p-Anisidine
Synonym(s):4-Aminoanisole;4-Methoxyaniline;4-Methoxyaniline, 4-Aminoanisole, 4-Aminophenyl methyl ether;p-Anisidine
- CAS NO.:104-94-9
- Empirical Formula: C7H9NO
- Molecular Weight: 123.15
- MDL number: MFCD00007864
- EINECS: 203-254-2
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
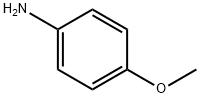
What is p-Anisidine?
Chemical properties
Anisidine exists as ortho-, meta-, and paraisomers. They have characteristic amine (fishy) odors. releases toxic nitrogen oxides when heated to decomposition (Sax and Lewis, 1987).
Physical properties
Yellow to light brown powder, leaflets, solid or crystals with a characteristic amine or ammonialike odor. soluble in ethanol and ether, slightly soluble in water.
The Uses of p-Anisidine
p-Anisidine is used mostly for producing dyes, and some smaller quantities are employed in making pharmaceuticals and liquid crystals.
What are the applications of Application
p-Anisidine is an aromatic compound used in the detection of aldehydes or ketones in oils
Definition
ChEBI: P-anisidine is a substituted aniline that is aniline in which the hydrogen para to the amino group has been replaced by a methoxy group. It is used as a reagent for the detection of oxidation products such as aldehydes and ketones in fats and oils. It has a role as a reagent and a genotoxin. It is a member of methoxybenzenes, a substituted aniline and a primary amino compound.
What are the applications of Application
p-Anisidine is used as a reagent to indicate the secondary stage of the oxidation, it is one of the three possible isomers of the Anisidine or methoxyaniline. The other two isomers are o-Anisidine (2-methoxyaniline) and m-Anisidine (3-methoxyaniline).
The p-anisidine is widely used as an intermediate in the production of numerous azo and triphenylmethane dyes, and pigments. It is also used in the production of pharmaceuticals including the guaiacol expectorant, as an antioxidant for polymercaptan resins, and as a corrosion inhibitor for steel. Apart from the beneficial use of p-anisidine, it is toxic for human beings. The acute exposure may cause skin irritation, whereas the chronic exposure may cause headaches, vertigo, and blood complications like sulfhemoglobin, and methemoglobin. The oral exposure to anisidine hydrochloride resulted in cancer of the urinary bladder in male and female rats.
https://www.longdom.org/open-access/physicochemical-and-spectroscopic-characterization-of-biofield-energytreated-panisidine-paco-1000102.pdf
Preparation
p-Anisidine is an important intermediate for synthesis of dye, medicine and perfume. Traditional preparation of p-Anisidine uses iron powder or sodium sulfide as reductant, which produces a large amount of waste and results in serious environment pollution problem. Liquid phase catalytic hydrogenation is not only an environmentally benign technique but also of high yield.
Synthesis of p-Anisidine by Hydrogenation with Raney-RuNiC as Catalyst
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 99, p. 98, 1977 DOI: 10.1021/ja00443a018
The Journal of Organic Chemistry, 49, p. 1434, 1984 DOI: 10.1021/jo00182a023
Tetrahedron Letters, 21, p. 2603, 1980 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)92816-8
General Description
P-anisidine appears as brown crystals or dark brown solid. Characteristic amine odor. (NTP, 1992)
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
p-Anisidine may be sensitive to heat, light and moisture. Reacts with acids, acid chlorides, acid anhydrides, chloroformates and strong oxidizing agents. Incompatible with alkaline materials. Incompatible with aldehydes, ketones and nitrates.
Hazard
Strong irritant. Toxic when absorbed through the skin. Questionable carcinogen.
Fire Hazard
p-Anisidine is flammable.
Safety Profile
Moderately toxic by several routes. A mild sensitizer. May cause a contact dermatitis. Mutation data reported. Questionable carcinogen. See also ANILINE. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Nox
Potential Exposure
Anisidines are used in the manufacture of azo dyes; pharmaceuticals; textile-processing chemicals Incompatibilities: Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine,bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Attacks some coatings and some forms of plastic and rubber.
Carcinogenicity
Available data were inadequate to evaluate the carcinogenicity of p-anisidine.
Shipping
UN2431 Anisidines, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials
Purification Methods
Crystallise p-anisidine from H2O or aqueous EtOH. Dry it in a vacuum oven at 35o for 6hours and store it in a dry box. [More et al. J Am Chem Soc 108 2257 1986.] Purify it also by vacuum sublimation [Guarr et al. J Am Chem Soc 107 5104 1985]. [Beilstein 13 IV 1015.]
Waste Disposal
Dissolve in combustible solvent (alcohols, benzene, etc.) and spray solution into furnace equipped with afterburner and scrubber, or burn spill residue on sand and soda ash absorbent in a furnace.
Properties of p-Anisidine
| Melting point: | 56-59 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 240-243 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.06 |
| vapor density | 4.28 |
| vapor pressure | 0.02 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5559 |
| Flash point: | 122 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | 21g/l |
| form | crystalline |
| pka | 5.34(at 25℃) |
| Specific Gravity | 1.07 |
| color | dark gray to brown |
| PH | 7.7 (1g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 21 g/L (20 ºC) |
| Merck | 14,667 |
| BRN | 471556 |
| Henry's Law Constant | (x 10-8 atm?m3/mol):
6.62 at 25 °C (thermodynamic method-GC/UV spectrophotometry, Altschuh et al., 1999) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 0.5 mg/m3, IDLH 50 mg/m3; OSHA PEL: TWA 0.5 mg/m3;
ACGIH TLV: TWA 0.1 ppm (adopted). |
| Dielectric constant | 8.8399999999999999 |
| Stability: | Hygroscopic, Material Darkens In Storage With No Loss In Purity |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 104-94-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 27, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzenamine, 4-methoxy-(104-94-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | p-Anisidine (104-94-9) |
Safety information for p-Anisidine
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H350:Carcinogenicity H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H400:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, acute hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P201:Obtain special instructions before use. P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for p-Anisidine
p-Anisidine manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 p-Anisidine 98%View Details
p-Anisidine 98%View Details -
 p-Anisidine 98%View Details
p-Anisidine 98%View Details -
 p-Anisidine, puriss, 99%+ CAS 104-94-9View Details
p-Anisidine, puriss, 99%+ CAS 104-94-9View Details
104-94-9 -
 Para AnisidineView Details
Para AnisidineView Details
104-94-9 -
 P-Anisidine CAS Number: 104-94-9View Details
P-Anisidine CAS Number: 104-94-9View Details
104-94-9 -
 Para AnisidineView Details
Para AnisidineView Details
104-94-9 -
 p-AnisidineView Details
p-AnisidineView Details
104-94-9 -
 Para Anisidine 99%, For LaboratoryView Details
Para Anisidine 99%, For LaboratoryView Details
104-94-9
