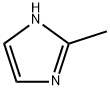
Methimazole
Synonym(s):1-Methyl-2-imidazolethiol;1-Methyl-2-mercaptoimidazole;2-Mercapto-1-methylimidazole;MET;Methimazole
- CAS NO.:60-56-0
- Empirical Formula: C4H6N2S
- Molecular Weight: 114.17
- MDL number: MFCD00179321
- EINECS: 200-482-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-02-23 21:28:46
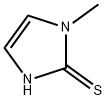
What is Methimazole?
Absorption
Absorption of methimazole after oral administration is rapid and extensive, with an absolute bioavailability of approximately 0.93 and a Tmax ranging from 0.25 to 4.0 hours. Cmax is slightly, but not significantly, higher in hyperthyroid patients, and both Cmax and AUC are significantly affected by the oral dose administered.
Toxicity
The oral LD50 of methimazole in rats is 2250 mg/kg. Signs and symptoms of methimazole overdose may include gastrointestinal distress, headache, fever, joint pain, pruritus, and edema. More serious adverse effects, such as aplastic anemia or agranulocytosis, may manifest within hours to days. Hepatitis, nephrotic syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis, and CNS effects such as neuropathy or CNS depression/stimulation are also potential, albeit less frequent, results of overdose.
Management of overdose involves supportive treatment as dictated by the patient's status. This may involve monitoring of the patient's vital signs, blood gases, serum electrolytes, or bone marrow function as indicated.
Chemical properties
White Solid
Originator
Favistan ,Asta
The Uses of Methimazole
Methimazole is a thiourea antithyroid agent that prevents iodine organification, thus inhibiting the synthesis of thyroxine. Antihyperthyroid
The Uses of Methimazole
Methimazole also directly disrupts thyroxine and triiodothyronin sysnthesis in the thyroid gland, and it is used for the same indications as propylthiouracil and methylthiouracil to treat hyperfunctioning thyroid glands in patients with Basedow’s disease.
The Uses of Methimazole
2-Mercapto-1-methylimidazole was employed as hydrophobic charge-induction chromatography ligand for antibody purification. It was also used in preparation of nitrile functionalized methimazole-based room temperature ionic liquids.
Background
Methimazole is a thionamide antithyroid agent that inhibits the synthesis of thyroid hormones. It was first introduced as an antithyroid agent in 1949 and is now commonly used in the management of hyperthyroidism, particularly in those for whom more aggressive options such as surgery or radioactive iodine therapy are inappropriate.
On a weight basis, methimazole is 10 times more potent than the other major antithyroid thionamide used in North America, propylthiouracil, and is the active metabolite of the pro-drug carbimazole, which is an antithyroid medication used in the United Kingdom and parts of the former British Commonwealth. Traditionally, methimazole has been preferentially used over propylthiouracil due to the risk of fulminant hepatotoxicity carried by the latter, with propylthiouracil being preferred in pregnancy due to a perceived lower risk of teratogenic effects. Despite documented teratogenic effects in its published labels, the true teratogenicity of methimazole appears to be unclear and its place in therapy may change in the future.
Indications
In the United States, methimazole is indicated for the treatment of hyperthyroidism in patients with Graves' disease or toxic multinodular goiter for whom thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy are not appropriate treatment options. Methimazole is also indicated for the amelioration of hyperthyroid symptoms in preparation for thyroidectomy or radioactive iodine therapy.
In Canada, methimazole carries the above indications and is also indicated for the medical treatment of hyperthyroidism regardless of other available treatment options.
What are the applications of Application
Methimazole is a JAK/STAT signaling pathway inhibitor
Definition
ChEBI: Methimazole is a member of the class of imidazoles that it imidazole-2-thione in which a methyl group replaces the hydrogen which is attached to a nitrogen. It has a role as an antithyroid drug.
Manufacturing Process
2 Methods of preparation of thiamazole:
1. To 2,2-diethoxyethylamine methylisothiocyanate was added and mixed after then 1-(2,2-diethoxy-ethyl)-3-methylthiourea was obtained.
The reaction of the 1-(2,2-diethoxyethyl)-3-methylthiourea with sulfuric acid yield thiamazole.
2. 1,1-Diethoxyethane was treated by bromine in the presence CaCO3 and 2- bromo-1,1-diethoxyethane was obtained.
Then to the 2-bromo-1,1-diethoxyethane methylamine was added, mixed and reaction mixture was heated to 120°-130°C in autoclave. As the result (2,2- diethoxyethyl)methylamine was obtained.
(2,2-Diethoxyethyl)methylamine reacted with potassium thiocyanate in the presence of hydrochloric acid and give the thiamazole, yellow crystallic precipitate, melting point 144°-147°C.
brand name
Tapazole (Jones); Tapazole (King) .
Therapeutic Function
Thyroid inhibitor
General Description
Methimazole, 1-methylimidazole-2-thiol (Tapazole), occurs as a white to off-white, crystallinepowder with a characteristic odor and is freely soluble inwater. A 2% aqueous solution has a pH of 6.7 to 6.9. It shouldbe packaged in well-closed, light-resistant containers.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Methimazole is a thiourea antithyroid agent that prevents iodine organification, thus inhibiting the synthesis of thyroxine.
Pharmacokinetics
Methimazole inhibits the synthesis of thyroid hormones resulting in an alleviation of hyperthyroidism. Onset of action occurs within 12 to 18 hours, and its duration of action is 36 to 72 hours, likely due to concentration of methimazole and some metabolites within the thyroid gland after administration.
