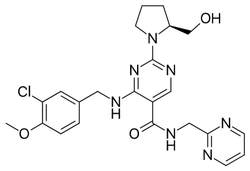
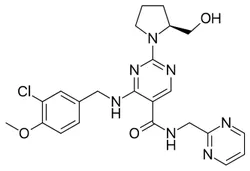
Avanafil
Synonym(s):(S)-2-(2-Hydroxymethyl-1-pyrrolidinyl)-4-(3-chloro-4-methoxybenzylamino)-5-[N-(2-pyrimidinylmethyl)carbamoyl]pyrimidine;(S)-4-[(3-Chloro-4-methoxybenzyl)amino]-2-[2-(hydroxymethyl)-1-pyrrolidinyl]-N-(2-pyrimidinylmethyl)-5-pyrimidinecarboxamide;4-[[(3-Chloro-4-methoxyphenyl)methyl]amino]-2-[(2S)-2-(hydroxymethyl)-1-pyrrolidinyl]-N-(2-pyrimidinylmethyl)-5-pyrimidinecarboxamide;
- CAS NO.:330784-47-9
- Empirical Formula: C23H26ClN7O3
- Molecular Weight: 483.95
- MDL number: MFCD11977961
- EINECS: 000-000-0
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-08-28 14:57:35
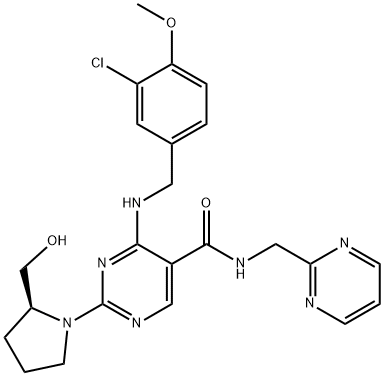
What is Avanafil?
Absorption
Avanafil is rapidly absorbed following oral administration (Tmax of 30-45 minutes) and appears to have low to moderate oral bioavailability, though formal studies have not been conducted. Administration with a meal results in a mean delay in Tmax of 1.12 to 1.25 hours, a 39% mean reduction in Cmax, and a negligible effect on AUC.
Toxicity
Experience with avanafil overdose is limited. Single doses of up to 800mg and repeat doses of up to 300mg have been administered - these patients experienced adverse effects similar to those seen at therapeutic doses but with increased incidence and severity. Patients experiencing an overdosage of avanafil should be treated with standard symptomatic and supportive measures. Dialysis is unlikely to be of benefit in cases of overdose as avanafil is highly protein-bound in plasma.
Description
Avanafil (Zepeed) was approved by the Korean Health Ministry for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED) in August 2011. Avanafil is a highly selective type 5 phosphodiesterase (PDE5) inhibitor. Avanafil is reported to be the most selective PDE5 inhibitor on the market. The onset of Tmax and half-life also varies among the marketed PDE5 inhibitors. Sildenafil has a Tmax at 1 h and a half-life of 3–5 h. Vardenafil is somewhat similar with a Tmax of 0.6 h and a half-life of 4–6 h. Tadalafil has the longest half-life among the marketed drugs with a half-life of 17 h. Avanafil has a fast onset of action reaching Tmax in 0.6 h with a half-life of 1.2 h. A synthesis of avanafil (TA-1790) is described in the patent literature. The main elimination route of avanafil is through the bile and feces. Avanafil was also found to be reabsorbed through enterohepatic recirculation.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma Corporation (Japan)
The Uses of Avanafil
Avanafil is a highly selective PDE5 inhibitor with IC50 of 1 nM.
The Uses of Avanafil
A phosphodiesterase (PDE5) inhibitor, used to treat erectile dysfunction.
Indications
Avanafil is indicated for the treatment of erectile dysfunction.
