4,4'-Methylenedianiline
Synonym(s):4,4′-Methylenedianiline;DAPM;MDA
- CAS NO.:101-77-9
- Empirical Formula: C13H14N2
- Molecular Weight: 198.26
- MDL number: MFCD00007914
- EINECS: 202-974-4
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-01-27 09:38:02
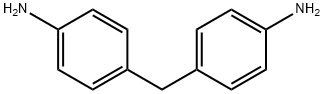
What is 4,4'-Methylenedianiline?
Description
4,4'-Methylenedianiline is an industrial chemical that is not known to occur naturally. It is also commonly known as diaminodiphenylmethane or MDA. It occurs as a colorless to pale yellow solid and has a faint odor. 4,4'-Methylenedianiline is used mainly for making polyurethane foams, which have a variety of uses, such as insulating materials in mailing containers. It is also used for making coating materials, glues, Spandex? fiber, dyes, and rubber. 4,4'-Methylenedianiline is also a by-product of azo dyes. It is also possibly formed by hydrolysis of diphenylmethane-4A'-diisocyanate.
Chemical properties
4,4-Diaminodiphenylmethane is a pale yellow crystalline solid (turns light brown on contact with air) with a faint amine-like odor that is unstable in the presence of light or air and emits toxic fumes of aniline and nitrogen oxides when heated to decomposition. 4,4'-Methylenedianiline is primarily used in industry as a chemical intermediate in the production of 4,4-methylenedianiline diisocyanates and polyisocyanates, but is also used as a cross-linking agent for the determination of tungsten and sulfates, and as a corrosion inhibitor. Exposure to this substance irritates the skin and eyes and causes liver damage. 4,4'-Methylenedianiline is reasonably anticipated to be a human carcinogen. (NCI05)
The Uses of 4,4'-Methylenedianiline
4,4'-methylenedianiline be used as organic intermediates. Mainly used for the synthesis of polyimide and as curing agent of epoxy resin.
The Uses of 4,4'-Methylenedianiline
As chemical intermediate in production of isocyanates and polyisocyantes for preparation of polyurethane foams, Spandex fibers; as curing agent for epoxy resins and urethane elastomers; in production of polyamides; in the determination of tungsten and sulfates; in preparation of azo dyes; as corrosion inhibitor.
The Uses of 4,4'-Methylenedianiline
4,4'-Diaminodiphenyl-methane is used in the determination of tungsten and sulfates; in the preparation of azo dyes; cross-linking agent for epoxy resins; in the preparation of isocyanates and polyisocyanates; in the rubber industry as a curative for neoprene, as an anti-frosting agent (antioxidant) in footwear; raw material in preparation of poly(amide-imide) resins (used in magnet-wire enamels); curing agent for epoxy res ins and urethane elastomers; corrosion inhibitor; rubber additive (accelerator, antidegradant, retarder) in tires and heavy rubber products; in adhesives and glues, laminates, paints and inks, PVC products, handbags, eyeglass frames, plastic jewelry, electric encapsulators, surface coatings, spandex clothing, hairnets, eyelash curlers, earphones, balls, shoe soles, face masks.
Definition
ChEBI: 4,4'-Methylenedianiline is an aromatic amine that is diphenylmethane substituted at the 4-position of each benzene ring by an amino group. It is primarily used in industry as a chemical intermediate in the production of 4,4-methylenedianiline diisocyanates and polyisocyanates.?
General Description
A tan flake or lump solid with a faint fishlike odor. May be toxic by inhalation or ingestion, and may be irritating to skin. Insoluble in water.
Air & Water Reactions
Oxidizes slowly in air in a reaction catalyzed by light. Somewhat hygroscopic. Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
4,4'-Methylenedianiline polymerizes if heated above 257° F. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents. 4,4'-Methylenedianiline is also incompatible with acids. Catalyzes isocyanate-alcohol and epoxide reactions. Flammable gaseous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides.
Health Hazard
TOXIC; inhalation, ingestion or skin contact with material may cause severe injury or death. Contact with molten substance may cause severe burns to skin and eyes. Avoid any skin contact. Effects of contact or inhalation may be delayed. Fire may produce irritating, corrosive and/or toxic gases. Runoff from fire control or dilution water may be corrosive and/or toxic and cause pollution.
Fire Hazard
Combustible material: may burn but does not ignite readily. When heated, vapors may form explosive mixtures with air: indoors, outdoors and sewers explosion hazards. Contact with metals may evolve flammable hydrogen gas. Containers may explode when heated. Runoff may pollute waterways. Substance may be transported in a molten form.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Confirmed carcinogen with experimental tumorigenic data. Human poison by ingestion. Poison by subcutaneous and intraperitoneal routes. Human systemic effects by ingestion: rigidity, jaundice, other liver changes. An eye irritant. Mutation data reported. It is not rapidly absorbed through the skin. Combustible when exposed to heat or flame. When heated to decomposition it emits highly toxic fumes of aniline and NOx.
