Guaiacol
Synonym(s):2-Methoxyphenol;Catechol monomethyl ether;Pyrocatechol monomethyl ether
- CAS NO.:90-05-1
- Empirical Formula: C7H8O2
- Molecular Weight: 124.14
- MDL number: MFCD00002185
- EINECS: 201-964-7
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-27 15:38:00
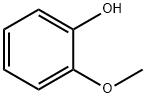
What is Guaiacol?
Absorption
In rats, guaiacol is rapidly absorbed, being present in the blood 5 minutes after oral administration, and reaching its peak plasma concentration in about 10 minutes. Its elimination from the blood is usually as rapid.
Description
Guaiacol, or?o-methoxyphenol, was first isolated from the tree resin guaiac by A. Sobrero in 1843. Today, it is manufactured by methylating catechol (o-dihydroxybenzene). It is used medically as an expectorant, antiseptic, and local anesthetic; it is also a precursor to flavorants and aromas,?including those incorporated in synthetic sandalwood.
Chemical properties
Guaiacol appears as white or slightly yellow crystals or colorless to light yellow transparent oily liquid. It has a distinctive scent. It is slightly soluble in water and benzene, also easily soluble in glycerol. And it is miscible with ethanol, ether, chloroform, oil and glacier acetic acid. Guaiacol is a phenolic natural product first isolated from Guaiac resin and the oxidation of lignin. It is also present in wood smoke, as a product of pyrolysis of lignin.
Occurrence
Detected in the distillation product from guaiac resin; guaiacol is found in castoreum oil, in the essential oil from fowers of Pandanus odoratissimus L , in the distillation waters of orange leaves, in the essential oil of Ruta Montana L and in the essential oil of tobacco leaves Also reported found in lemon peel oil, bog blueberry, asparagus, cabbage, celery, onion, chive, tomato, peppermint oil, rye bread, Parmesan cheese, butter, smoked fsh, meats, barley, dried bonito, malt, hardwood smoke, cognac, beer, brandy, rum, whiskies, sherry, grape wines, cocoa, coffee, tea, peanuts, popcorn, soybeans, avocado, beans, mushroom, sesame seed, mango, tamarind, rice dill, licorice, corn oil, cuttlefsh and other sources
The Uses of Guaiacol
Guaiacol is a precursor of vanillin and santalidol (a synthetic sandal- wood fragrance). it is obtained from wood tar by the destructive distillation of hardwood, by the distillation of the phenol fraction of coal tar, or through the use of o-dichlorobenzene. it is processed to yield vanillin. It is used as a reducing co-substrate for COX reactions. It is also used in the synthesis of spices and drugs (expectorants).
Background
Guaiacol is an agent thought to have disinfectant properties and used as an expectorant. Guaiacol is a phenolic natural product first isolated from Guaiac resin and the oxidation of lignin. Guaiacol is also present in wood smoke, as a product of pyrolysis of lignin. Guaiacol has been found in the urine of patients with neuroblastoma and pheochromocytoma.
Indications
Guaiacol is used in clinical applications as an expectorant, antiseptic and local anaesthetic. It is used as a traditional endodontic sedative. Pharmacological studies have shown that Guaiacol has the property of inducing cell proliferation and scavenging reactive oxygen radicals, and its free radical scavenging activity may be related to its effect on cell proliferation.
What are the applications of Application
Guaiacol is a phenolic natural product and reducing co-substrate for COX reactions
Definition
ChEBI: Guaiacol is a monomethoxybenzene that consists of phenol with a methoxy substituent at the ortho position. It has a role as an expectorant, a disinfectant, a plant metabolite and an EC 1.1.1.25 (shikimate dehydrogenase) inhibitor. It is functionally related to a catechol.
Preparation
Guaiacol can be obtained by diazotization and hydrolysis of anthranium anisole or obtained from fractionated of wood oil.
In the nature of guaiacol is presented in the guaiacum or pine oil. In the creosote oil obtained from wood dry distillation, guaiacol is the major ingredient. This product could be obtained through fractional distillation of creosote oil. Japan Osaka Refining Company takes o-nitrochlorobenzene as raw material, first synthesizes o-nitroanisole, and then reduces it to o-anisidine, and finally obtains the goods. China's production method is roughly the same. Ingredient consumption quota: 1250 kg / t of amino-containing anisole, 1500 kg / t of sulfuric acid (93%), 700 kg / t of sodium nitrite and 400 kg / t of copper sulfate.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 3 to 31 ppb; aroma characteristics at 1.0%: phenolic, smoky, spicy, medicinal, vanilla, savory meaty, woody with a bourbon whiskey casky nuance.
