Acetyl chloride
Synonym(s):Acetic acid chloride, Acetoxy chloride;Acetyl chloride
- CAS NO.:75-36-5
- Empirical Formula: C2H3ClO
- Molecular Weight: 78.5
- MDL number: MFCD00000719
- EINECS: 200-865-6
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
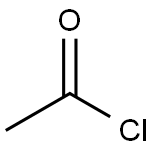
What is Acetyl chloride?
Description
Acetyl chloride is a colourless to light yellow liquid with a pungent and choking odour. Acetic chloride is highly flammable and reacts violently with DMSO, water, lower alcohols, and amines to generate toxic fumes. Along with air, acetic chloride may form an explosive mixture. It is incompatible with water, alcohols, amines, strong bases, strong oxidising agents, and most common metals. On decomposition when heated, acetic chloride produces carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen chloride, and phosgene.
Chemical properties
colourless to light yellow liquid with a pungent
Chemical properties
Acetic chloride is a colorless to light yellow liquid with a pungent and choking odor. Acetic chloride is highly flammable, reacts violently with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), water, lower alcohols, and amines to generate toxic fumes. Together with air, acetic chloride may form an explosive mixture. It is incompatible with water, alcohols, amines, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents, and most common metals. On decomposition when heated, acetic chloride produces carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen chloride, and phosgene.
Chemical properties
Acetyl chloride is a highly flammable, colorless, fuming liquid with a pungent odor
Occurence
Acetyl chloride is not expected to exist in nature, because contact with water would hydrolyze it into acetic acid and hydrogen chloride. In fact, if handled in open air it releases white "smoke" resulting from hydrolysis due to the moisture in the air. The smoke is actually small droplets of hydrochloric acid and acetic acid formed by hydrolysis.
The Uses of Acetyl chloride
Acetyl chloride acts as a reagent for the preparation of esters and amides of acetic acid. It is also useful an important reactant in Friedel-Crafts reactions as well as the introduction of an acetyl group. It serves as a starting material in the production of pharmaceutical, new plating complexing agent, acylation agent and synthetic organic intermediates.
The Uses of Acetyl chloride
Acetylating agent; in testing for cholesterol, determination of H2O in organic liquids.
The Uses of Acetyl chloride
Acetyl chloride can be used as:
- A degradation agent in the degradation of polyoxyethylene glycol monoalkyl ethers to determine the degree of ethoxylation using chromatography-mass spectrometry (MS).
- A reagent with alcohols for the esterification of carboxylic acids, N-boc deprotection, and phosphoramide solvolysis reactions.
Definition
A liquid acyl chloride used as an acetylating agent.
Synthesis
To a mixture of the SM (65 mg, 0.22 mmol) and TEA (67 mg, 0.66 mmol) in THF (5 mL) was added acetyl chloride (34 mg, 0.44 mmol) at RT. The reaction mixture was stirred at RT for 3 h. After concentration, the residue was purified by Prep HPLC to provide the product as a white solid. [52 mg, 70%]
General Description
A colorless, fuming liquid with a pungent odor. Density 9.2 lb / gal. Flash point 40°F. Vapor, which is heavier than air, irritates the eyes and mucous membranes. Corrosive to metals and tissue.
Acetyl chloride, CH30CCI, can be prepared by treatment ofacetic acid with various reagents, such as PCl3 SOCl2 or COCI2. It can be prepared by chlorination of acetic anhydride in several different ways, by reaction of methyl chloride with carbon monoxide in the presence of catalysts, by reaction ofketene with HCI, or by partial hydrolysis of 1, 1, l-trichloroethane, Acetyl chloride hydrolyzes in the presence of water to give acetic acid. It reacts with ammonia and amines to give acetamides. Reaction with alcohols gives the corresponding acetate esters. Acetyl chloride will add across unsaturated bonds in the presence ofsuitable catalysts to give halogenated ketones.
Reactivity Profile
Acetyl chloride reacts violently with water, steam, methanol or ethanol to form hydrogen chloride and acetic acid. Reacts vigorously with bases, both organic and inorganic. Incompatible with oxidizing agents and alcohols. Produces highly toxic fumes of phosgene gas and chlorine when heated to decomposition [Sax, 9th ed., 1996, p. 35]. Reaction in a confined space with even a small amount of water may cause a violent eruption of gases [Bretherick, 5th ed., 1995, p. 281]. Vapor forms an explosive mixture with air [Kirk-Othmer, 3rd ed., Vol. 1, 1978, p. 162]. Polymerization reaction with dimethyl sulfoxide is particularly violent [Buckley, A., J. Chem. Ed., 1965, 42, p. 674]. May react vigorously or explosively if mixed with diisopropyl ether or other ethers in the presence of trace amounts of metal salts [J. Haz. Mat., 1981, 4, 291].
Health Hazard
Vapor irritates mucous membranes. Ingestion of liquid or contact with eyes or skin causes severe irritation.
Health Hazard
Exposure to acetic chloride causes severe health effects. It is corrosive and causes severe skin burns. On contact with the eyes and skin and accidental ingestion, acetic chloride causes permanent eye damage and serious burns to the mouth and stomach. The spray mist or liquid causes tissue damage (mucous membranes of eyes, mouth, and upper respiratory tract). Inhalation of the spray mist causes severe irritation of the respiratory tract, with symptoms of a burning sensation, coughing, wheezing, laryngitis, shortness of breath, headache, nausea, and vomiting. Prolonged periods of inhalation of acetic chloride may be fatal as a result of spasm, infl ammation, and edema of the larynx and bronchi, chemical pneumonitis, and pulmonary edema characterized by coughing, choking, or shortness of breath. However, there is no published information about the carcinogenicity, mutagenicity, teratogenicity, and developmental toxicity of acetic chloride in animals and humans.