What are the applications of Application
Avanafil is a derivative of pyrimidine that acts as PDE5 (phosphodiesterase-5) inhibitor
Background
Avanafil is a phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction. In comparison with other drugs of the same class, it shows greater selectivity for PDE5 over PDE6 than both sildenafil and vardenafil but less selectivity than tadalafil, suggesting a relatively lower risk of visual disturbances associated with off-target PDE6 inhibition.
It first received FDA approval on April 27, 2012, with subsequent EMA approval in June 2013.
Definition
ChEBI: A monocarboxylic acid amide obtained by formal condensation of the carboxy group of 4-[(3-chloro-4-methoxybenzyl)amino]-2-[(2S)-2-(hydroxymethyl)pyrrolidin-1-yl]pyrimidine-5-carboxylic acid with the amino group of pyrimidin-2-ylmethylamine Used for treatment of erectile dysfunction.
brand name
Zepeed
Pharmacokinetics
Avanafil is a strong competitive inhibitor of phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE5) with a demonstrated in vitro IC50 of 5.2 nM. Its inhibitory effects on PDE5 are 100-fold more potent than on PDE6 and >1000-fold more potent than on other PDE enzymes, meaning it is less likely to cause visual disturbances and cardiovascular adverse effects when compared with less selective PDE5 inhibitors such as sildenafil and vardenafil. It has a relatively quick onset of action allowing for administration as early as 15 minutes prior to sexual activity.
PDE5 inhibitors like avanafil can cause significant drug interactions when administered alongside certain antihypertensive agents (e.g. alpha blockers, substantial amounts of alcohol). PDE5 inhibitors have also been associated with the development of non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION), a rare condition that typically presents as sudden loss of vision in one or both eyes and appears to be more common in patients with a "crowded" optic disc. Patients presenting with any degree of vision loss should immediately discontinue use of all PDE5 inhibitors and seek medical attention. In some jurisdictions, a history of NAION or other degenerative retinal disorders is considered a contraindication to avanafil therapy.
Clinical Use
Avanafil was originally discovered at Tanabe Seiyaku (now Mitsubishi Tanabe). JW Pharmaceutical (previously Choongwae Pharma) and VIVUS have since developed and launched avanafil, which is an oral PDE5 inhibitor for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). Although many marketed PDE5 inhibitors (e.g. sildenafil, vardenafil and tadalafil) are available for the treatment of ED, many patients are still unable to achieve the desired results and experience undesired side-effects with these existing medications. As such, second-generation PDE5 inhibitors with enhanced PDE5 selectivity, shorter systemic half-lives, and improved tolerability are desired. Developed to meet these criteria, Avanafil exhibited good oral bioavailability and PDE5 selectivity in both preclinical studies and clinical trials. Avanafil had a short onset of action (35 min) and short half-life (1.5 h).
Synthesis
The synthesis presented is based on the published patent procedure and is outlined in the scheme. Commercially available 4-chloro-2-(methylsulfanyl)pyrimidine- 5-carboxylic acid ethyl ester (25) was treated with 3- chloro-4-methoxybenzylamine (26) and triethylamine at room temperature to give 4-benzylaminopyrimidine derivative 27 in 96% yield. Sulfide 27 was then oxidized with m-chloroperbenzoic acid (m-CPBA), followed bytreatment with L-prolinol and triethylamine to afford ethyl pyrimidinate 28 in 83% yield. This ester was then saponified with 10% sodium hydroxide to give pyrimidine- 5-carboxylic acid 29 in 80% yield, which then underwent conventional amide bond formation using 2-(aminomethyl) pyrimidine (29a), N-(3-dimethylaminopropal)-N0-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDCI) and 1-hydroxybenzotriazole hydrate (HOBt) to give avanafil (IV) in 83% yield.

Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Alpha-blockers: enhanced hypotensive effect -
maximum dose 50 mg.
Antibacterials: concentration possibly increased
by clarithromycin and telithromycin - avoid;
concentration increased by erythromycin - reduce
avanafil dose; concentration reduced by rifampicin -
avoid.
