Baricitinib
- CAS NO.:1187594-09-7
- Empirical Formula: C16H17N7O2S
- Molecular Weight: 371.42
- MDL number: MFCD21608464
- EINECS: 691-421-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-03-07 18:45:43
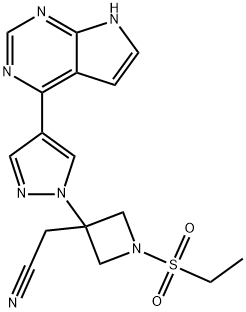
What is Baricitinib?
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of baricitinib is approximately 80%. The Cmax was reached after one hour of oral drug administration. A high-fat meal decreased the mean AUC and Cmax of baricitinib by approximately 11% and 18%, respectively, and delayed Tmax by 0.5 hours.
Toxicity
The oral lowest published toxic dose (TDLo) is 1820 g/kg in mice and 5096 g/kg in rats.
In clinical trials, single doses up to 40 mg and multiple doses of up to 20 mg daily for 10 days did not result in any dose-limiting toxicity. Pharmacokinetic data of a single dose of 40 mg in healthy volunteers indicate that more than 90% of the administered dose is expected to be eliminated within 24 hours. In case of an overdose, it is recommended that patients are monitored for signs and symptoms of drug-related adverse reactions, which should be responded with appropriate treatment.
Description
Baricitinib (1187594-09-7), approved by the FDA for two inflammatory disorders, rheumatoid arthritis and alopecia areata, selectively inhibits Janus kinase 1 (IC50?= 5.9 nM) and 2 (5.7 nM), over 3 (0.56 μM).1?It thereby blocks JAK/STAT signaling, reducing cytokine release and suppressing the innate and adaptive immune systems.1,2?Was recently shown to significantly improve COVID-19 symptoms in a preliminary human trial, presumably through suppression of the cytokine release syndrome (“cytokine storm”) induced by SARS-CoV-2 infection.3
Description
Baricitinib, a rheumatoid arthritis drug, is under development by Incyte (Wilmington, DE) and Eli Lilly (Indianapolis). It was approved for use under some conditions by the European Union in 2017 and by the US Food and Drug Administration in 2018. Its mechanism of action against rheumatoid arthritis is inhibition of janus kinase enzymes, specifically subtypes JAK1 and JAK2.
Because of current events, baricitinib may have a more urgent application. About a month ago, Justin Stebbing and colleagues at Imperial College London and the artificial intelligence drug discovery company BenevolentAI (London) reported that their AI software turned up an existing drug—baricitinib—that may limit the effects of COVID-19, the coronavirus that is rapidly spreading worldwide.
The researchers used available information about?COVID-19 to identify the enzyme adaptor-associated protein kinase 1 (AAK1) as a possible coronavirus target. The AI software then canvassed known AAK1 inhibitors for possible leads to a?COVID-19 drug. Baricitinib stood out for its strong affinity for the kinase and its low toxicity.
The authors believe that baricitinib may be able to reduce the ability of the virus to infect lung cells. But they cautioned that their findings should not be considered medical advice; rather, baricitinib could be a clue for other researchers to find treatments for the virus.
Characteristics
Primary targets: JAK1/2
Class: non-receptor tyrosine kinase
Treatment: rheumatoid arthritis
Oral bioavailability = 79%
Elimination half-life = 12.5 h
Protein binding = 50%
The Uses of Baricitinib
Baricitinib is a JAK1 and JAK2 inhibitor and have been used as a promising treatment for rheumatoid arthritis.
Indications
In the US and Europe, baricitinib is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with moderately to severely active rheumatoid arthritis who have had an inadequate response to one or more TNF blockers. Baricitinib may be used as monotherapy or in combination with methotrexate or other DMARDs.
In Europe, baricitinib is indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe atopic dermatitis in adult patients who are candidates for systemic therapy.
In the US, baricitinib is also indicated for the treatment of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) in hospitalized adults requiring supplemental oxygen, non-invasive or invasive mechanical ventilation, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Recently, it is also approved as the treatment for severe alopecia areata in adults.
Background
Baricitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor. JAKs are tyrosine protein kinases that play an important role in pro-inflammatory signaling pathways. Overactive JAKs have been implicated in autoimmune disorders, such as rheumatoid arthritis. By inhibiting the actions of JAK1 and JAK2, baricitinib attenuates JAK-mediated inflammation and immune responses.
Baricitinib was first approved by the European Commission (EC) in February 2017 for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in adults and was later approved by the FDA in 2018. The EC later approved baricitinib for the treatment of atopic dermatitis, making it the first JAK inhibitor used for this indication in Europe. While baricitinib was granted emergency use as a treatment for COVID-19 in combination with remdesivir under the Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) in November 2020, the FDA fully approved the use of baricitinib for the treatment of COVID-19 in May 2022.
