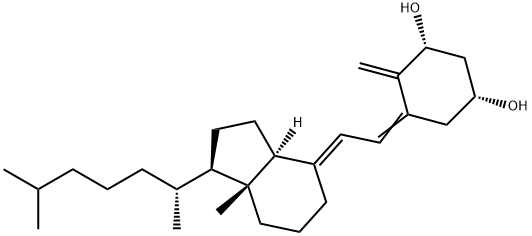
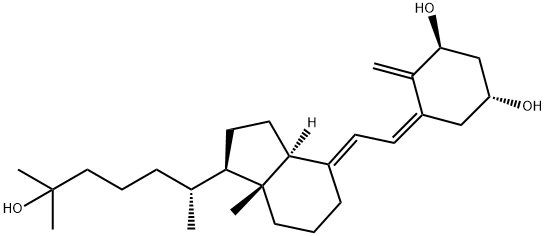
Alfacalcidol
Synonym(s):1α-Hydroxycholecalciferol;1α-Hydroxyvitamin D3;1α-OH-D₃;Alfacalcidol;Vitamin D₃, 1α-Hydroxy- - CAS 41294-56-8 - Calbiochem
- CAS NO.:41294-56-8
- Empirical Formula: C27H44O2
- Molecular Weight: 400.64
- MDL number: MFCD00868328
- EINECS: 255-297-1
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-23 21:28:46
What is Alfacalcidol?
Absorption
Alfacalcidol is absorbed passively and almost completely in the small intestine.
Toxicity
There is a discrepancy across a number of reported LD50 values for alfacalcidol, which can be attributed to differences in the procedures used in laboratories. Oral LD50 in mice ranges from 440 to 490 mcg/kg. Intravenous in mice was 290 mcg/kg; however, another source presented 56 mcg/kg in female mice and 71 mcg/kg in male mice. Oral LD50 in rats ranges from 340 to 720 mcg/kg.
In case of an acute accidental overdose following oral administration, emesis or gastric lavage can be induced to prevent further drug absorption. Mineral oil may be used to promote fecal drug elimination in instances where the drug was already absorbed in the stomach.
Alfacalcidol overdose can lead to hypercalcemia, hypercalciuria, and hyperphosphatemia. Similarly, a high intake of calcium and phosphate concurrently with a therapeutic dose of alfacalcidol can result in those conditions. Hypercalcemia most commonly presents with headache, weakness, hypertension, somnolence, dizziness, sweating, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation, polyuria, polydipsia and muscle and bone pain, and metallic taste. Hypercalcemia should be responded to with discontinuation of alfacalcidol, a low calcium diet and withdrawal of calcium supplements. Prolonged hypercalcemia can lead to nephrocalcinosis, nephrolithiasis, and reduced kidney function. In cases of severe hypercalcemia, general supportive measures are recommended, which may include forced diuresis and close monitoring of renal function, electrolytes, and electrocardiographs. Monitoring for abnormalities is especially critical in patients receiving digitalis glycosides. Management with glucocorticosteroids, loop diuretics, bisphosphonates, and calcitonin, as well as hemodialysis with low calcium content, may be considered.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
One-Alpha ,Leo ,UK ,1978
The Uses of Alfacalcidol
A synthetic analog of Calcitiol (the hormonal form of vitamin D3), which shows identical potency with respect to stimulation of intestinal calcium absorption and bone mineral mobilization. Vitamin D source
Background
Alfacalcidol, or 1-alpha-hydroxycholecalciferol or 1-alpha-hydroxyvitamin D3, is a non-endogenous analogue of vitamin D. It plays an essential function in calcium homeostasis and bone metabolism. Alfacaldisol is activated by the enzyme 25-hydroxylase in the liver to mediate its effects in the body, or most importantly, the kidneys and bones. The pharmacological actions of alfacalcidol are prolonged than vitamin D because a negative feedback mechanism regulates the final activation step of vitamin D in the kidneys.
Alfacalcidol is available in oral and intravenous formulations. In Canada, it is marketed as ONE-ALPHA, which manages hypocalcemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, and osteodystrophy in adults with chronic renal failure. In approving European countries, alfacalcidol is also indicated for managing nutritional and malabsorptive rickets and osteomalacia, vitamin D-dependent rickets and osteomalacia, and hypophosphataemic vitamin D resistant rickets and osteomalacia.
What are the applications of Application
1α-Hydroxyvitamin D3 is a form of vitamin D that helps the body absorb calcium from food
Indications
Alfacalcidol is indicated in adult patients with chronic renal failure for the management of hypocalcemia, secondary hyperparathyroidism, or osteodystrophy.
Alfacalcidol is indicated in the management of nutritional and malabsorptive rickets and osteomalacia, vitamin D-dependent rickets and osteomalacia, and hypophosphataemic vitamin D resistant rickets and osteomalacia.
