Biphenyl
Synonym(s):Biphenyl
- CAS NO.:92-52-4
- Empirical Formula: C12H10
- Molecular Weight: 154.21
- MDL number: MFCD00003054
- EINECS: 202-163-5
- SAFETY DATA SHEET (SDS)
- Update Date: 2025-09-25 17:15:13
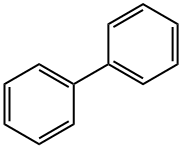
What is Biphenyl?
Description
Biphenyl, also called diphenyl, consists of two benzene rings joined by a single bond. It exists as colorless to yellowish crystals, has a distinctive odor, and occurs naturally in oil, natural gas, and coal tar.
Description
Biphenyl is an organic compound with chemical formula of C12H10. It is a white crystalline powder, insoluble in water, soluble in ether, ethanol, carbon tetrachloride, dioxane, aromatic hydrocarbons, etc. it is mainly used as solvent, heat transfer agent, fruit mildew inhibitor and organic synthesis.
Chemical properties
1,1'-Biphenyl is a clear colorless liquid with a pleasant odor and stable organic compound. It is combustible at high temperatures, producing carbon dioxide and water when combustion is complete. Partial combustion produces carbon monoxide, smoke, soot, and low molecular weight hydrocarbons. It is used extensively in the production of heat-transfer fl uids, for example, as an intermediate for polychlorinated biphenyls, and dye carriers for textile dyeing. It is also used as a mold retardant in citrus fruit wrappers, in the formation of plastics, optical brighteners, and hydraulic fluids.
Physical properties
White scales with a pleasant but peculiar odor. Odor threshold concentration is 0.83 ppb (quoted, Amoore and Hautala, 1983).
Occurrence
Reported found in coal tar, bilberry, carrots, peas, potato, bell pepper, rum, cocoa, tomato, coffee, roasted peanuts, olive (Olea europae), buckwheat and tamarind (Tamarindus indica L).
The Uses of Biphenyl
Biphenyl is used to prevent fungal attack on stored citrus fruit. It is impregnated into fruit wraps.
The Uses of Biphenyl
Biphenyl is used as an antifungal agent to preserve citrus fruit, in citrus wrappers to retard mold growth, in heat transfer fluids, in dye carriers for textiles and copying paper, as a solvent in pharmaceutical production, in optical brighteners, and as an intermediate for the production of a wide range of organic compounds.
The Uses of Biphenyl
As heat transfer agent; fungistat for oranges (applied to inside of shipping container or wrappers); in organic syntheses.
Definition
ChEBI: A benzenoid aromatic compound that consists of two benzene rings connected by a single covalent bond. Biphenyl occurs naturally in coal tar, crude oil, and natural gas. Formerly used as a fungicide for citrus crops.
What are the applications of Application
Biphenyl is a starting material for the production of polychlorinated biphenyls
Preparation
By thermal dehydrogenation of benzene.
Definition
An organic compound having a structure in which two phenyl groups are joined by a C–C bond.
What are the applications of Application
Biphenyl is an important organic raw material, which is widely used in medicine, pesticide, dye, liquid crystal materials and other fields. It can be used to synthesize plasticizers and preservatives, and can also be used to manufacture fuels, engineering plastics and high-energy fuels. Biphenyls are found in coal tar, crude oil and natural gas. The preparation methods of biphenyl include chemical synthesis of biphenyl by pyrolysis of benzene and separation and extraction of biphenyl from various coal tar oil fractions. The mass fraction of biphenyl in coal tar is 0.20% - 0.40%. Coal tar extraction and chemical synthesis coexist. Biphenyl is combustible. In case of high temperature, open fire and oxidant, it is dangerous to burn. It should be stored in a cool and ventilated warehouse away from kindling and heat source. It should be stored separately from oxidants and strong acids. It should be loaded and unloaded gently to keep the package intact. Biphenyl is used as heat exchanger and impregnator of fruit packaging paper. Biphenyl can be used in organic synthesis. Biphenyl is the raw material of engineering plastics polysulfone. It is used to prepare Trichlorobenzene and pentachlorophenyl. Biphenyl is used as heat carrier, preservative, dye and so on. Biphenyl is used as a reference material for chromatographic analysis. Biphenyl is the intermediate of rodenticides rodenticide modek and bromadine, and it is an organic carrier with good performance.
