinitropyridine 1-(4-(aminomethyl)benzyl)urea hydrochloride 2-aminopropyl benzoate hydrochloride diethyl 2-(2-((tertbutoxycarbonyl)amino) ethyl)malonate tert-butyl 4- (ureidomethyl)benzylcarbamate Ethyl-2-chloro((4-methoxyphenyl)hydrazono)acetateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran






You may like
-
 2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 98%View Details
2033-24-1 -
 1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 98%View Details
1975-50-4 -
 2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
2-HYDROXY BENZYL ALCOHOL 98%View Details
90-01-7 -
 2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
2-Chloro-1,3-Bis(Dimethylamino)Trimethinium Hexafluorophosphate 221615-75-4 98%View Details
221615-75-4 -
 61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 CIS BROMO BENZOATE 98%View Details
61397-56-6 -
 14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 (2-Hydroxyphenyl)acetonitrile 98+View Details
14714-50-2 -
 118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 98+View Details
118753-70-1 -
 733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8 5-broMo-2-chloro-N-cyclopentylpyriMidin-4-aMine 98+View Details
733039-20-8