Definition
ChEBI: A member of the class of D3 vitamins that is calciol in which the hydrogen at the 1alpha position is replaced by a hydroxy group. It is an active metabolite of cholecalciferol, which performs important functions in reg lation of the calcium balance and the bone metabolism.
Manufacturing Process
1. Preparation of 1,4-cyclized adduct of cholesta-1,5,7-trien-β-ol and 4-
phenyl-1,2,4-triazoline-3,5-dione: a solution of 400 mg of cholesta-1,5-7-
trien-3β-ol in 30 ml of tetrahydrofuran is cooled with ice, and 190 mg of 4-
phenyl-1,2,4-triazoline-3,5-dione is added little by little to the solution under
agitation. The mixture is agitated at room temperature for 1 hour and the
solvent is distilled under reduced pressure. The residue is purified by
chromatography using a column packed with silica gel. Fractions eluted with
ether-hexane (7:3 v/v) are collected and recrystallization from ether gives
550 mg of a 1,4-cyclized adduct of cholesta-1,5,7-trien-3β-ol and 4-phenyl-
1,2,4-triazoline-3,5-dione having a melting point of 178°C to 182°C.
2. Preparation of 1,4-cyclized adduct of cholesta-5,7-dien-3β-ol-1α-epoxide
and 4-phenyl-1,2,4-triazoline-3,5-dione: 1.25 g of the 1,4-cyclized adduct of
cholesta-1,5,7-trien-3β-ol and 4-phenyl-1,2,4-triazoline-3,5-dione is dissolved
in 50 ml of chloroform, and 560 mg of m-chloroperbenzoic acid is added to
the solution. The mixture is agitated for 20 hours at room temperature, and
200 mg of m-chloroperbenzoic acid is further added and the mixture is
agitated again for 20 hours. The reaction mixture liquid is diluted with
chloroform, washed with a 10% aqueous solution of potassium carbonate and
dried with magnesium sulfate. Then, the solvent is distilled under reduced
pressure. The residue is purified by silica gel chromatography, and first
effluent fractions eluted with ether are collected, and recrystallization from
methanol gives 680 g of a crystal melting at 172°C to 173°C. The second
ether effluent fractions are collected, and recrystallization from methanol gives
400 mg of a 1,4-cyclized adduct of cholesta-5,7-dien-3β-ol-1α,2α-epoxide and
4-phenyl-1,2,4-triazoline-3,5-dione having a melting point of 152°C to 154°C.
3. Preparation of cholesta-5,7-diene-1α,3β-diol: a solution of 500 mg of the
1,4-cyclized adduct of cholesta-5,7-dien-3β-ol-1α,2α-epoxide and 4-phenyl-
1,2,4-triazoline-3,5-dione in 40 ml of tetrahydrofuran is added dropwise under
agitation to a solution of 600 mg of lithium aluminum hydride in 30 ml of THF.
Then, the reaction mixture liquid is gently refluxed and boiled for 1 hour and
cooled, and a saturated aqueous solution of sodium sulfate is added to the
reaction mixture to decompose excessive lithium aluminum hydride. The
organic solvent layer is separated and dried, and the solvent is distilled. The residue is purified by chromatography using a column packed with silica gel.
Fractions eluted with ether-hexane (7:3 v/v) are collected, and
recrystallization from the methanol gives 400 mg of cholesta-5,7-diene-1α,3β-
diol.
4. Preparation of 1α,3β-dihydroxyprovitamin D3: a solution of 25 mg of
cholesta-5,7-diene-1α,3β-diol in 650 ml of ether is subjected to radiation of
ultraviolet rays for 14 minutes in an argon gas atmosphere by passing it
through a Vycor filter using a 200-W high pressure mercury lamp (Model
654A-36 manufactured by Hanobia). The solvent is distilled at room
temperature under reduced pressure. This operation is repeated twice, and 50
mg of the so obtained crude product is fractionated by chromatography using
a column packed with 20 g of Sephadex LH-20. The first effluent fractions
eluted with chloroform-hexane (65:35 v/v) give 13.5 mg of oily 1α,3β-
dihydroxyprovitamin D3. The composition exhibits a maximum ultraviolet
absorption at 260 nm in an ether solution.
5. Preparation of 1α-hydroxycholecalciferol: a solution of 13.5 mg of 1α,3β-
dihydroxyprovitamin D3 in 200 mi of ether is allowed to stand still in the dark
at room temperature in an argon gas atmosphere for 2 weeks. During this
period, the position of the maximum ultraviolet absorption is shifted from 260
nm to 264 nm, and the absorption intensity becomes 1.6 times as high as the
original intensity. The solvent is distilled at room temperature under reduced
pressure, and the residue is purified by chromatography using a column
packed with 10 g of Sephadex LH-20. The fractions eluted with chloroformhexane
(65:35 v/v) give 6.5 mg of oily 1α-hydroxycholecalciferol.