Aroma threshold values
Detection: 0.5 ppb
Synthesis Reference(s)
Journal of the American Chemical Society, 83, p. 1251, 1961 DOI: 10.1021/ja01466a056
Tetrahedron Letters, 25, p. 391, 1984 DOI: 10.1016/S0040-4039(00)99891-5
General Description
A clear colorless liquid with a pleasant odor. Flash point 180°F. Insoluble in water. Vapors are heavier than air. Used to manufacture other chemicals and as a fungicide.
Air & Water Reactions
Insoluble in water.
Reactivity Profile
Biphenyl is incompatible with oxidizers.
Health Hazard
Exposures to 1,1’-biphenyl cause acute effects with symptoms that include, but are not limited to, polyuria, accelerated breathing, lacrimation, anorexia, weight loss, muscular weakness, coma, fatty liver cell degeneration, and severe nephrotic lesions. Exposure to biphenyl fumes for short periods of time causes nausea, vomiting, irritation of the eyes and respiratory tract, and bronchitis. Breathing small amounts of 1,1’-biphenyl over long periods of time causes damage to the liver and the nervous system of exposed workers. Breathing the mists, vapors, or fumes may irritate the nose, throat, and lungs. Depending on the concentration and duration of exposure, the symptoms include, but are not limited to, sore throat, coughing, labored breathing, sneezing, a burning sensation, and the effects of CNS depression. Symptoms may include headache, excitation, euphoria, dizziness, incoordination, drowsiness, light-headedness, blurred vision, fatigue, tremors, convulsions, loss of consciousness, coma, respiratory arrest, and death, depending on the concentration and duration of exposure
Fire Hazard
Combustible. Emits toxic fumes under fire conditions.
Flammability and Explosibility
Non flammable
Safety Profile
Poison by intravenous route.Moderately toxic by ingestion. A powerful irritant byinhalation in humans. Human systemic effects byinhalation of very small amounts: flaccid paralysis, nauseaor vomiting, and other unspecified gastrointestinal effects.Que
Potential Exposure
Biphenyl is a fungicide (pesticide). It is also used as a heat transfer agent, dye carrier, and as an intermediate in organic synthesis.
First aid
If this chemical gets into the eyes, remove anycontact lenses at once and irrigate immediately for at least 15 min, occasionally lifting upper and lower lids. Seek medical attention immediately. If this chemical contacts theskin, remove contaminated clothing and wash immediatelywith soap and water. Seek medical attention immediately. Ifthis chemical has been inhaled, remove from exposure,begin rescue breathing (using universal precautions, including resuscitation mask) if breathing has stopped and CPR ifheart action has stopped. Transfer promptly to a medicalfacility. When this chemical has been swallowed, get medical attention. Do not induce vomiting.
Source
Present in coal tar at a concentration of 2.72 mg/g (Lao et al., 1975). Detected in woodpreserving creosotes at a concentration of 2.1 wt % (Nestler, 1974). Typical concentration of biphenyl in a heavy pyrolysis oil is 2.3 wt % (Chevron Phillips, May 2003).
