Ammonium thiocyanate
Synonym(s):Ammonium rhodanide;Ammonium rhodanide solution;Ammonium sulfocyanide;Ammonium sulfocyanide, Ammonium rhodanide, Thiocyanic acid ammonium salt, Ammonium sulfocyanate;Ammonium thiocyanate
- CAS NO.:1762-95-4
- Empirical Formula: CHNS.H3N
- Molecular Weight: 76.12
- MDL number: MFCD00011428
- EINECS: 217-175-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-17 09:49:53

What is Ammonium thiocyanate?
Description
Ammonium thiocyanate is a colorless solid which absorbs moisture and becomes liquid. Molecularweight= 76.12; Boiling point= 115℃; Freezing/Meltingpoint=160℃, decomposes at 170℃; Heat of solution=3.1 3 105 J/kg. Hazard Identification (based on NFPA-704 M Rating System): Health 2, Flammability 1,Reactivity 1, Corrosive. Soluble in water.
Chemical properties
colourless or white crystals or powder
Chemical properties
Ammonium thiocyanate is a colorless solid which absorbs moisture, becoming liquid, known as the “liquor.”
The Uses of Ammonium thiocyanate
Colorless deliquescent crystals made by boiling an aqueous solution of ammonium cyanide with sulfur or polysulfides. It must be kept in a well-sealed container. The principal use for ammonium thiocyanate was in gold-toning formulas, but it was also used in a 5 percent solution to dissolve gelatin in overexposed carbon prints.
The Uses of Ammonium thiocyanate
Applied in the formation of novel two-dimensional Cd-SCN coordination solids with unusual and tailorable, checkerboard- or herringbone-patterned structures these structures are important steps toward technologically useful materials.1
The Uses of Ammonium thiocyanate
Used as a determination of iron, mercury, and silver.
The Uses of Ammonium thiocyanate
In matches; double-dyeing fabrics; photography; improving and increasing strength of silks weighted with tin salts; producing grayish-black coating on Zn; manufacture of transparent artificial resins, thiourea; in pesticides. Detection and determination of small quantities of Fe; determination of Ag, Hg, etc.
What are the applications of Application
Ammonium thiocyanate is an agent for the degradation of peptides
Definition
ammonium thiocyanate: A colourless, soluble crystalline compound,NH4NCS. It is made by theaction of hydrogen cyanide on ammoniumsulphide or from ammoniaand carbon disulphide in ethanol. Onheating, it turns into its isomerthiourea, SC(NH2)2. Its solutions givea characteristic blood-red colour withiron(III) compounds and so are employedas a test for ferric iron. Ammoniumthiocyanate is used as arapid fixative in photography and asan ingredient in making explosives.
Preparation
(NH4)2S is obtained from reacting hydrogen sulfide with excess of ammonia:
H2S + 2NH3 → (NH4)2S.
Production Methods
Ammonium thiocyanate (plus ammonium sulfide) [CAS: 12135-76-1] may be made by reaction of ammonia and carbon disulfide, a reaction which probably accounts for the presence of ammonium thiocyanate in the products of the destructive distillation of coal. This reaction corresponds to the formation of ammonium cyanate from ammonia and carbon dioxide.
General Description
Ammonium thiocyanate is a colorless crystalline solid. Ammonium thiocyanate is soluble in water. The primary hazard is the threat posed to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Ammonium thiocyanate is used in chemical analysis, in photography, as a fertilizer, and for many other uses.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Ammonium thiocyanate can release ammonia vapors if mixed with a chemical base or with an acid. Violent or explosive reactions have occurred when thiocyanates are mixed with oxidizing agents (such as chlorates(potassium chlorate), nitrates, nitric acid, and peroxides). Nitric acid violently oxidized a thiocyanate solution [Bretherick 1979 p. 121]. An explosion of guanidine nitrate demolished an autoclave built to withstand 50 atmospheres, in which Ammonium thiocyanate was being made from Ammonium thiocyanate and lead nitrate [C. Angew. Chem. 49:23 1936].
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust causes irritation of nose and throat. Ingestion causes dizziness, cramps, nervous disturbances. Dust irritates eyes. Can be absorbed through skin; prolonged contact may produce various skin eruptions, dizziness, cramps, nausea, and mild to severe disturbance of the nervous system.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Decomposes to form ammonia, hydrogen sulfide, and hydrogen cyanide. Oxides of nitrogen may also form. All of these products are toxic.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: hallucinations and distorted perceptions, nausea or vomiting, and other gastrointestinal effects. See also THIOCYANATES. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of NH3, NOx, SO,, and CN-. Incompatible with KClO3 and mixtures with Pb(NO3)2.
Potential Exposure
