Boron oxide
Synonym(s):BO;Boric anhydride;Boron trioxide;Boric Oxide;Boron Trioxide, Boric oxide
- CAS NO.:1303-86-2
- Empirical Formula: B2O3
- Molecular Weight: 69.62
- MDL number: MFCD00011315
- EINECS: 215-125-8
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-11 17:37:59
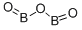
What is Boron oxide?
Description
Boron oxide is a noncombustible, colorless,semitransparent lumps or hard, white, odorless crystals,with slightly bitter taste. Molecular weight=69.64; Boilingpoint=about 1860℃; Freezing/Melting point=about450℃. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 MRating System): Health 2, Flammability 0, Reactivity 0.Moderately soluble in water; solubility=(moderate) 3%;slow reaction.
Chemical properties
white powder or glassy flakes
Chemical properties
Boron oxide is a noncombustible, colorless, semitransparent lumps or hard, white, odorless crystals, with slightly bitter taste.

Physical properties
Colorless glassy solid or vitreous crystal; hexagonal crystal system; slightly bitter taste; hygroscopic; density 2.55 g/cm3; melts at 450°C; vaporizes at 1,500°C; slightly soluble in cold water (3.3%), soluble in alcohol and boiling water (20%).
The Uses of Boron oxide
Boron oxide was used as the intermediate glass layer at a bonding temperature of 450°C. In preparation of fluxes; component of enamels and glass; catalyst in organic reaction.
In metallurgy; in analysis of silicates to determine SiO2 and alkalies; in blowpipe analysis.
The Uses of Boron oxide
A saturated solution of H3BO3 contains about 2% of the compound at 0 C, increasing to about 39% at 100 C. The compound also is soluble in alcohol. In preparations, solutions of boric acid are nonirritating and slightly astringent with antiseptic properties. Although no longer used as a preservative for meats, boric acid finds extensive use in mouthwashes, nasal sprays, and eye-hygiene formulations. Boric acid (sometimes with borax) is used as a fire-retardant. A commercial preparation of this type (Minalith) consists of diammonium phosphate, ammonium sulfate, sodium tetraborate, and boric acid. The tanning industry uses boric acid in the deliming of skins where calcium borates, soluble in H2O, are formed. As sold commercially, boric acid is B3O3·3H2O, prepared by adding HCl or H2SO4 to a solution of borax.
The Uses of Boron oxide
In preparation of fluxes; component of enamels and glass; catalyst in organic reaction
Production Methods
Boric oxide is produced by thermal fusion of boric acid, forming a clear transparent glass-like solid that is subsequently ground into white vitreous granules. It is used principally in the manufacture of glass and vitreous products.
Preparation
Boric oxide is produced by treating borax with sulfuric acid in a fusion furnace. At temperatures above 750°C, the molten boric acid layer separates out from sodium sulfate. It then is decanted, cooled, and obtained in 96-97% purity. Boric acid above 99% purity may be obtained by fusing granular material.
Boric oxide may be prepared by heating boric acid.
2B(OH)3 → B2O3 + 3H2O
Definition
ChEBI: Diboron trioxide is a boron oxide with formula B2O3.
General Description
Colorless, semi-transparent glassy lumps or hard white odorless crystals. Mp 450°C; bp: 1860°C. Density: 2.46 g cm-3. Moderately soluble in water. Used as an insecticide; as the starting material for the synthesis of other boron compounds; as a fluxing agent in enamels and glasses; and in mixture with 2-6% boron nitride, as a bonding agent in the hot isostatic pressing of boron nitride ceramics.
Reactivity Profile
Boron oxide is non-combustible. Of generally low chemical reactivity. Reacts exothermically but slowly with water to form boric acid, a weak acid. Reacts exothermically with strong bases. May react with strong reducing agents such as metal hydrides, metal alkyls to generate flammable or explosive gases. May react violently on contact with bromine pentafluoride. Corrosive to metals in the presence of air.
Hazard
Eye and upper respiratory tract irritant.
Health Hazard
Boron oxide is an eye and respiratory irritant. In 113 workers exposed to boron oxide and boric acid dusts, there were statistically significant increases in symptoms of eye irrita- tion; dryness of the mouth, nose, and throat; sore throat; and productive cough compared with controls. The mean exposure level was 4.1mg/m3 , with a range of 1.2–8.5mg/m3 . Exposures may occasionally have exceeded 10 mg/m3 . Because of mixed exposures, the study does not indicate whether boron oxide or boric acid dust is more important in causing symp- toms, nor does it indicate the minimum duration of exposure necessary to produce symptoms.
Excessive absorption of boron oxide may lead to cardiovascular collapse, alterations in temperature regulation, and coma.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Boric anhydride is an oxide of boron that shows antimicrobial property along with lower aminoalcohols.
Potential Exposure
Boron oxide is used in glass manufacture and the production of other boron compounds. It is used in fluxes, enamels, drying agents, and as a catalyst.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contactsthe skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately.If this chemical has been inhaled, remove fromexposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing hasstopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemical hasbeen swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Storage
Color Code—Green: General storage may be used.Store in tightly closed containers in a dry, well-ventilatedarea away from incompatible materials listed above andwater.
Shipping
UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9—Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with bromine pentafluoride, calcium oxide. Reacts slowly with water, forming boric acid. Reacts exothermically with alkaline material and strong bases. May react with strong reducing agents such as metal hydrides, metal alkyls to generate flammable or explosive gases. May react violently on contact with bromine pentafluoride. Corrosive to metals in the presence of air.
Properties of Boron oxide
| Melting point: | 450 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 1860 °C |
| Density | 2.46 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | >1 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 1Pa |
| Flash point: | 1860°C |
| storage temp. | Inert atmosphere,Room Temperature |
| solubility | 36g/l |
| form | pellets |
| color | White |
| Specific Gravity | 2.46 +/- 0.01 |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 4 (10g/l, H2O, 25℃) |
| Water Solubility | 36 g/L (25 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,1337 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 10 mg/m3 OSHA: TWA 15 mg/m3 NIOSH: IDLH 2000 mg/m3; TWA 10 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Moisture sensitive. Incompatible with water. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1303-86-2(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Diboron trioxide(1303-86-2) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Boric oxide (1303-86-2) |
Safety information for Boron oxide
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Health Hazard GHS08 |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. P405:Store locked up. P501:Dispose of contents/container to..… |
Computed Descriptors for Boron oxide
| InChIKey | JKWMSGQKBLHBQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Boron oxide manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Boron Trioxide 98%View Details
Boron Trioxide 98%View Details -
 BORON OXIDE 99%View Details
BORON OXIDE 99%View Details -
 Boric anhydride 98%View Details
Boric anhydride 98%View Details -
 Boric anhydride 98%View Details
Boric anhydride 98%View Details -
 Boric Oxide, 96%, For LaboratoryView Details
Boric Oxide, 96%, For LaboratoryView Details
1303-86-2 -
 Boron Oxide Powder, For Ceramics, 98%View Details
Boron Oxide Powder, For Ceramics, 98%View Details
1303-86-2 -
 Boron Oxide Powder, For Laboratory, 99.9%View Details
Boron Oxide Powder, For Laboratory, 99.9%View Details
1303-86-2 -
 Boron Trioxide CAS 1303-86-2View Details
Boron Trioxide CAS 1303-86-2View Details
1303-86-2
