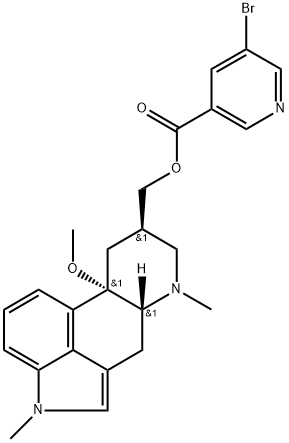
Cabergoline
Synonym(s):Cabergoline;Dostinex;Cabaser;1-[(6-Allylergoline-8β-yl)carbonyl]-1-[3-(dimethylamino)-propyl]-3-ethylurea;1-Ethyl-3-(3′-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-(6′-allylergoline-8′β-carbonyl)urea
- CAS NO.:81409-90-7
- Empirical Formula: C26H37N5O2
- Molecular Weight: 451.6
- MDL number: MFCD00867887
- EINECS: 200-419-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-26 16:58:18

What is Cabergoline?
Absorption
First-pass effect is seen, however the absolute bioavailability is unknown.
Toxicity
Overdosage might be expected to produce nasal congestion, syncope, or hallucinations.
Description
Cabergoline is a potent, selective, and long-lasting dopamine D2 receptor agonist launched in 1993 in Belgium as a prolactin inhibitor. A single 1 mg dose of cabergoline effectively prevents puerperal lactation for up to 14 days, remarkably superior to other drugs that require a daily regimen. It has a low rate of rebound breast activity and good tolerability. Cabergoline is also in clinical trials for Parkinson's disease, breast cancer, and hyperprolactinaemia.
Chemical properties
White Crystalline Solid
Originator
Kabi Pharmacia (Sweden)
The Uses of Cabergoline
Cabergoline is an ergot derivative and a dopamine D2-receptor agonist (1,2,3). It inhibits the secretion of prolactin and growth hormone.
The Uses of Cabergoline
A dopamine D2-receptor agonist.
The Uses of Cabergoline
receptor stimulant
Background
Cabergoline, an ergot derivative, is a long-acting dopamine agonist and prolactin inhibitor. It is used to treat hyperprolactinemic disorders and Parkinsonian Syndrome. Cabergoline possesses potent agonist activity on dopamine D2 receptors.
Indications
For the treatment of hyperprolactinemic disorders, either idiopathic or due to prolactinoma (prolactin-secreting adenomas). May also be used to manage symptoms of Parkinsonian Syndrome as monotherapy during initial symptomatic management or as an adjunct to levodopa therapy during advanced stages of disease.
What are the applications of Application
Cabergoline is a D2-like agonist
Definition
ChEBI: An N-acylurea that is (8R)-ergoline-8-carboxamide in which the hydrogen attached to the piperidine nitrogen (position 6) is substituted by an allyl group and the hydrogens attached to the carboxamide nitrogen are substit ted by a 3-(dimethylamino)propyl group and an N-ethylcarbamoyl group. A dopamine D2 receptor agonist, cabergoline is used in the management of Parkinson's disease and of disorders associated with hyperprolactinaemia.
Manufacturing Process
A mixture of 6-(2-propenyl)-8β-carboxy-ergoline and N-(3- dimethylaminopropyl)-N-ethyl carbodiimide in tetrahydrofuran were refluxed, with stirring and under nitrogen, for 24 h. The resultant solution was evaporated in vacuo to dryness and the residue taken up with chloroform and 5% sodium hydroxide solution. The organic phase was separated, dried over anhydrous sodium sulfate and evaporated in vacuo. The residue was chromatographed on silica (eluant chloroform with 1% methanol) to give the title compound N-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-N-((ethylamino)carbonyl)-8β- carboxamide-6-(2-propenyl)ergoline.
brand name
Dostinex (Pharmacia & Upjohn).
