Sodium thiocyanate
Synonym(s):Sodium thiocyanate;Sodium thiocyanate solution;Sodium isothiocyanate;Sodium rhodanate;Sodium rhodanide
- CAS NO.:540-72-7
- Empirical Formula: CNNaS
- Molecular Weight: 81.07
- MDL number: MFCD00011123
- EINECS: 208-754-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-12-19 17:28:17
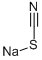
What is Sodium thiocyanate?
Chemical properties
white crystalline powder
Physical properties
Colorless crystals or white powder; deliquescent; melts at 287°C; very soluble in water; soluble in alcohol.
The Uses of Sodium thiocyanate
Sodium Thiocyanate is used widely in chemical synthesis as source of thiocyanate anion such as in the conversion of alkyl halides to alkylthiocyanates.
The Uses of Sodium thiocyanate
manufacture of other thiocyanates, especially organic.
What are the applications of Application
Sodium thiocyanate is a compound used to convert alkyl halides into the corresponding alkylthiocyanates
Definition
ChEBI: An organic sodium salt which is the monosodium salt of thiocyanic acid.
Preparation
Sodium thiocyanate is prepared by boiling an aqueous solution of sodium cyanide with sulfur: NaCN + S → NaSCN.
Reactions
Sodium thiocyanate is an analytical reagent for measuring iodide. Other uses are dyeing and printing textiles, preparing thiocyanate salts, and nickel plating. Used in titrimetry.
General Description
Odorless white solid. Sinks and mixes with water.
Air & Water Reactions
Water soluble.
Reactivity Profile
Nitric acid violently oxidized a thiocyanate solution [Bretherick 1979 p. 121]. Caution should be exercised in treating a thiocyanate with an oxidizing agent such as a peroxide or chlorate as such mixtures have been known to explode. Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating oxides of sulfur and nitrogen may form in fire [USCG, 1999]. Carbonyl sulfide is produced in a violent reaction by the mixture of sulfuric acid and Sodium thiocyanate.
Health Hazard
Inhalation of dust causes irritation of nose and throat. Ingestion of large doses causes vomiting, extreme cerebral excitement, convulsions, and death in 10-48 hrs.; chronic poisoning can cause flu-like symptoms, skin rashes, weakness, fatigue, vertigo, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, confusion. Contact with eyes causes irritation. Prolonged contact with skin may produce various skin eruptions, dizziness, cramps, nausea, and mild to severe disturbance of the nervous system.
Fire Hazard
Special Hazards of Combustion Products: Irritating oxides of sulfur and nitrogen may form in fire.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Poison by ingestion, intravenous, and subcutaneous routes. Moderately toxic by intraperitoneal route. Large doses taken internally cause vomiting, convulsions. Chronic poisoning is manifested by weakness, confusion, diarrhea, and skin rashes. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx, SOx, and Na2O. See also THIOCYANATES.
Purification Methods
It is recrystallised from EtOH or Me2CO, and the mother liquor is removed from the crystals by centrifugation. It is very deliquescent and should be kept in an oven at 130o before use. It can be dried in a vacuum at 120o/P2O5 [Partington & Winterton Trans Faraday Soc 30 1104 1934]. Its solubility in H2O is 113% at 10o, 178% at 46o, 225.6% at 101.4o; in MeOH 35% at 15.8o, 51% at 48o, 53.5% at 52.3o; in EtOH 18.4% at 18.8o, 24.4% at 70.9o; and in Me2CO 6.85% at 18.8o and 21.4% at 56o [Hughes & Mead J Chem Soc 2282 1929]. Sodium thiocyanate has also been recrystallised from water, acetonitrile or from MeOH using Et2O for washing, then dried at 130o, or dried under vacuum at 60o for 2days. [Strasser et al. J Am Chem Soc 107 789 1985, Szezygiel et al. J Am Chem Soc 91 1252 1987.] (The latter purification removes material reacting with iodine.) Sodium thiocyanate solutions can be freed from traces of iron by repeated batch extractions with Et2O.
Properties of Sodium thiocyanate
| Melting point: | 287 °C (dec.) (lit.) |
| Density | 1.295 g/mL at 20 °C |
| vapor pressure | <1 hPa (20 °C) |
| storage temp. | Store at +5°C to +30°C. |
| solubility | H2O: 8 M at 20 °C, clear, colorless |
| form | Solid |
| color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| PH | 6-8 (100g/l, H2O, 20℃) |
| Water Solubility | 139 g/100 mL (21 ºC) |
| Sensitive | Hygroscopic |
| Merck | 14,9327 |
| BRN | 3594965 |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH: IDLH 25 mg/m3 |
| Stability: | Stable. Incompatible with acids, strong bases. May decompose on exposure to light. Contact with acid liberates highly toxic gas. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 540-72-7(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Sodium thiocyanate (540-72-7) |
Safety information for Sodium thiocyanate
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Corrosion Corrosives GHS05  Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H318:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H412:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. |
Computed Descriptors for Sodium thiocyanate
| InChIKey | VGTPCRGMBIAPIM-UHFFFAOYSA-M |
Sodium thiocyanate manufacturer
Rasayan Trading Co.
New Products
Indole Methyl Resin tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Boc-His(Boc)-OH 2-CTC Resin 4-Chloro-7-tosy1-7Hpyrrolo[2,3-d]pyrimidine 5,7-Dibromo-1H-indole 2,5-dichloro-N-hydroxy-4,6-dimethylpyridine-3-carboximidamide 2,2-Dimethoxy-7-azaspiro[3.5]nonane hydrochloride 4-chloromethyl-5-methyl-1,3-dioxol-2-one (DMDO-Cl) R-2-BENZYLOXY PROPIONIC ACID 1,1’-CARBONYLDIIMIDAZOLE 1,1’-CARBONYLDI (1,2-4 TRIAZOLE) N-METHYL INDAZOLE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID 4-((2-hydroxyethyl)thio)benzoic acid 1-(TERT-BUTOXYCARBONYL)-2-PYRROLIDINONE Methyl 6-methylnicotinate 3-Pyridineacrylic acid tert-Butyl carbazate TETRAHYDRO-2H-PYRAN-3-OL 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 1,3-Diethyl-1,3-Diphenylurea Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylateRelated products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 Sodium thiocyanate 98%View Details
Sodium thiocyanate 98%View Details -
 Sodium thiocyanate, For analysis ACS CAS 540-72-7View Details
Sodium thiocyanate, For analysis ACS CAS 540-72-7View Details
540-72-7 -
 Sodium thiocyanate, For analysis ACS CAS 540-72-7View Details
Sodium thiocyanate, For analysis ACS CAS 540-72-7View Details
540-72-7 -
 Sodium thiocyanate, For analysis ACS CAS 540-72-7View Details
Sodium thiocyanate, For analysis ACS CAS 540-72-7View Details
540-72-7 -
 Sodium Thiocyanate CASView Details
Sodium Thiocyanate CASView Details -
 SODIUM THIOCYANATE, 25kgView Details
SODIUM THIOCYANATE, 25kgView Details
540-72-7 -
 Sodium Thiocyanate Powder, Grade Standard: Technical GradeView Details
Sodium Thiocyanate Powder, Grade Standard: Technical GradeView Details
540-72-7 -
 Sodium Thiocyanate, 25kgView Details
Sodium Thiocyanate, 25kgView Details
540-72-7