Safety Profile
Poison by inhalation. Moderately toxic by ingestion. A human systemic irritant by inhalation. Violent hydrolysis reaction with water or steam produces heat, acetic acid, HCl, and other corrosive chlorides. May decompose during preparation. Dangerous fire hazard when exposed to heat or flame. Explosion hazard by spontaneous chemical reaction with dimethyl sulfoxide or ethanol. Also incompatible with Pcb. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of phosgene and Cl-. To fight fire, use CO2 or dry chemical. See also CHLORIDES
Potential Exposure
Acetyl chloride is used in organic synthesis as an acetylating agent and in testing for water and/ or cholesterol in organic liquids, in the pharmaceutical industry and in pesticide manufacture.
Storage
Acetic chloride should be stored in a segregated and approved area, away from incompatibles such as oxidizing agents, alkalis and moisture. The container of acetic chloride should be kept in a cool, well-ventilated area, tightly sealed until ready for use. Users should avoid all possible sources of ignition, i.e., spark or flames.
Shipping
UN1717 Acetyl chloride, Hazard Class: 3; Labels: 3-Flammable liquid, 8-Corrosive material
Purification Methods
Reflux acetyl chloride with PCl5 for several hours to remove traces of acetic acid, then distil it. Redistil it from one-tenth its volume of dimethylaniline or quinoline to remove free HCl. A.R. quality is freed from HCl by pumping it for 1hour at -78o and distilling it into a trap at -196o. [Beilstein 2 IV 395.] LACHRYMATORY.
Incompatibilities
ticide manufacture. Incompatibilities: Avoid contact with moisture, steam, water, alcohols, dimethylsulfoxide, strong bases; phosphorus trichloride; oxidizers, and amines, since violent reactions may occur. Keep away from heat, fire, and welding operations.
Waste Disposal
Consult with environmental regulatory agencies for guidance on acceptable disposal practices. Generators of waste containing this contaminant (≥100 kg/mo) must conform with EPA regulations governing storage, transportation, treatment, and waste disposal. May be mixed slowly with sodium bicarbonate solution and then flushed to sewer with large volumes of water. May also be incinerated.
Properties of Acetyl chloride
| Melting point: | -112 °C |
| Boiling point: | 52 °C(lit.) |
| Density | 1.104 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
| vapor density | 2.7 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 11.69 psi ( 20 °C) |
| refractive index | n |
| Flash point: | 40 °F |
| storage temp. | Store below +15°C. |
| solubility | Miscible with acetone, chloroform, glacial acetic acid, petroleum ether, ether and benzene. |
| form | Liquid |
| appearance | Colorless liquid |
| color | Clear colorless |
| Specific Gravity | approximate 1.11 |
| Odor | Strong pungent odor |
| explosive limit | 7.3-19%(V) |
| Water Solubility | Decomposes violently in water |
| Sensitive | Moisture Sensitive |
| Merck | 14,85 |
| BRN | 605303 |
| Dielectric constant | 16.9(2℃) |
| Stability: | Stability Highly flammable. Reacts violently with DMSO, water, lower alcohols, and amines to generate toxic fumes. May form an explosive mixture with air. Note low flash point. Incompatible with water, alcohols, amines, strong bases, strong oxidizing agents, most common metals. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 75-36-5(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Acetyl chloride(75-36-5) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Acetyl chloride (75-36-5) |
Safety information for Acetyl chloride
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Flame Flammables GHS02  Corrosion Corrosives GHS05 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H225:Flammable liquids H314:Skin corrosion/irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P210:Keep away from heat/sparks/open flames/hot surfaces. — No smoking. P233:Keep container tightly closed. P240:Ground/bond container and receiving equipment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P303+P361+P353:IF ON SKIN (or hair): Remove/Take off Immediately all contaminated clothing. Rinse SKIN with water/shower. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Acetyl chloride
| InChIKey | WETWJCDKMRHUPV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Acetyl chloride manufacturer
VJ CHEMTRADE PVT LTD
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 75-36-5 98%View Details
75-36-5 98%View Details
75-36-5 -
 Acetyl chloride CAS 75-36-5View Details
Acetyl chloride CAS 75-36-5View Details
75-36-5 -
 Acetyl chloride CAS 75-36-5View Details
Acetyl chloride CAS 75-36-5View Details
75-36-5 -
 Acetyl chloride CAS 75-36-5View Details
Acetyl chloride CAS 75-36-5View Details
75-36-5 -
 Acetyl chloride CAS 75-36-5View Details
Acetyl chloride CAS 75-36-5View Details
75-36-5 -
 Acetyl chloride 98% CAS 75-36-5View Details
Acetyl chloride 98% CAS 75-36-5View Details
75-36-5 -
 Acetyl Chloride Liquid, Grade Standard: Technical Grade, Packaging Size: 25 Kg,50 Kg And 200 Kg DrumView Details
Acetyl Chloride Liquid, Grade Standard: Technical Grade, Packaging Size: 25 Kg,50 Kg And 200 Kg DrumView Details
75-36-5 -
 Powder Acetyl Chloride CAS: 75-36-5, For Industrial, Packaging Type: BagView Details
Powder Acetyl Chloride CAS: 75-36-5, For Industrial, Packaging Type: BagView Details
75-36-5