The most serious potential side effect of methimazole therapy is agranulocytosis, and patients should be instructed to monitor for, and report, any signs or symptoms of agranulocytosis such as fever or sore throat. Other cytopenias may also occur during methimazole therapy. There also exists the potential for severe hepatic toxicity with the use of methimazole, and monitoring for signs and symptoms of hepatic dysfunction, such as jaundice, anorexia, pruritus, and elevation in liver transaminases, is prudent in patients using this therapy.
Clinical Use
Methimazole is indicated in the treatment of hyperthyroidism.It is more potent than propylthiouracil. The side effectsare similar to those of propylthiouracil. As with otherantithyroid drugs, patients using this drug should be undermedical supervision. Also, like the other antithyroid drugs,methimazole is most effective if the total daily dose is subdividedand given at 8-hour intervals.
Safety Profile
Poison by subcutaneous route. Moderately toxic by ingestion and intraperitoneal routes. Human teratogenic effects. An experimental teratogen. Experimental reproductive effects. Questionable carcinogen with experimental neoplastigenic data. Human mutation data reported. An antithyroid drug. When heated to decomposition it emits very toxic fumes of NOx and SOx. See also MERCAPTANS.
Synthesis
Methimazole, 1-methyl-2-imidazolthiol (25.2.5), is synthesized by reacting aminoacetic aldehyde diethylacetal with methylisothiocyanate and subsequent hydrolysis of the acetal group of the resulting disubstituted urea derivative 25.2.4 by a solution of sulfuric acid, during which a simultaneous cyclization reaction takes place, forming the imidazole ring of the desired methimazole .

Veterinary Drugs and Treatments
Methimazole is considered by most clinicians to be the agent
of choice when using drugs to treat feline hyperthyroidism.
Propylthiouracil has significantly higher incidences of adverse
reactions
when compared to methimazole and is rarely used today.
Transdermal methimazole (in PLO gel; 2.5 mg twice daily) has been
used with some therapeutic success in cats that do not tolerate oral
dosing. Efficacy may require four or more weeks to detect. Studies
are ongoing.
Methimazole appears to be useful for the prophylactic prevention
of cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in dogs.
Metabolism
Methimazole is rapidly and extensively metabolized by the liver, mainly via the CYP450 and FMO enzyme systems. Several metabolites have been identified, though the specific enzyme isoforms responsible for their formation are not entirely clear. One of the first methimazole metabolites identified, 3-methyl-2-thiohydantoin, may contribute to antithyroid activity - its antithyroid activity has been demonstrated in rats and may explain the prolonged duration of iodination inhibition following administration despite methimazole's relatively short half-life.
A number of metabolites have been investigated as being the culprits behind methimazole-induced hepatotoxicity. Both glyoxal and N-methylthiourea have established cytotoxicity and are known metabolic products of methimazole's dihydrodiol intermediate. Sulfenic and sulfinic acid derivatives of methimazole are thought to be the ultimate toxicants responsible for hepatotoxicity, though their origin is unclear - they may arise from direct oxidation of methimazole via FMO, or from oxidation of N-methylthiourea further downstream in the metabolic process.
Purification Methods
Crystallise it from EtOH. UV: at 251nm (H2O), 260nm (EtOH) and 267nm (CHCl3). [Lawson max & Morley J Chem Soc 1103 1956, Beilstein 24 H 17, 24 III/IV 61.]
Properties of Methimazole
| Melting point: | 144-147 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 280 °C |
| Density | 1.176 (estimate) |
| refractive index | 1.5000 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 280°C |
| storage temp. | 2-8°C |
| solubility | 200g/l |
| pka | 12.37±0.50(Predicted) |
| form | Crystalline Powder |
| color | White to slightly cream or pale buff |
| Water Solubility | soluble |
| Merck | 14,5971 |
| BRN | 108646 |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 60-56-0(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 3 (Vol. 79) 2001 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Methimazole(60-56-0) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Methimazole (60-56-0) |
Safety information for Methimazole
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Health Hazard GHS08 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H302:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P312:IF SWALLOWED: call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician IF you feel unwell. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. P308+P313:IF exposed or concerned: Get medical advice/attention. |
Computed Descriptors for Methimazole
Methimazole manufacturer
Related products of tetrahydrofuran
![2-Ethylhexyl 10-ethyl-4-[[2-[(2-ethylhexyl)oxy]-2-oxoethyl]thio]-4-methyl-7-oxo-8-oxa-3,5-dithia-4-stannatetradecanoate](https://img.chemicalbook.in/CAS/GIF/57583-34-3.gif)

You may like
-
 Methimazole 98%View Details
Methimazole 98%View Details
60-56-0 -
 2-Mercapto-1-methylimidazole CAS 60-56-0View Details
2-Mercapto-1-methylimidazole CAS 60-56-0View Details
60-56-0 -
 Methimazole 99% CAS 60-56-0View Details
Methimazole 99% CAS 60-56-0View Details
60-56-0 -
 Methimazole CAS 60-56-0View Details
Methimazole CAS 60-56-0View Details
60-56-0 -
 Methimazole CAS 60-56-0View Details
Methimazole CAS 60-56-0View Details
60-56-0 -
 2-Mercapto-1-methylimidazole CAS 60-56-0View Details
2-Mercapto-1-methylimidazole CAS 60-56-0View Details
60-56-0 -
 Methimazole CAS 60-56-0View Details
Methimazole CAS 60-56-0View Details
60-56-0 -
 Methimazole CAS 60-56-0View Details
Methimazole CAS 60-56-0View Details
60-56-0