Potential Exposure
Used as an intermediate and as a curing agent. Approximately 99% of the DDM produced is con- sumed in its crude form (occasionally containing not more than 50% DDM and ply-DDM) at its production site by reac- tion with phosgene in the preparation of isocyanates and poly- isocyanates. These isocyanates and polyisocyanates are employed in the manufacture of rigid polyurethane foams which find application as thermal insulation. Polyisocyanates are also used in the preparation of the semiflexible polyure- thane foams used for automotive safety cushioning. DDM is also used as: an epoxy hardening agent; a raw material in the production of polyurethane elastomers; in the rubber industry as a curative for Neoprene and as an antifrosting agent (anti- oxidant) in footwear; a raw material in the production of Quana nylon; and a raw material in the preparation of poly (amide-imide) resins (used in magnet wire enamels).
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seekmedical attention immediately. If this chemical contactsthe skin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediately with soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical has been inhaled, remove fromexposure, begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing hasstopped and CPR if heart action has stopped. Transferpromptly to a medical facility. When this chemical hasbeen swallowed, get medical attention. Give large quantities of water and induce vomiting. Do not make an unconscious person vomit.
Carcinogenicity
4,4′-Methylenedianiline and its dihydrochloride salt are reasonably anticipated to be human carcinogens based on sufficient evidence of carcinogenicity from studies in experimental animals.
Environmental Fate
MDA is a pale brown crystalline powder with a faint aminelike
odor. Exposure to air and light results in polymerization and
oxidation of MDA. When heated, MDA produces toxic fumes of
aniline and nitrogen oxides.
Most MDA enters the environment when it is produced or
used to make other compounds. Forty-five percent of the
produced compound is released to deep soil, 52.6% to the air,
and 2.4% to land and water. Once in the environment, it will
be mainly present as tiny particles in the air and it is removed
from the atmosphere by dry deposition, rain, and snow
scavenging. A small amount is transformed by reaction with
hydroxyl radicals. In water, most of MDA will attach to
particles and sediments, and will eventually settle to the
bottom.
The estimated half-life of biodegradation in surface water,
groundwater, and soil is 1–7 days, 2–14 days, and 1–7 days,
respectively. With respect to aquatic ecosystems, bioconcentration
factor values of 3.0–14 suggest that bioconcentration
is low, in addition this compound does not tend
to build up in the food chain. When released to soil, it is
expected to have slight to no mobility. Similarly, volatilization
from both moist and dry soil surfaces is not expected to be
important.
storage
Color Code—Blue: Health Hazard/Poison: Storein a secure poison location. Prior to working with thischemical you should be trained on its proper handling andstorage. Store in tightly closed containers in a cool, wellventilated area away from strong oxidizers (such as chlorine, bromine, and fluorine). A regulated, marked areashould be established where this chemical is handled, used,or stored in compliance with OSHA Standard 1910.1045.
Shipping
UN2651 4,40 -Diaminodiphenyl methane, Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1-Poisonous materials.
Purification Methods
Crystallise the amine from water, 95% EtOH or *benzene. [Beilstein 13 IV 390.]
Toxicity evaluation
Currently, the mechanism of action is not completely understood
and has been mostly assessed from information on
structurally similar compounds. Many of the toxic properties of
MDA have been attributed to metabolic intermediates, as these
compounds are metabolically activated by N-oxidation to
metabolites, such as N-hydroxymethylenedianiline, that react
with DNA, RNA, and proteins.
Different studies suggest that both liver and thyroid are
targets for MDA toxicity in humans and animals. Liver
toxicity has been linked to impair mitochondrial function
and structure, apoptosis, and increased oxidative stress. It
may be caused by a reactive electrophile formed during
metabolism since liver has the enzymatic routes necessary for
such activation. Experimental studies indicate that biliary
epithelial cells are damaged earlier than parenchymal cells
and bile is a major route of exposure to MDA. The mechanism
of thyroid toxicity has not yet been resolved. It has
been observed that MDA exposure can induce a slight
decrease in thyroid hormones in rats, thus triggering secretion
of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), which induced
thyroid hyperplasia. Some of the induced adverse effects
observed after MDA exposure (e.g., reduced food consumption,
lower body weight gain, and effects on red cells,
lymphocytes, and clotting parameters) could be explained as
secondary responses.
