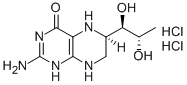
(6R,S)-5,6,7,8-TETRAHYDRO-L-BIOPTERIN DIHYDROCHLORIDE
- CAS NO.:62989-33-7
- Empirical Formula: C9H15N5O3
- Molecular Weight: 241.25
- MDL number: MFCD00069326
- EINECS: 636-312-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2023-05-04 17:34:40
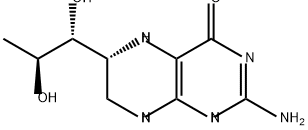
What is (6R,S)-5,6,7,8-TETRAHYDRO-L-BIOPTERIN DIHYDROCHLORIDE?
The Uses of (6R,S)-5,6,7,8-TETRAHYDRO-L-BIOPTERIN DIHYDROCHLORIDE
Treatment of mild-to-moderate phenylketonuria (PKU).
Indications
For the treatment of tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) deficiency.
Background
Sapropterin (tetrahydrobiopterin or BH4) is a cofactor in the synthesis of nitric oxide. It is also essential in the conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine by the enzyme phenylalanine-4-hydroxylase; the conversion of tyrosine to L-dopa by the enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase; and conversion of tryptophan to 5-hydroxytryptophan via tryptophan hydroxylase.
Definition
ChEBI: Sapropterin is a tetrahydropterin that is 2-amino-5,6,7,8-tetrahydropteridin-4(3H)-one in which a hydrogen at position 6 is substituted by a 1,2-dihydroxypropyl group (6R,1'R,2'S-enantiomer). It has a role as a coenzyme, a diagnostic agent, a human metabolite and a cofactor.
Pharmacokinetics
Tetrahydrobiopterin (BH4) is used to convert several amino acids, including phenylalanine, to other essential molecules in the body including neurotransmitters. Tetrahydrobiopterin deficiency can be caused by mutations in GTP cyclohydrolase 1 (GCH1), 6-pyruvoyl-tetrahydropterin synthase/dimerization cofactor of hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 alpha (PCBD1), 6-pyruvoyltetrahydropterin synthase (PTS), and quinoid dihydropteridine reductase (QDPR) genes. These genes make the enzymes that are critical for producing and recycling tetrahydrobiopterin. If one of the enzymes fails to function correctly because of a gene mutation, little or no tetrahydrobiopterin is produced. As a result, phenylalanine from the diet builds up in the bloodstream and other tissues and can damage nerve cells in the brain. High levels of phenylalanine can result in signs and symptoms ranging from temporary low muscle tone to mental retardation, movement disorders, difficulty swallowing, seizures, behavioral problems, progressive problems with development, and an inability to control body temperature.
Metabolism
Not Available
Properties of (6R,S)-5,6,7,8-TETRAHYDRO-L-BIOPTERIN DIHYDROCHLORIDE
| Boiling point: | 506.6±60.0 °C(Predicted) |
| Density | 1.89±0.1 g/cm3(Predicted) |
| storage temp. | Keep in dark place,Sealed in dry,2-8°C |
| pka | 5.05(at 25℃) |
Safety information for (6R,S)-5,6,7,8-TETRAHYDRO-L-BIOPTERIN DIHYDROCHLORIDE
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for (6R,S)-5,6,7,8-TETRAHYDRO-L-BIOPTERIN DIHYDROCHLORIDE
New Products
2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 2-CHLORO-5-METHYLPYRIDIN-4-AMINE 2,4 Dichloro-5-methyl pyridine Ethyl 3,3- diethoxypropionate 4-pyridine methanol Methyl 3-bromo-2-(bromomethyl)propionate 1-Bromo-3-phenylpropane N N' DimethylEthylenediamine Lead II Bromide Variamine Blue B Diazonium salt N Ethylmethylamine Ethyl Methanesulfonate N N N'Trimethyl ethylenediamine (R)-2-Methylpyrolidine-2-carboxylic acid (De Mepro) Boc-L-Tyr(tBu)-OH Boc Leucine Fmoc-L-Glu-OtBu Sacubitril- Valsartan RamiprilRelated products of tetrahydrofuran





You may like
-
 62989-33-7 Sapropterin 98%View Details
62989-33-7 Sapropterin 98%View Details
62989-33-7 -
 2-Bromo Isonicotinic Methyl Ester 98%View Details
2-Bromo Isonicotinic Methyl Ester 98%View Details -
 2-Amino-5-nitro-3-bromopyridine 98%View Details
2-Amino-5-nitro-3-bromopyridine 98%View Details -
 2-Amino Methyl Picolinate Ester 98%View Details
2-Amino Methyl Picolinate Ester 98%View Details -
 2-Nitro 3,4-Dimethoxy Acetophenone 98%View Details
2-Nitro 3,4-Dimethoxy Acetophenone 98%View Details -
 5-Amino 2-Chloro 6-Methyl 98%View Details
5-Amino 2-Chloro 6-Methyl 98%View Details -
 7-Deacetyl azadirone 98%View Details
7-Deacetyl azadirone 98%View Details -
 120013-39-0 2,3-Dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2-(4-piperidinylmethyl)-1H-inden-1-one hydrochloride 99%+View Details
120013-39-0 2,3-Dihydro-5,6-dimethoxy-2-(4-piperidinylmethyl)-1H-inden-1-one hydrochloride 99%+View Details
120013-39-0