Definition
ChEBI: Baricitinib is a pyrrolopyrimidine that is 7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine substituted by a 1-[3-(cyanomethyl)-1-(ethanesulfonyl)azetidin-3-yl]-1H-pyrazol-4-yl group at position 5. It is an FDA approved selective Janus Kinase 1 and 2 (JAK1 and JAK2) inhibitor used for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. It has a role as an antirheumatic drug, an EC 2.7.10.2 (non-specific protein-tyrosine kinase) inhibitor, an anti-inflammatory agent, an immunosuppressive agent and an antiviral agent. It is a pyrrolopyrimidine, a member of pyrazoles, a member of azetidines, a sulfonamide and a nitrile.
Mechanism of action
Baricitinib is a Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitor that inhibits JAK protein activity and regulates various interleukin, interferon, and growth factor signalling pathways. Studies have also shown that it reduces the proliferation of JAK1/JAK2 expression in mutant cells and induces apoptosis.
Pharmacokinetics
Baricitinib is a disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) used to ameliorate symptoms and slow down the progression of rheumatoid arthritis. In animal models of inflammatory arthritis, baricitinib was shown to have significant anti-inflammatory effects but also led to the preservation of cartilage and bone, with no detectable suppression of humoral immunity or adverse hematologic effects. Baricitinib decreased the levels of immunoglobulins and serum C-reactive protein in patients with rheumatoid arthritis.
Clinical Use
Janus kinase inhibitor:
Treatment of moderate to severe active rheumatoid
arthritis
Enzyme inhibitor
This selective, ATP-competitive protein kinase inhibitor (FW = 371.42 g/mol; CAS 1187594-09-7; Solubility: 70 mg/mL DMSO, <1 mg/mL H2O), also known by its code names LY3009104 and INCB028050 as well as its systematic name 1-(ethylsulfonyl)-3-[4-(7H-pyrrolo[2,3-d]-pyrimidin-4-yl)- 1H-pyrazol-1-yl]-3-azetidineacetonitrile, targets JAK1 and JAK2, with respective IC50 values of 5.9 nM and 5.7 nM, showing little effect on JAK3 (IC50 = 560 nM). In cell-based assays, INCB028050 proved to be a potent inhibitor of JAK signaling and function. Primary Mode of Inhibitory Action: Janus kinases JAK1, JAK2, JAK3, and the related enzyme TYK2 are critical components of signaling mechanisms used by many cytokines and growth factors, including several that are elevated in patients with RA. Cytokines such as interleukin-6, -12 and -23 and both type 1 and type 2 interferons signal through these pathways. JAK-dependent cytokines have been implicated in the pathogenesis of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases, suggesting that JAK inhibitors may be useful for the treatment of a broad range of inflammatory conditions. At concentrations <50 nM, baricitinib inhibits intracellular signaling of multiple proinflammatory cytokines including IL-6 and IL-23. Significant efficacy, as assessed by improvements in clinical, histologic and radiographic signs of disease, was achieved in a rat adjuvant arthritis model with baricitinib providing partial and/or periodic inhibition of JAK1/JAK2 and no inhibition of JAK3. Such findings suggest that fractional inhibition of JAK1 and JAK2 may be sufficient for significant pharmacological activity in autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis. A related JAK inhibitor, Tofacitinib, is approved in the U.S. for the treatment of RA. Target(s): Baricitinib shows moderate (~10x) selectivity against Tyk2 (IC50 = 53 nM) and marked selectivity over the unrelated c-Met (IC50 > 10,000 nM) and Chk2 (IC50 > 1,000 nM) kinases as well as ~100x higher IC50 values against Abl, Akt1, AurA, AurB, CDC2, CDK2, CDK4, CHK2, c-kit, EGFR, EphB4, ERK1, ERK2, FLT-1, HER2, IGF1R, IKKα, IKKβ, JNK1, Lck, MEK1, p38α, p70S6K, PKA, PKCα, Src, and ZAP70.
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Avoid with other DMARDs due to increased
immunosuppression.
Use with care with other immunosuppressants.
Antipsychotics: increased risk of agranulocytosis
with clozapine - avoid.
Live vaccines: avoid concomitant use
Metabolism
Baricitinib is metabolized by CYP3A4. Approximately 6% of the orally administered dose was identified as metabolites in urine and feces; however, no metabolites of baricitinib were quantifiable in plasma.