Environmental Fate
Biological. Reported biodegradation products include 2,3-dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybi phenyl, 2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl, 2-hydroxy-6-oxo-6-phenylhexa-2,4-dienoate, 2-hydroxy-
3-phenyl-6-oxohexa-2,4-dienoate, 2-oxopenta-4-enoate, phenylpyruvic acid (Verschueren,
1983), 2-hydroxybiphenyl, 4-hydroxybiphenyl and 4,4′-hydroxybiphenyl (Smith and
Rosazza, 1974). Under aerobic conditions, Beijerinckia sp. degraded biphenyl to cis-2,3-
dihydro-2,3-dihydroxybiphenyl. In addition, Oscillatoria sp. and Pseudomonas putida
degraded biphenyl to 4-hydroxybiphenyl and benzoic acid, respectively (Kobayashi and
Rittman, 1982). The microbe Candida lipolytica degraded biphenyl into the following
products: 2-, 3- and 4-hydroxybiphenyl, 4,4′-dihydroxybiphenyl and 3-methoxy-4-hydrox ybiphenyl (Cerniglia and Crow, 1981). With the exception of 3-methoxy-4-hydroxybiphe nyl, these products were also identified as metabolites by Cunninghanella elegans (Dodge
et al., 1979). In activated sludge, 15.2% mineralized to carbon dioxide after 5 days (Freitag
et al., 1985).
Photolytic. A carbon dioxide yield of 9.5% was achieved when biphenyl adsorbed on
silica gel was irradiated with light (λ >290 nm) for 17 hours. Irradiation of biphenyl (λ >300 nm) in the presence of nitrogen monoxide resulted in the formation of
Chemical/Physical. The aqueous chlorination of biphenyl at 40°C over a pH range of
6.2 to 9.0 yielded o-chlorobiphenyl and m-chlorobiphenyl (Snider and Alley, 1979). In an
acidic aqueous solution (pH 4.5) containing bromide ions and a chlorinatin
Biphenyl will not hydrolyze since it has no hydrolyzable functional group.
Metabolic pathway
Biphenyl is a stable compound. It has a restricted use as a fungistat applied to citrus packing material. This has generated studies on its toxicity and metabolism in mammals and residue studies in stored fruit. Only limited information on its environmental fate has been published.
Storage
1,1’-Biphenyl should be kept stored in tightly closed containers in a cool, dry, isolated, and properly ventilated area, away from heat, sources of ignition, incompatibles, and contact with strong oxidizers.
Shipping
UN2811 Toxic solids, organic, n.o.s., Hazard Class: 6.1; Labels: 6.1—Poisonous materials, Technical Name Required.
Purification Methods
Crystallise biphenyl from EtOH, MeOH, aqueous MeOH, pet ether (b 40-60o) or glacial acetic acid. Free it from polar impurities by passage through an alumina column in *benzene, followed by evaporation. The residue has been purified by distillation in a vacuum and by zone refining. Treatment with maleic anhydride removes anthracene-like impurities. It has been recrystallised from EtOH followed by repeated vacuum sublimation and passage through a zone refiner. [Taliani & Bree J Phys Chem 88 2351 1984, Beilstein 5 H 576, 5 I 271, 5 II 479, 5 III 1726, 5 IV 1807.]
Degradation
Biphenyl is not subject to hydrolysis.
Incompatibilities
Mist may form explosive mixture with air. Incompatible with oxidizers (chlorates, nitrates, peroxides, permanganates, perchlorates, chlorine, bromine, fluorine, etc.); contact may cause fires or explosions. Keep away from alkaline materials, strong bases, strong acids, oxoacids, epoxides.
Waste Disposal
Dissolve or mix the material with a combustible solvent and burn in a chemical incinerator equipped with an afterburner and scrubber. All federal, state, and local environmental regulations must be observed.