Therapeutic Function
Prolactin inhibitor
General Description
Cabergoline, (6aR,9R,10aR)-7-allyl-N-(3-(dimethylamino)propyl)-N-(ethylcarbamoyl)-4,6,6a,7,8,9,10,10a-octahydroindolo[4,3-fg]quinoline-9-carboxamide (Dostinex), is a white powder soluble inalcohol, chloroform, and N,N-dimethylformamide; slightlysoluble in acidic solutions and in n-hexane; and insoluble inwater. Following oral administration, peak plasma concentrationsare reached within 2 to 3 hours. Cabergoline ismoderately bound to plasma proteins in a concentrationindependentmanner. The absolute bioavailability of cabergolineis unknown. Cabergoline is extensively metabolizedby the liver, predominantly via hydrolysis of the acylureabond of the urea moiety. CYP450 metabolism appears to beminimal. The major metabolites identified thus far do not contribute to the therapeutic effect of cabergoline. Lessthan 4% is excreted unchanged in the urine. Fecal excretionrepresents the main route of cabergoline elimination. Thereare no reports of interactions of cabergoline with other antiparkinsonianagents. Clarithromycin may elevate theplasma concentration of cabergoline by the inhibition ofboth CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein.Cabergoline is a potentD2 receptor agonist and is indicated for the treatment ofhyperprolactinemic disorders, either idiopathic or causedby pituitary adenomas.
Biological Activity
Selective D 2 -like dopamine receptor agonist (K i values are 0.7, 1.5, 9.0 and 165 nM for D 2 , D 3 , D 4 and D 5 receptors respectively) that also displays high affinity for several serotonin receptor subtypes (K i = 1.2-20.0 nM for 5-HT 1A , 5-HT 1D , 5-HT 2A and 5-HT 2B ). Inhibits secretion of prolactin and growth hormone and reverses levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinsonian monkeys.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Cabergoline, a lysergic acid amide derivative, is a potent dopamine D2 receptor agonist. It also acts on dopamine receptors in lactophilic hypothalamus cells to suppress prolactin production in the pituitary gland. It has been used for monotherapy of Parkinson′s disease in the early phase; combination therapy, together with levodopa and a decarboxylase inhibitor such as carbidopa, in progressive-phase Parkinson′s disease and adjunctive therapy of prolactin-producing pituitary gland tumors (microprolactinomas).
Pharmacokinetics
Cabergoline stimulates centrally-located dopaminergic receptors resulting in a number of pharmacologic effects. Five dopamine receptor types from two dopaminergic subfamilies have been identified. The dopaminergic D1 receptor subfamily consists of D1 and D5 subreceptors, which are associated with dyskinesias. The dopaminergic D2 receptor subfamily consists of D2, D3 and D4 subreceptors, which are associated with improvement of symptoms of movement disorders. Thus, agonist activity specific for D2 subfamily receptors, primarily D2 and D3 receptor subtypes, are the primary targets of dopaminergic antiparkinsonian agents. It is thought that postsynaptic D2 stimulation is primarily responsible for the antiparkinsonian effect of dopamine agonists, while presynaptic D2 stimulation confers neuroprotective effects. This semisynthetic ergot derivative exhibits potent agonist activity on dopamine D2- and D3-receptors. It also exhibits: agonist activity (in order of decreasing binding affinities) on 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT)2B, 5-HT2A, 5-HT1D, dopamine D4, 5-HT1A, dopamine D1, 5-HT1B and 5-HT2C receptors and antagonist activity on α2B, α2A, and α2C receptors. Parkinsonian Syndrome manifests when approximately 80% of dopaminergic activity in the nigrostriatal pathway of the brain is lost. As this striatum is involved in modulating the intensity of coordinated muscle activity (e.g. movement, balance, walking), loss of activity may result in dystonia (acute muscle contraction), Parkinsonism (including symptoms of bradykinesia, tremor, rigidity, and flattened affect), akathesia (inner restlessness), tardive dyskinesia (involuntary muscle movements usually associated with long-term loss of dopaminergic activity), and neuroleptic malignant syndrome, which manifests when complete blockage of nigrostriatal dopamine occurs. High dopaminergic activity in the mesolimbic pathway of the brain causes hallucinations and delusions; these side effects of dopamine agonists are manifestations seen in patients with schizophrenia who have overractivity in this area of the brain. The hallucinogenic side effects of dopamine agonists may also be due to 5-HT2A agonism. The tuberoinfundibular pathway of the brain originates in the hypothalamus and terminates in the pituitary gland. In this pathway, dopamine inhibits lactotrophs in anterior pituitary from secreting prolactin. Increased dopaminergic activity in the tuberoinfundibular pathway inhibits prolactin secretion.