It has many uses in making matches, fabric processing; metals processing; chemical manufacturing, electroplating; zinc coating; liquid rocket propellents, fabric dyeing, polymerization catalyst, in photography. Used as a laboratory chemical. May be used as an agricultural chemical: herbicides, weed killers, defoliants.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and inducevomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Storage
Color Code—White: Corrosive or Contact Hazard;Store separately in a corrosion-resistant location. Prior to nitrate, since violent reactions occur. Store in tightly closedcontainers in a cool, well-ventilated area away from moisture, acid, acid fumes, or chlorine because toxic fumes arereleased. Where possible, automatically pump liquid fromdrums or other storage containers to process containers.working with this chemical you should be trained on itsproper handling and storage. Ammonium thiocyanate mustbe stored to avoid contact with Potassium chlorate and Lead
Shipping
UN2672 Ammonia solutions, relative density between 0.880 and 0.957 at 15 C in water, with . 10 % but not . 35 % ammonia, Hazard class: 8; Labels: 8- Corrosive material. UN3082 Environmentally hazardous substances, liquid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9- Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required. UN3077 Environmentally hazardous substances, solid, n.o.s., Hazard class: 9; Labels: 9-Miscellaneous hazardous material, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it three times from dilute HClO4 to give material optically transparent at wavelengths longer than 270nm. It has also been crystallised from absolute MeOH or from acetonitrile.
Incompatibilities
Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides. Acts as an acid; incompatible with lead nitrate, chlorates, nitric acid, acid, acid fumes. In the presence of moisture, this chemical is corrosive to brass, copper, iron. Ammonium thiocyanate liquor can release ammonia vapors if mixed with a chemical base or with an acid. Violent or explosive reactions have occurred when thiocyanates are mixed with oxidizing agents . Nitric acid violently oxidized a thiocyanate solution . An explosion of guanidine nitrate demolished an autoclave built to withstand 50 atmospheres, in which it was being made from ammonium thiocyanate and lead nitrate .
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. Slowly add to large container of water. Stir in slight excess of soda ash. Decant or siphon liquid from sludge, neutralize with HCl and flush to sewer. Sludge may be landfilled.
Properties of Ammonium thiocyanate
| Melting point: | 152-154 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 262.85°C |
| Density | 1.3 |
| vapor pressure | <1 hPa (20 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.5300 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 190 °C |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 1 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| color | clear colorless or white |
| Specific Gravity | 1.305 |
| PH Range | 4.5 - 6.0 |
| PH | 4.8-5.8 (50g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Water Solubility | 163 g/100 mL (20 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Light Sensitive & Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,561 |
| BRN | 3595135 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH: IDLH 25 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with strong acids, strong oxidizing agents. Forms explosive mixtures with lead nitrate. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 1762-95-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Ammonium thiocyanate (1762-95-4) |
Safety information for Ammonium thiocyanate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Ammonium thiocyanate
Ammonium thiocyanate manufacturer
JSK Chemicals
ASM Organics
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran
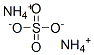

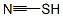

You may like
-
 AmmoniumThiocyanate 99%View Details
AmmoniumThiocyanate 99%View Details -
 Ammonium thiocyanate 98%View Details
Ammonium thiocyanate 98%View Details -
 Ammonium thiocyanate CAS 1762-95-4View Details
Ammonium thiocyanate CAS 1762-95-4View Details
1762-95-4 -
 Ammonium thiocyanate CAS 1762-95-4View Details
Ammonium thiocyanate CAS 1762-95-4View Details
1762-95-4 -
 Ammonium thiocyanate 1M (1N) standardized solution CAS 1762-95-4View Details
Ammonium thiocyanate 1M (1N) standardized solution CAS 1762-95-4View Details
1762-95-4 -
 Ammonium Thiocyanate ACS CAS 1762-95-4View Details
Ammonium Thiocyanate ACS CAS 1762-95-4View Details
1762-95-4 -
 Ammonium thiocyanate solution CASView Details
Ammonium thiocyanate solution CASView Details -
 Ammonium thiocyanate solution CASView Details
Ammonium thiocyanate solution CASView Details