Metabolism
Baricitinib is hepatically metabolism by CYP3A4, <10% of the dose identified as undergoing biotransformation. No metabolites were detected in plasma. In a clinical pharmacology study, baricitinib was excreted mainly as the unchanged active substance in urine (69%) and faeces (15%) and only 4 minor oxidative metabolites were identified (3 in urine; 1 in faeces) constituting approximately 5% and 1% of the dose, respectively
Side Effects
Common side effects of Baricitinib include: upper respiratory tract infection, body aches or pains, chest tightness, chills, cough, difficulty breathing, ear congestion, fever, headache, hoarseness or loss of voice, muscle aches, pain or pressure around the eyes and cheekbones, runny or stuffy nose, sneezing, sore throat, difficulty swallowing. Decreased white blood cell count, elevated cholesterol, or elevated liver enzyme levels are less common. Serious side effects can be seen as low red or white blood cell counts, increased risk of blood clots, herpes zoster, skin infections (called cellulitis), and in rare cases, hepatitis or tuberculosis.
storage
Store at -20°C
References
1) Fridman?et al.?(2010),?Selective Inhibition of JAK1 and JAK2 Is Efficacious in Rodent Models of Arthritis: Preclinical Characterization of INCB028050; J. Immunol. Biol.,?184?5298 2) Kubo?et al.?(2018),?Janus Kinase Inhibitor Baricitinib Modulates Human Innate and Adaptive Immune System; Front. Immunol.,?9?1510 3) Cantini?et al.?(2020),?Baricitinib Therapy in COVID-19: A Pilot Study on Safety and Clinical Impact; J. Infect.,?81?318
Properties of Baricitinib
| Melting point: | 212-215°C |
| Density | 1.56 |
| storage temp. | -20°C |
| solubility | Soluble in DMSO (up to 30 mg/ml) or in DMF (up to 50 mg/ml). |
| form | solid |
| appearance | white crystals or powder |
| pka | 11.66±0.50(Predicted) |
| color | White or off-white |
| Stability: | Stable for 2 years from date of purchase as supplied. Solutions in DMSO or DMF may be stored at -20°C for up to 3 months. |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C16H17N7O2S/c1-2-26(24,25)22-9-16(10-22,4-5-17)23-8-12(7-21-23)14-13-3-6-18-15(13)20-11-19-14/h3,6-8,11H,2,4,9-10H2,1H3,(H,18,19,20) |
Safety information for Baricitinib
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Baricitinib
| InChIKey | XUZMWHLSFXCVMG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | N1(S(CC)(=O)=O)CC(N2C=C(C3N=CN=C4NC=CC4=3)C=N2)(CC#N)C1 |
Baricitinib manufacturer
New Products
8-Bromoisoquinoline 3-pyridine carboxaldehyde 7-bromoquinoxalin-2(1H)-one 1-Benzyl-4-[(5,6-dimethoxy-1-oxoindan-2-ylidene)methyl]piperidine 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-amino-, hydrochloride (1:1) Trans-methyl 4-aminocyclohexane- carboxylate HCl 4-[2-(DIMETHYLAMINO)ETHOXY]BENZYLAMINE Xanomeline Suzetrigine 5-(5,5-Dimethyl-1,3,2-dioxaborinan-2-yl)-3-methyl-1,3-benzoxazol-2(3H)-one Dimethyl 4-aminothiophene-2,3-dicarboxylate hydrochloride Remibrutinib 1H-Indole-1-carboxylic acid, 5-hydroxy-7-methyl-, 1,1-dimethylethyl ester N N N'Trimethyl ethylenediamine Variamine Blue B Diazonium salt Lead II Bromide N N' DimethylEthylenediamine Ethyl Methanesulfonate N Ethylmethylamine Zinc Chloride Solution (All Grades) Calcium Alphaketoglutarate* L-Glycine methyl ester.HCl H-Ser(t-Bu)-Ser(t-Bu)-Gly-OH Fmoc-L-Glu(OtBu)-OH.H2ORelated products of tetrahydrofuran
![(1S,4Z,7S,10S,11E,20R)-4-ethylidene-7,20-dipropan-2-yl-9-oxa-15,16-dit hia-3,6,18,21-tetrazabicyclo[8.7.6]tricos-11-ene-2,5,8,19,22-pentone](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/128517-07-7.gif)
You may like
-
 1187594-09-7 Baricitinib 98%View Details
1187594-09-7 Baricitinib 98%View Details
1187594-09-7 -
 Baricitinib 98%View Details
Baricitinib 98%View Details -
 Baricitinib 98%View Details
Baricitinib 98%View Details
1187594-09-7 -
 Baricitinib API 1187594-09-7 98%View Details
Baricitinib API 1187594-09-7 98%View Details
1187594-09-7 -
 Baricitinib 98%View Details
Baricitinib 98%View Details
1187594-09-7 -
 Baricitinib 98% CAS 1187594-09-7View Details
Baricitinib 98% CAS 1187594-09-7View Details
1187594-09-7 -
 KT-474 98+View Details
KT-474 98+View Details
2432994-31-3 -
 7646-85-7 Zinc Chloride Solution (All Grades) As requiredView Details
7646-85-7 Zinc Chloride Solution (All Grades) As requiredView Details
7646-85-7