MDA is carcinogenic to animals. The mechanism of liver or
thyroid tumor development remains unclear. Even if cell
injury may give indications of a nongenotoxic mechanism, it
remains still unproved, and there are also positive genotoxic
data in vitro and in vivo which indicate that a genotoxic
mechanism may be related to the formation of a reactive
metabolic intermediate cannot be excluded. Regarding thyroid
cancer, hypersecretion of TSH may have a contribution to
tumor formation.
Incompatibilities
Dust forms and explosive mixture with air. May polymerize in temperatures .125℃ . A weak base. Incompatible with strong oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong acids. Flammable gas- eous hydrogen may be generated in combination with strong reducing agents, such as hydrides .
Waste Disposal
Controlled incineration (oxides of nitrogen are removed from the effluent gas by scrubbers and/or thermal devices).
Properties of 4,4'-Methylenedianiline
| Melting point: | 89-91 °C(lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 242 °C2 mm Hg(lit.) |
| Density | 1.15 |
| vapor pressure | 0Pa at 25℃ |
| refractive index | 1.5014 (estimate) |
| Flash point: | 430 °F |
| solubility | water: soluble |
| form | neat |
| pka | 5.32±0.25(Predicted) |
| color | White to Light yellow |
| Water Solubility | Slightly soluble. <0.1 g/100 mL at 19 ºC |
| Merck | 14,2980 |
| BRN | 474706 |
| Exposure limits | ACGIH: TWA 0.1 ppm (Skin) OSHA: STEL 100 ppb |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 101-77-9(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| IARC | 2B (Vol. 39, Sup 7) 1987 |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Benzenamine, 4,4'-methylenebis-(101-77-9) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | 4,4'-Methylenedianiline (101-77-9) |
Safety information for 4,4'-Methylenedianiline
| Signal word | Danger |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Skull and Crossbones Acute Toxicity GHS06  Health Hazard GHS08  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H301:Acute toxicity,oral H317:Sensitisation, Skin H341:Germ cell mutagenicity H350:Carcinogenicity H370:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure H373:Specific target organ toxicity, repeated exposure H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P202:Do not handle until all safety precautions have been read and understood. P260:Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P280:Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection. P301+P310:IF SWALLOWED: Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. |
Computed Descriptors for 4,4'-Methylenedianiline
New Products
3-Iodophenylacetic acid 3-Pyridineacetonitrile, α-hydroxy- 2-Propanamine, 1-chloro-, hydrochloride (9CI) 3-(hexyloxy)-4-(pyridin-3-yl)-1,2,5-thiadiazole 2-Hexyn-1-ol Dibenzo-18-crown-6 Nickel(II) perchlorate hexahydrate, 98% 4-Bromophenylacetonitrile, 95% 3-Bromo-4-fluoroaniline, 97% Sodium tetraborate decahydrate, 98% Palladium(II) acetate, trimer, Pd 99% 4-Bromo-2-chlorotoluene, 97% N N Dimethylformamide Dimethyl Acetal (Dmf Dma) 2,3-Dichloro Benzoyl Cyanide [Side Chain] Bis(2-Chloroethyl) Amine Hydrochloride L-Glutamic Acid Diethyl Ester Hydrochloride 5-(Difluoromethoxy)-2-Mercaptobenzimidazole 1-Ethyl-3-(3-Dimethylaminopropyl)-Carbodiimide Hydrochloride [EDC Hcl] 1,4-Napthoquinone Bromoiodomethane Sodium Bicarbonate Methylene Dichloride (MDC) Ethyl Acetate Indole-3-Carbinol (I3C)Related products of tetrahydrofuran



You may like
-
 4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane CAS 101-77-9View Details
4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane CAS 101-77-9View Details
101-77-9 -
 4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane CAS 101-77-9View Details
4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane CAS 101-77-9View Details
101-77-9 -
 4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane CAS 101-77-9View Details
4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane CAS 101-77-9View Details
101-77-9 -
 4,4′-Diaminodiphenylmethane CAS 101-77-9View Details
4,4′-Diaminodiphenylmethane CAS 101-77-9View Details
101-77-9 -
 4,4′-Diaminodiphenylmethane CAS 101-77-9View Details
4,4′-Diaminodiphenylmethane CAS 101-77-9View Details
101-77-9 -
 4,4′-Diaminodiphenylmethane CAS 101-77-9View Details
4,4′-Diaminodiphenylmethane CAS 101-77-9View Details
101-77-9 -
 101-77-9 4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane 99%View Details
101-77-9 4,4'-Diaminodiphenylmethane 99%View Details
101-77-9 -
 132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6 (S)-1-Boc-3-methanesulfonyloxy-pyrrolidine 98+View Details
132945-75-6