Antifungals: concentration increased by ketoconazole
- avoid and fluconazole - reduce avanafil dose;
concentration possibly increased by itraconazole and
voriconazole - avoid.
Antivirals: concentration possibly increased by
atazanavir, indinavir and saquinavir - avoid;
concentration possibly reduced by efavirenz - avoid;
concentration possibly increased by fosamprenavir
- reduce avanafil dose; concentration significantly
increased by ritonavir - avoid.
Aprepitant: concentration possibly increased by
aprepitant - reduce avanafil dose.
Calcium channel blockers: concentration possibly
increased by diltiazem and verapamil - reduce
avanafil dose.
Cobicistat: concentration of avanafil possibly
increased - avoid.
Nicorandil: possibly enhanced hypotensive effect -
avoid.
Nitrates: enhanced hypotensive effect - avoid.
Riociguat: possibly enhanced hypotensive effect -
avoid.
Metabolism
Avanafil is extensively metabolized, primarily by CYP3A4 and to a lesser extent by CYP2C9. There are two major metabolites formed, M4 and M16, which exist in the plasma at concentrations 23% and 29% that of the parent compound, respectively. The M16 metabolite lacks pharmacologic effect, but the M4 metabolite has an inhibitory potency for PDE5 18% that of avanafil and accounts for approximately 4% of the observed pharmacologic activity of avanafil.
Metabolism
Avanafil is metabolised in the liver mainly by the cytochrome P450 isoenzyme CYP3A4 and to a minor extent by the CYP2C isoform. Two major metabolites are produced, one of which is active. Avanafil is excreted as metabolites mainly in the faeces (approximately 63%) in the urine (approximately 21%).
References
[1] kotera j, mochida h, inoue h, noto t, fujishige k, sasaki t, kobayashi t, kojima k, yee s, yamada y, kikkawa k, omori k. avanafil, a potent and highly selective phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor for erectile dysfunction. j urol. 2012 aug;188(2):668-74.
[2] cui ys, li n, zong ht, yan hl, zhang y. avanafil for male erectile dysfunction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. asian j androl. 2014 may-jun;16(3):472-7.
Properties of Avanafil
| Melting point: | 150-152°C |
| Density | 1.372 |
| storage temp. | Sealed in dry,Store in freezer, under -20°C |
| solubility | DMSO (Slightly), Methanol (Slightly, Heated) |
| form | Solid |
| pka | 11.84±0.46(Predicted) |
| color | White to Off-White |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 330784-47-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
Safety information for Avanafil
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Avanafil
| InChIKey | WEAJZXNPAWBCOA-INIZCTEOSA-N |
| SMILES | C1(N2CCC[C@H]2CO)=NC=C(C(NCC2=NC=CC=N2)=O)C(NCC2=CC=C(OC)C(Cl)=C2)=N1 |
Avanafil manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Avanafil 98% (HPLC) CAS 330784-47-9View Details
Avanafil 98% (HPLC) CAS 330784-47-9View Details
330784-47-9 -
 Avanafil API PowderView Details
Avanafil API PowderView Details
330784-47-9 -
 Avanafil API Powder, Neutral Pharma, 1 KgsView Details
Avanafil API Powder, Neutral Pharma, 1 KgsView Details
330784-47-9 -
 Avanafil IP PowderView Details
Avanafil IP PowderView Details
330784-47-9 -
 Avanafil, Tablet, Packaging Size: 25 Kg Fiber DrumView Details
Avanafil, Tablet, Packaging Size: 25 Kg Fiber DrumView Details
330784-47-9 -
 Avanafil APIView Details
Avanafil APIView Details
330784-47-9 -
 Avanafil Powder API, Grade Standard: USPView Details
Avanafil Powder API, Grade Standard: USPView Details
330784-47-9 -
 Active Pharma Avanafil PowderView Details
Active Pharma Avanafil PowderView Details
330784-47-9