Therapeutic Function
Calcium regulator, Vitamin
General Description
Has biological properties similar to 1α-Hydroxyvitamin D2 (Cat. No. 679100). Converted to active Calcitriol (1α,25-Dihydroxyvitamin D3; Cat. No. 679101) in vivo. Inhibits the formation of nephrocalcinosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats fed on low zinc diets.
Pharmacokinetics
Alfacalcidol works to increase serum levels of calcium by stimulating intestinal calcium absorption, reabsorption of calcium from bone, and possibly the renal reabsorption of calcium. It also modestly promotes intestinal phosphorus absorption. In patients with renal failure, alfacalcidol increased intestinal calcium and phosphorus absorption in a dose-related manner. This increase in calcium and phosphorus levels occurs within three days following drug administration: this effect was reversed within three days of drug discontinuation. In patients with chronic renal failure, serum calcium levels were elevated while parathyroid hormone and alkaline phosphatase levels returned to normal levels within five days following alfacalcidol administration. Since alfacalcidol suppresses parathyroid hormone, a reduction in parathyroid hormone levels is achieved more rapidly in patients on intermittent intravenous therapy, with significant reductions occurring within three months of therapy. In patients receiving daily oral therapy of alfacalcidol, the time it takes alfacalcidol to normalize plasma calcium levels may be up to several months, possibly reflecting calcium being utilized for bone mineralization. In patients with nutritional osteomalacia, alfacalcidol increased calcium absorption with six hours of oral administration and the effects peaked at 24 hours.
Clinical Use
Vitamin D analogue:
Increase serum calcium levels
Suppression of PTH production
Drug interactions
Potentially hazardous interactions with other drugs
Carbamazepine, fosphenytoin, phenytoin,
phenobarbital and primidone may increase
metabolism of alfacalcidol, necessitating larger doses
than normal to produce the desired effect.
Metabolism
Alfacalcidol is rapidly converted in the liver to 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D, which is essentially the metabolite of vitamin D that regulates calcium and phosphate metabolism. Alfacalcidol is further metabolized to other polar inactive metabolites, excreted primarily through the bile.
Metabolism
Alfacalcidol is hydroxylated in the liver by the enzyme vitamin D 25-hydroxylase to form the active 1,25-dihydroxycolecalciferol (calcitriol). Calcitriol is inactivated in both the kidney and the intestine, through the formation of a number of intermediates including the formation of the 1,24,25-trihydroxy derivatives. Vitamin D compounds and their metabolites are excreted mainly in the bile and faeces with only small amounts appearing in urine; there is some enterohepatic recycling but it is considered to have a negligible contribution to vitamin D status.
Properties of Alfacalcidol
| Melting point: | 134-136°C |
| Boiling point: | 531.5±50.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.01±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | −20°C |
| solubility | Practically insoluble in water, freely soluble in ethanol (96 per cent), soluble in fatty oils. |
| form | White crystalline solid |
| pka | 14.43±0.40(Predicted) |
| color | White to Almost white |
| λmax | 264nm(Diethyl ether)(lit.) |
| Merck | 14,4819 |
| Stability: | Light Sensitive |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 41294-56-8(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Alphacalcidol (41294-56-8) |
Safety information for Alfacalcidol
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H300:Acute toxicity,oral |
Computed Descriptors for Alfacalcidol
| InChIKey | OFHCOWSQAMBJIW-GITLSTMWSA-N |
| SMILES | [C@@H]1(O)CC(=C/C=C2\CCC[C@@]3(C)[C@@]\2([H])CC[C@@H]3[C@H](C)CCCC(C)C)C(=C)[C@H](O)C1 |
Alfacalcidol manufacturer
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran


You may like
-
 41294-56-8 98%View Details
41294-56-8 98%View Details
41294-56-8 -
 Alfacalcidol 99%View Details
Alfacalcidol 99%View Details -
 Alfacalcidol 99%View Details
Alfacalcidol 99%View Details -
 Alfacalcidol CAS 41294-56-8View Details
Alfacalcidol CAS 41294-56-8View Details
41294-56-8 -
 Alfacalcidol 41294-56-8 99%View Details
Alfacalcidol 41294-56-8 99%View Details
41294-56-8 -
 Alfacalcidol 99%View Details
Alfacalcidol 99%View Details
41294-56-8 -
 Alfacalcidol CAS 41294-56-8View Details
Alfacalcidol CAS 41294-56-8View Details
41294-56-8 -
 1α-Hydroxyvitamin D3 CAS 41294-56-8View Details
1α-Hydroxyvitamin D3 CAS 41294-56-8View Details
41294-56-8