Clinical Use
Endocrine disorders
Adjunct to levodopa (with a decarboxylase inhibitor)
in Parkinson’s disease
Inhibition / suppression of lactation
Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
For dogs, cabergoline may be useful for inducing estrus, treatment
of primary or secondary anestrus, pseudopregnancy, and pregnancy
termination in the second half of pregnancy. Cabergoline may be
useful in treating some cases of pituitary-dependent hyperadrenocorticism
(Cushing’s).
In cats, cabergoline, with or without a prostaglandin, may be useful
for pregnancy termination, particularly earlier in pregnancy.
Preliminary work has been done in psittacines (primarily
Cockatiels) for adjunctive treatment of reproductive-related disorders,
particularly persistent egg laying.
In humans, cabergoline is indicated for the treatment of disorders
associated with hyperprolactenemia or the treatment of Parkinson’s
disease.
in vitro
receptor binding studies have demonstrated that cabergoline has high in vitro selectivity and affinity for the subtype d2 of the dopamine receptor. in rat anterior pituitary cells, the concentration of cabergoline required to inhibit prl secretory activity by 50% were 0.1 nmol/l [1].
in vivo
in various animal models, cabergoline markedly reduced plasma prl levels in vivo after single or multiple doses, and the prl-lowering effects appeared 2 - 8 h after administration lasting for 72 h or longer. in addition, a single dose of cabergoline 0.6 mg/kg to rats, inhibited the serum levels of prl for 6 days significantly [1].
Metabolism
Hepatic. Cabergoline is extensively metabolized, predominately via hydrolysis of the acylurea bond of the urea moiety. Cytochrome P-450 mediated metabolism appears to be minimal. The main metabolite identified in urine is 6-allyl-8b-carboxy-ergoline (4-6% of dose). Three other metabolites were identified urine (less than 3% of dose).
Metabolism
Cabergoline is subject to first-pass metabolism and is extensively metabolised to several metabolites that do not appear to contribute to its pharmacological activityCabergoline is mainly eliminated via the faeces (72%); a small proportion is excreted in the urine (18%).
Storage
Store at +4°C
References
[1] annamaria colao, gaetano lombardi & lucio annunziato. cabergoline. exp. opin. pharmacother. (2000) 1(3):555-574
Properties of Cabergoline
| Melting point: | 102-104°C |
| Density | 1.156±0.06 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | DMSO: ≥10mg/mL |
| form | powder |
| pka | 13.05±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| optical activity | [α]/D 61 to 68°, c = 0.5 in dichloromethane |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 81409-90-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Cabergoline
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Cabergoline
| InChIKey | KORNTPPJEAJQIU-KJXAQDMKSA-N |
| SMILES | [C@]12([H])C[C@H](CN(CC=C)[C@]1([H])CC1=CNC3C=CC=C2C1=3)C(=O)N(CCCN(C)C)C(=O)NCC |&1:0,3,9,r| |
Cabergoline manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 81409-90-7 Cabergoline (Crude) 98%View Details
81409-90-7 Cabergoline (Crude) 98%View Details
81409-90-7 -
 81409-90-7 Cabergoline 99%View Details
81409-90-7 Cabergoline 99%View Details
81409-90-7 -
 Cabergoline CAS 81409-90-7View Details
Cabergoline CAS 81409-90-7View Details
81409-90-7 -
 Cabergoline CAS 81409-90-7View Details
Cabergoline CAS 81409-90-7View Details
81409-90-7 -
 Cabergoline API Powder CAS NO 81409-90-7View Details
Cabergoline API Powder CAS NO 81409-90-7View Details
81409-90-7 -
 Cabergoline Api PowderView Details
Cabergoline Api PowderView Details
81409-90-7 -
 Cabergoline 0.5mg TabletView Details
Cabergoline 0.5mg TabletView Details
81409-90-7 -
 99% Cabergoline Powder Api, Drum, Non prescriptionView Details
99% Cabergoline Powder Api, Drum, Non prescriptionView Details
81409-90-7