Precautions
Occupational workers should be careful during use and chemical management because the fi nely dispersed particles of 1,1’-biphenyl form explosive mixtures in air
Properties of Biphenyl
| Melting point: | 68-70 °C (lit.) |
| Boiling point: | 255 °C (lit.) |
| Density | 0.992 |
| vapor density | 5.31 (vs air) |
| vapor pressure | 9.46 mm Hg ( 115 °C) |
| refractive index | 1.475 |
| FEMA | 3129 | BIPHENYL |
| Flash point: | 113 °C |
| storage temp. | Store below +30°C. |
| solubility | Soluble in alcohol and ether |
| form | Crystalline Powder, Crystals or Flakes |
| color | White to faint yellow |
| Specific Gravity | 0.992 |
| Odor | pleasant odor |
| explosive limit | 0.6%, 111°F |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
| Merck | 14,3314 |
| JECFA Number | 1332 |
| BRN | 1634058 |
| Henry's Law Constant | 2.92 at 25 °C (air stripping-GC, Destaillats and Charles, 2002) |
| Exposure limits | NIOSH REL: TWA 0.2 ppm, IDLH 100 mg/m3; OSHA PEL: TWA
0.2 ppm; ACGIH TLV: TWA 0.2 ppm. |
| Dielectric constant | 20.0(Ambient) |
| Stability: | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidising agents. |
| CAS DataBase Reference | 92-52-4(CAS DataBase Reference) |
| NIST Chemistry Reference | Biphenyl(92-52-4) |
| EPA Substance Registry System | Biphenyl (92-52-4) |
Safety information for Biphenyl
| Signal word | Warning |
| Pictogram(s) |
 Exclamation Mark Irritant GHS07  Environment GHS09 |
| GHS Hazard Statements |
H315:Skin corrosion/irritation H319:Serious eye damage/eye irritation H335:Specific target organ toxicity, single exposure;Respiratory tract irritation H410:Hazardous to the aquatic environment, long-term hazard |
| Precautionary Statement Codes |
P261:Avoid breathing dust/fume/gas/mist/vapours/spray. P264:Wash hands thoroughly after handling. P264:Wash skin thouroughly after handling. P271:Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area. P273:Avoid release to the environment. P302+P352:IF ON SKIN: wash with plenty of soap and water. P305+P351+P338:IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. Remove contact lenses, if present and easy to do. Continuerinsing. |
Computed Descriptors for Biphenyl
| InChIKey | ZUOUZKKEUPVFJK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
Biphenyl manufacturer
New Products
4,4-Difluoropiperidine hydrochloride tert-butyl 9-methoxy-3-azaspiro[5.5]undecane-3-carboxylate Indole Methyl Resin N-Isopropylurea N,N-Dicyclohexylcarbodiimide(DCC) MELDRUMS ACID 5-METHYLISOXAZOLE-4-CARBOXYLIC ACID Magnessium Bis glycinate Zinc ascorbate 1-bromo-2-butyne 2-acetamidophenol 9(10H)-anthracenone Erythrosin B, 4-Piperidinopiperidine 2-((4-morpholinophenylamino) (methylthio) methylene) malononitrile 2,4-dihydroxybenzaldehyde 3-(4-morpholinophenylamino)-5-amino-1H-pyrazole-4-carbonitrile Methyl 2-methylquinoline-6-carboxylate 2,6-dichloro-4-nitropyridine 4-Bromo-2-chlorobenzonitrile 2-(benzylamino)acetic acid hydrochloride 4-(tert-Butoxycarbonylamino)but- 2-ynoic acid 3,4-dihydro-2H-benzo[b][1,4]dioxepine 1-Phenyl-1-cycloprppanecarboxylicacidRelated products of tetrahydrofuran

You may like
-
 Biphenyl 98%View Details
Biphenyl 98%View Details -
 Biphenyl, puriss, 99%+ CAS 92-52-4View Details
Biphenyl, puriss, 99%+ CAS 92-52-4View Details
92-52-4 -
 Biphenyl Zone Refined (number of passes:24) CAS 92-52-4View Details
Biphenyl Zone Refined (number of passes:24) CAS 92-52-4View Details
92-52-4 -
 Biphenyl CAS 92-52-4View Details
Biphenyl CAS 92-52-4View Details
92-52-4 -
 Biphenyl extrapure CAS 92-52-4View Details
Biphenyl extrapure CAS 92-52-4View Details
92-52-4 -
 Biphenyl Cas 92 52 4View Details
Biphenyl Cas 92 52 4View Details
92-52-4 -
 BIPHENYL (CAS N0-92-52-4)View Details
BIPHENYL (CAS N0-92-52-4)View Details
92-52-4 -
 Biphenyl (for synthesis), PowderView Details
Biphenyl (for synthesis), PowderView Details
92-52-4