Taste threshold values
Taste characteristics at 2.0 ppm: woody, phenolic, bacon, savory, smoky and medicinal.
General Description
Guaiacol is a colorless to amber crystals or liquid. Density (of solid) 1.129 g / cm3. Solidifies at 28°C (82.4°F), but may remain liquid for a long time even at a much lower temperature. Slightly water soluble . Soluble in aqueous sodium hydroxide. It is an agent thought to have disinfectant properties and used as an expectorant.
Air & Water Reactions
Sensitive to air and light (darkens). Slightly water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Guaiacol may react with oxidizing materials. Guaiacol forms salts readily with bases.
Hazard
Toxic by ingestion and skin absorption.
Fire Hazard
Guaiacol is combustible.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Guaiacol, along with 2,4,6-trichloroanisole, is responsible for cork taint in wine. A method has been developed for extraction and quantitation of the two compounds.
Synthesis
Obtained from hardwood tar or synthetically from o-nitrophenol via o-anisidine.
Purification Methods
Crystallise guaiacol from *benzene/pet ether or distil it in a vacuum. [Beilstein 6 H 768, 6 IV 5563.]
Toxicity evaluation
LD50:900 mg / kg (rat, subcutaneous).
LD50: 3.7 mg / kg (rabbit, intravenously).
Oral administration of large amount can stimulate the esophagus and stomach, resulting in heart failure, collapse and death.
Side Effects
Guaiacol may cause moderate inflammation of the skin on contact; repeated exposure can result in contact dermatitis manifested by redness, swelling and blisters. Other possible side effects include sweating, intense thirst, nausea and vomiting, diarrhoea, cyanosis, restlessness, coma, hypotension, hyperventilation, abdominal pain, anaemia, convulsions, coma, swelling of the lungs followed by pneumonia.
Properties of Guaiacol
| Melting point: | 26-29 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 205 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 1.129 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.) |
| vapor density | 4.27 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 0.11 mm Hg ( 25 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| FEMA | 2532 | GUAIACOL |
| Flash point: | 180 °F |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | H2O: insoluble |
| form | Liquid After Melting |
| pka | 9.98(at 25℃) |
| color | Clear colorless to light yellow |
| PH | 5.4 (10g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | at 1.00 % in dipropylene glycol. phenolic smoke spice vanilla woody |
| Odor Threshold | 0.0074ppm |
| Water Solubility | 17 g/L (15 ºC) |
| FreezingPoint | 28℃ |
| Sensitive | Air Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,4553 |
| JECFA Number | 713 |
| BRN | 508112 |
| Dielectric constant | 11.0(-18℃) |
| Stability: | Stable, but air and light sensitive. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 90-05-1(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Phenol, 2-methoxy-(90-05-1) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Guaiacol (90-05-1) |
Safety information for Guaiacol
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P270:Do not eat, drink or smoke when using this product. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Guaiacol
| InChIKey | LHGVFZTZFXWLCP-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Guaiacol manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
Triveni Interchem Private Limited (Group Of Triveni Chemicals)
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
You may like
-
 Guaiacol supplierView Details
Guaiacol supplierView Details
90-05-1 -
 Guaiacol 98%View Details
Guaiacol 98%View Details -
 Guaiacol 98%View Details
Guaiacol 98%View Details -
 Ortho Guaiacol CAS No. 90-05-1View Details
Ortho Guaiacol CAS No. 90-05-1View Details
90-05-1 -
 Guaiacol, Grade Standard: Technical Grade, Packaging Size: 225View Details
Guaiacol, Grade Standard: Technical Grade, Packaging Size: 225View Details
90-05-1 -
 GuaiacolView Details
GuaiacolView Details
90-05-1 -
 Guaiacol Chemical for Consult Your Pharmacist Or PhysicianView Details
Guaiacol Chemical for Consult Your Pharmacist Or PhysicianView Details
90-05-1 -
 Guaiacol (2-Methoxyphenol) C7H8O2View Details
Guaiacol (2-Methoxyphenol) C7H8O2View Details
103-64-0
